Abstract
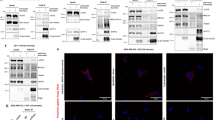
The mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 plays key roles in cell progression, differentiation, inflammation, and apoptosis. p38 is activated by a variety of extracellular stimuli such as UV and proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). It has been demonstrated that destruction of microtubules with different reagents led to impaired p38 activation in response to various extracellular stimuli. However, several other groups have reported that microtubule-interfering agents stimulate the activation of MAPK superfamily members including p38 in certain cell context. The discrepancy suggests that destruction of microtubules stimulates the activation of MAPK superfamily members and thereby induces certain feedback inhibitor(s) of p38 signaling. In this article, we report that nocodazole, a widely used microtubule-interfering agent, antagonized UV- or TNF-α-induced p38 activation, even though this drug by itself weakly activated p38. The RNA synthesis inhibitor actinomycin D, but not p38-specific inhibitor SB203580, reversed the inhibitory effect of nocodazole on TNF-α-induced p38 activation. Nocodazole also weakly activated JNK, but significantly activated ERK. The inhibition by nocodazole of TNF-α-induced p38 activation was abolished by ERK-specific inhibitor U0126. Further exploration revealed that nocodazole significantly enhanced MKP-1 expression via the ERK activity. Thus, nocodazole increases the ERK activity to enhance MKP-1 expression which inhibits p38 activation induced by TNF-α.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han J, Lee JD, Bibbs L, Ulevitch RJ (1994) A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science 265:808–811
Rouse J, Cohen P, Trigon S, Morange M, Alonso-Llamazares A, Zamanillo D (1994) A novel kinase cascade triggered by stress and heat shock that stimulates MAPK- AP kinase-2 and phosphorylation of the small heat shock proteins. Cell 78:1027–1037
Zarubin T, Han J (2005) Activation and signaling of the p38 MAP kinase pathway. Cell Res 15:11–18
Karin M (1995) The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem 270:16483–16486
Lin A (2003) Activation of the JNK signaling pathway: breaking the brake on apoptosis. Bioessays 25:17–24
Franklin CC, Kraft AS (1997) Conditional expression of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase MKP-1 preferentially inhibits p38 MAPK and stress-activated protein kinase in U937 cells. J Biol Chem 272:16917–16923
Bhattacharyya S, Brown DE, Brewer JA, Vogt SK, Muglia LJ (2007) Macrophage glucocorticoid receptors regulate Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory responses by selective inhibition of p38 MAP kinase. Blood 109:4313–4319
Zhu QY, Liu Q, Chen JX, Lan K, Ge BX (2010) MicroRNA-101 targets MAPK phosphatase-1 to regulate the activation of MAPKs in macrophage. J Immunol 185:7435–7442
Jordan MA, Wilson L (2004) Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 255:253–265
Subbaramaiah K, Hart JC, Norton L, Dannenberg AJ (2000) Microtubule-interfering agents stimulate the transcription of cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem 275:14838–14845
Nagata K, Puls A, Futter C, Aspenstrom P, Schaefer E, Nakata T (1998) The MAP kinase kinase kinase MLK2 co-localizes with activated JNK along microtubules and associates with kinesin superfamily motor KIF3. EMBO J 17:149–158
Gundersen GG, Cook TA (1999) Microtubules and signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:81–94
Verhey KJ, Rapoport TA (2001) Kinesin carries the signal. Trends Biochem Sci 26:545–550
Morrison DK, Davis RJ (2003) Regulation of MAP kinase signaling modules by scaffold proteins in mammals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 19:91–118
Cheung PY, Zhang Y, Long J, Lin S, Zhang M, Jiang Y (2004) p150Glued, Dynein, and microtubules are specifically required for activation of MKK3/6 and p38 MAPKs. J Biol Chem 279:45308–45311
Prickett TD, Brautigen DL (2007) Cytokine activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and apoptosis is opposed by alpha-4 targeting of protein phosphatase 2A for site-specific dephosphorylation of MEK3. Mol Cell Biol 27:4217–4227
Schmid-Alliana A, Menou L, Manie S, Schmid-Antomarchi H, Millet MA, Giuriato S (1998) Microtubule integrity regulates src-like and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activities in human pro-monocytic cells: importance for interleukin-1 production. J Biol Chem 273:3394–3400
Lee LF, Li G, Templeton DJ, Ting JP (1998) Paclitaxel (Taxol)-induced gene expression and cell death are both mediated by the activation of c-Jun NH2- terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK). J Biol Chem 273:28253–28260
Wang TH, Wang HS, Ichijo H, Giannakakou P, Foster JS, Fojo T (1998) Microtubule-interfering agents activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase through both Ras and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase pathways. J Biol Chem 273:4928–4936
Fortin J, Patenaude A, Deschesnes RG, Cote MF, Petitclerc E, Gaudreault RC (2010) ASK1-p38 pathway is important for anoikis induced by microtubule-targeting aryl chloroethylureas. J Pharm Pharm Sci 13:175–190
De Brabander MJ, Van de Veire RML, Aerts FEM, Borgers M, Janssen PAJ (1976) The effects of methyl (5-(2-Thienylcarbonyl)-IH-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate, (R 17934; NSC 238159), a new synthetic antitumoral drug interfering with microtubules, on mammalian cells cultured in vitro. Cancer Res 36:905–916
Lee JC, Field DJ, Lee LL (1980) Effects of nocodazole on structures of calf brain tubulin. Biochemistry 19:6209–6215
Zhang J, Bui TN, Xiang J, Lin A (2006) Cyclic AMP inhibits p38 activation via CREB-induced dynein light chain. Mol Cell Biol 26:1223–1234
Zhang J, Shen B, Lin A (2007) Novel strategies for inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway. Trends Pharmaco Sci 28:286–295
Brancho D, Tanaka N, Jaeschke A, Ventura JJ, Kelkar N, Tanaka Y (2003) Mechanism of p38 MAP kinase activation in vivo. Genes Dev 17:1969–1978
Derijard B, Raingeaud J, Barrett T, Wu IH, Han J, Ulevitch RJ (1995) Independent human MAP kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science 267:682–685
Lin A, Minden A, Martinetto H, Claret FX, Lange-Carter C, Mercurio F (1995) Identification of a dual specificity kinase that activates the Jun kinases and p38-Mpk2. Science 268:286–290
Han J, Lee JD, Jiang Y, Li Z, Feng L, Ulevitch RJ (1996) Characterization of the structure and function of a novel MAP kinase kinase (MKK6). J Biol Chem 271:2886–2891
Zhang J, Wang Q, Zhu N, Yu M, Shen B, Xiang J (2008) Cyclic AMP inhibits JNK activation by CREB-mediated induction of c-FLIPL and MKP-1, thereby antagonizing UV-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 15:1654–1662
Boulton TG, Nye SH, Robbins DJ, Ip NY, Radziejewska E, Morgenbesser SD (1991) ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to Insulin and NGF. Cell 65:663–675
Favata MF, Horiuchi KY, Manos EJ, Daulerio AJ, Stradley DA, Feeser WS (1998) Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem 273:18623–18632
Keyse SM (2008) Dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs) and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 27:253–261
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (30973547, 31100544), Key Natural Science Program of Beijing (7101008), and National Key Basic Research Program of China (2010CB911904).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiangrui Guo and Xueying Zhang contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Zhang, X., Li, Y. et al. Nocodazole increases the ERK activity to enhance MKP-1 expression which inhibits p38 activation induced by TNF-α. Mol Cell Biochem 364, 373–380 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1239-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1239-5