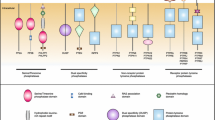
Abstract
There are ten mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatases (MKPs) that act as negative regulators of MAPK activity in mammalian cells and these can be subdivided into three groups. The first comprises DUSP1/MKP-1, DUSP2/PAC1, DUSP4/MKP-2 and DUSP5/hVH-3, which are inducible nuclear phosphatases. With the exception of DUSP5, these MKPs display a rather broad specificity for inactivation of the ERK, p38 and JNK MAP kinases. The second group contains three closely related ERK-specific and cytoplasmic MKPs encoded by DUSP6/MKP-3, DUSP7/MKP-X and DUSP9/MKP-4. The final group consists of three MKPs DUSP8/hVH-5, DUSP10/MKP-5 and DUSP16/MKP-7 all of which preferentially inactivate the stress-activated p38 and JNK MAP kinases. Abnormal MAPK signalling will have important consequences for processes critical to the development and progression of human cancer. In addition, MAPK signalling also plays a key role in determining the response of tumour cells to conventional cancer therapies. The emerging roles of the dual-specificity MKPs in the regulation of MAPK activities in normal tissues has highlighted the possible pathophysiological consequences of either loss (or gain) of function of these enzymes as part of the oncogenic process. This review summarises the current evidence implicating the dual-specificity MKPs in the initiation and development of cancer and also on the outcome of treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALL:
-
acute lymphocytic leukaemia
- AML:
-
acute myeloid leukaemia
- BM:
-
bone marrow
- DUSP:
-
dual-specificity protein phosphatase
- ERK:
-
extracellular-signal regulated kinase
- JNK:
-
c-Jun amino-terminal kinase
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MEF:
-
mouse embryo fibroblast
- MKK or MEK:
-
MAPK kinase
- MKKK or MEKK:
-
MAPK kinase kinase
- MKP:
-
MAP kinase phosphatase
- NSCLC:
-
non-small cell lung cancer
- SCA:
-
serous ovarian carcinoma
- SAGE:
-
serial analysis of gene expression
- SBT:
-
serous borderline ovarian tumour
References
Wada, T., & Penninger, J. M. (2004). Mitogen-activated protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene, 23(16), 2838–2849.
Davis, R. J. (2000). Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell, 103(2), 239–252.
Chang, L., & Karin, M. (2001). Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature, 410(6824), 37–40.
Johnson, G. L., & Lapadat, R. (2002). Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science, 298(5600), 1911–1912.
Pearson, G., Robinson, F., Beers Gibson, T., Xu, B. E., Karandikar, M., Berman, K., et al. (2001). Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocrine Reviews, 22(2), 153–183.
Marshall, C. J. (1994). MAP kinase kinase kinase, MAP kinase kinase and MAP kinase. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 4(1), 82–89.
Cohen, P. (1997). The search for physiological substrates of the MAP and SAP kinases in mammalian cells. Trends in Cell Biology, 7, 353–361.
Dhillon, A. S., Hagan, S., Rath, O., & Kolch, W. (2007). MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene, 26(22), 3279–3290.
Kennedy, N. J., & Davis, R. J. (2003). Role of JNK in tumor development. Cell Cycle, 2(3), 199–201.
Kennedy, N. J., Sluss, H. K., Jones, S. N., Bar-Sagi, D., Flavell, R. A., & Davis, R. J. (2003). Suppression of Ras-stimulated transformation by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Genes & Development, 17(5), 629–637.
Dolado, I., Swat, A., Ajenjo, N., De Vita, G., Cuadrado, A., & Nebreda, A. R. (2007). p38alpha MAP kinase as a sensor of reactive oxygen species in tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell, 11(2), 191–205.
Ventura, J. J., Tenbaum, S., Perdiguero, E., Huth, M., Guerra, C., Barbacid, M., et al. (2007). p38alpha MAP kinase is essential in lung stem and progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. Nature Genetics, 39(6), 750–758.
Sun, P., Yoshizuka, N., New, L., Moser, B. A., Li, Y., Liao, R., et al. (2007). PRAK is essential for ras-induced senescence and tumor suppression. Cell, 128(2), 295–308.
Han, J., & Sun, P. (2007). The pathways to tumor suppression via route p38. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 32(8), 364–371.
Marshall, C. J. (1995). Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell, 80(2), 179–185.
Keyse, S. M. (2000). Protein phosphatases and the regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 12(2), 186–192.
Saxena, M., & Mustelin, T. (2000). Extracellular signals and scores of phosphatases: All roads lead to MAP kinase. Seminars in Immunology, 12(4), 387–396.
Theodosiou, A., & Ashworth, A. (2002). MAP kinase phosphatases. Genome Biol, 3(7), REVIEWS3009.
Kondoh, K., & Nishida, E. (2007). Regulation of MAP kinases by MAP kinase phosphatases. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 1773(8), 1227–1237.
Owens, D. M., & Keyse, S. M. (2007). Differential regulation of MAP kinase signalling by dual-specificity protein phosphatases. Oncogene, 26(22), 3203–3213.
Farooq, A., & Zhou, M. M. (2004). Structure and regulation of MAPK phosphatases. Cell Signal, 16(7), 769–779.
Dickinson, R. J., & Keyse, S. M. (2006). Diverse physiological functions for dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases. Journal of Cell Science, 119(Pt 22), 4607–4615.
Chi, H., Barry, S. P., Roth, R., Wu, J. J., Jones, E. A., Bennett, A. M., et al. (2006). Dynamic regulation of pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines by MKP-1 in innate immune responses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 2274–2279.
Hammer, M., Mages, J., Dietrich, H., Servatius, A., Howells, N., Cato, A. C., et al. (2006). Dual specificity phosphatase 1 (DUSP1) regulates a subset of LPS-induced genes and protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 203(1), 15–20.
Abraham, S. M., Lawrence, T., Kleiman, A., Warden, P., Medghalchi, M., Tuckermann, J., et al. (2006). Antiinflammatory effects of dexamethasone are partly dependent on induction of dual specificity phosphatase 1. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 203(8), 1883–1889.
Zhao, Q., Wang, X., Nelin, L. D., Yao, Y., Matta, R., Manson, M. E., et al. (2006). MAP kinase phosphatase 1 controls innate immune responses and suppresses endotoxic shock. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 203(1), 131–140.
Wu, J. J., Roth, R. J., Anderson, E. J., Hong, E. G., Lee, M. K., Choi, C. S., et al. (2006). Mice lacking MAP kinase phosphatase-1 have enhanced MAP kinase activity and resistance to diet-induced obesity. Cell Metabolism, 4(1), 61–73.
Zhang, Y., Blattman, J. N., Kennedy, N. J., Duong, J., Nguyen, T., Wang, Y., et al. (2004). Regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses by MAP kinase phosphatase 5. Nature, 430(7001), 793–797.
Jeffrey, K. L., Brummer, T., Rolph, M. S., Liu, S. M., Callejas, N. A., Grumont, R. J., et al. (2006). Positive regulation of immune cell function and inflammatory responses by phosphatase PAC-1. Nature Immunology, 7(3), 274–283.
Li, C., Scott, D. A., Hatch, E., Tian, X., & Mansour, S. L. (2007). Dusp6 (Mkp3) is a negative feedback regulator of FGF-stimulated ERK signaling during mouse development. Development, 134(1), 167–176.
Eblaghie, M. C., Lunn, J. S., Dickinson, R. J., Munsterberg, A. E., Sanz-Ezquerro, J. J., Farrell, E. R., et al. (2003). Negative feedback regulation of FGF signaling levels by Pyst1/MKP3 in chick embryos. Current Biology, 13(12), 1009–1018.
Christie, G. R., Williams, D. J., Macisaac, F., Dickinson, R. J., Rosewell, I., & Keyse, S. M. (2005). The dual-specificity protein phosphatase DUSP9/MKP-4 is essential for placental function but is not required for normal embryonic development. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 25(18), 8323–8333.
Loda, M., Capodieci, P., Mishra, R., Yao, H., Corless, C., Grigioni, W., et al. (1996). Expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in the early phases of human epithelial carcinogenesis. American Journal of Pathology, 149(5), 1553–1564.
Zhang, L., Zhou, W., Velculescu, V. E., Kern, S. E., Hruban, R. H., Hamilton, S. R., et al. (1997). Gene expression profiles in normal and cancer cells. Science, 276(5316), 1268–1272.
Emslie, E. A., Jones, T. A., Sheer, D., & Keyse, S. M. (1994). The CL100 gene, which encodes a dual specificity (Tyr/Thr) MAP kinase phosphatase, is highly conserved and maps to human chromosome 5q34. Human Genetics, 93(5), 513–516.
Li, M., Zhou, J. Y., Ge, Y., Matherly, L. H., & Wu, G. S. (2003). The phosphatase MKP1 is a transcriptional target of p53 involved in cell cycle regulation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(42), 41059–41068.
Keyse, S. M., & Emslie, E. A. (1992). Oxidative stress and heat shock induce a human gene encoding a protein-tyrosine phosphatase. Nature, 359(6396), 644–647.
Laderoute, K. R., Mendonca, H. L., Calaoagan, J. M., Knapp, A. M., Giaccia, A. J., & Stork, P. J. (1999). Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) expression is induced by low oxygen conditions found in solid tumor microenvironments. A candidate MKP for the inactivation of hypoxia-inducible stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274(18), 12890–12897.
Leav, I., Galluzzi, C. M., Ziar, J., Stork, P. J., Ho, S. M., & Loda, M. (1996). Mitogen-activated protein kinase and mitogen-activated kinase phosphatase-1 expression in the Noble rat model of sex hormone-induced prostatic dysplasia and carcinoma. Laboratory Investigation, 75(3), 361–370.
Magi-Galluzzi, C., Montironi, R., Cangi, M. G., Wishnow, K., & Loda, M. (1998). Mitogen-activated protein kinases and apoptosis in PIN. Virchows Archiv, 432(5), 407–413.
Magi-Galluzzi, C., Mishra, R., Fiorentino, M., Montironi, R., Yao, H., Capodieci, P., et al. (1997). Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 is overexpressed in prostate cancers and is inversely related to apoptosis. Laboratory Investigation, 76(1), 37–51.
Srikanth, S., Franklin, C. C., Duke, R. C., & Kraft, R. S. (1999). Human DU145 prostate cancer cells overexpressing mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 are resistant to Fas ligand-induced mitochondrial perturbations and cellular apoptosis. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 199(1–2), 169–178.
Denkert, C., Schmitt, W. D., Berger, S., Reles, A., Pest, S., Siegert, A., et al. (2002). Expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) in primary human ovarian carcinoma. International Journal of Cancer, 102(5), 507–513.
Wang, H. Y., Cheng, Z., & Malbon, C. C. (2003). Overexpression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases MKP1, MKP2 in human breast cancer. Cancer Letters, 191(2), 229–237.
Small, G. W., Shi, Y. Y., Higgins, L. S., & Orlowski, R. Z. (2007). Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 is a mediator of breast cancer chemoresistance. Cancer Research, 67(9), 4459–4466.
Sanchez-Perez, I., Martinez-Gomariz, M., Williams, D., Keyse, S. M., & Perona, R. (2000). CL100/MKP-1 modulates JNK activation and apoptosis in response to cisplatin. Oncogene, 19(45), 5142–5152.
Wang, Z., Xu, J., Zhou, J. Y., Liu, Y., & Wu, G. S. (2006). Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 is required for cisplatin resistance. Cancer Research, 66(17), 8870–8877.
Vicent, S., Garayoa, M., Lopez-Picazo, J. M., Lozano, M. D., Toledo, G., Thunnissen, F. B., et al. (2004). Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and is an independent predictor of outcome in patients. Clinical Cancer Research, 10(11), 3639–3649.
Lim, E. H., Aggarwal, A., Agasthian, T., Wong, P. S., Tan, C., Sim, E., et al. (2003). Feasibility of using low-volume tissue samples for gene expression profiling of advanced non-small cell lung cancers. Clinical Cancer Research, 9(16 Pt 1), 5980–5987.
Chattopadhyay, S., Machado-Pinilla, R., Manguan-Garcia, C., Belda-Iniesta, C., Moratilla, C., Cejas, P., et al. (2006). MKP1/CL100 controls tumor growth and sensitivity to cisplatin in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene, 25(23), 3335–3345.
Small, G. W., Shi, Y. Y., Edmund, N. A., Somasundaram, S., Moore, D. T., & Orlowski, R. Z. (2004). Evidence that mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 induction by proteasome inhibitors plays an antiapoptotic role. Molecular Pharmacology, 66(6), 1478–1490.
Sieben, N. L., Oosting, J., Flanagan, A. M., Prat, J., Roemen, G. M., Kolkman-Uljee, S. M., et al. (2005). Differential gene expression in ovarian tumors reveals Dusp 4 and Serpina 5 as key regulators for benign behavior of serous borderline tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 23(29), 7257–7264.
Yip-Schneider, M. T., Lin, A., & Marshall, M. S. (2001). Pancreatic tumor cells with mutant K-ras suppress ERK activity by MEK-dependent induction of MAP kinase phosphatase-2. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 280(4), 992–997.
Givant-Horwitz, V., Davidson, B., Goderstad, J. M., Nesland, J. M., Trope, C. G., & Reich, R. (2004). The PAC-1 dual specificity phosphatase predicts poor outcome in serous ovarian carcinoma. Gynecologic Oncology, 93(2), 517–523.
Kim, S. C., Hahn, J. S., Min, Y. H., Yoo, N. C., Ko, Y. W., & Lee, W. J. (1999). Constitutive activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in human acute leukemias: Combined role of activation of MEK, hyperexpression of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and downregulation of a phosphatase, PAC1. Blood, 93(11), 3893–3899.
Furukawa, T., Yatsuoka, T., Youssef, E. M., Abe, T., Yokoyama, T., Fukushige, S., et al. (1998). Genomic analysis of DUSP6, a dual specificity MAP kinase phosphatase, in pancreatic cancer. Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics, 82(3–4), 156–159.
Warmka, J. K., Mauro, L. J., & Wattenberg, E. V. (2004). Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-3 is a tumor promoter target in initiated cells that express oncogenic Ras. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(32), 33085–33092.
Croonquist, P. A., Linden, M. A., Zhao, F., & Van Ness, B. G. (2003). Gene profiling of a myeloma cell line reveals similarities and unique signatures among IL-6 response, N-ras-activating mutations, and coculture with bone marrow stromal cells. Blood, 102(7), 2581–2592.
Bloethner, S., Chen, B., Hemminki, K., Muller-Berghaus, J., Ugurel, S., Schadendorf, D., et al. (2005). Effect of common B-RAF and N-RAS mutations on global gene expression in melanoma cell lines. Carcinogenesis, 26(7), 1224–1232.
Marchetti, S., Gimond, C., Roux, D., Gothie, E., Pouyssegur, J., & Pages, G. (2004). Inducible expression of a MAP kinase phosphatase-3-GFP chimera specifically blunts fibroblast growth and ras-dependent tumor formation in nude mice. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 199(3), 441–450.
Furukawa, T., Sunamura, M., Motoi, F., Matsuno, S., & Horii, A. (2003). Potential tumor suppressive pathway involving DUSP6/MKP-3 in pancreatic cancer. American Journal of Pathology, 162(6), 1807–1815.
Furukawa, T., Fujisaki, R., Yoshida, Y., Kanai, N., Sunamura, M., Abe, T., et al. (2005). Distinct progression pathways involving the dysfunction of DUSP6/MKP-3 in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Modern Pathology, 18(8), 1034–1042.
Xu, S., Furukawa, T., Kanai, N., Sunamura, M., & Horii, A. (2005). Abrogation of DUSP6 by hypermethylation in human pancreatic cancer. Journal of Human Genetics, 50(4), 159–167.
Leach, S. D. (2004). Mouse models of pancreatic cancer: the fur is finally flying!. Cancer Cell, 5(1), 7–11.
Levy-Nissenbaum, O., Sagi-Assif, O., Raanani, P., Avigdor, A., Ben-Bassat, I., & Witz, I. P. (2003). cDNA microarray analysis reveals an overexpression of the dual-specificity MAPK phosphatase PYST2 in acute leukemia. Methods in Enzymology, 366, 103–113.
Levy-Nissenbaum, O., Sagi-Assif, O., Raanani, P., Avigdor, A., Ben-Bassat, I., & Witz, I. P. (2003). Overexpression of the dual-specificity MAPK phosphatase PYST2 in acute leukemia. Cancer Letters, 199(2), 185–192.
Levy-Nissenbaum, O., Sagi-Assif, O., Kapon, D., Hantisteanu, S., Burg, T., Raanani, P., et al. (2003). Dual-specificity phosphatase Pyst2-L is constitutively highly expressed in myeloid leukemia and other malignant cells. Oncogene, 22(48), 7649–7660.
Muda, M., Boschert, U., Smith, A., Antonsson, B., Gillieron, C., Chabert, C., et al. (1997). Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase, MKP-4. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272(8), 5141–5151.
Dickinson, R. J., Williams, D. J., Slack, D. N., Williamson, J., Seternes, O. M., & Keyse, S. M. (2002). Characterization of a murine gene encoding a developmentally regulated cytoplasmic dual-specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase. Biochemical Journal, 364(Pt 1), 145–155.
Liu, Y., Lagowski, J., Sundholm, A., Sundberg, A., & Kulesz-Martin, M. (2007). Microtubule disruption and tumor suppression by mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 4. Cancer Research, 67(22), 10711–10719.
Acknowledgements
Work in my laboratory is supported by Cancer Research UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keyse, S.M. Dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs) and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 27, 253–261 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-008-9123-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-008-9123-1