Abstract
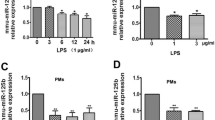
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced in macrophages is critical for microbial killing, but they also take part in inflammation and antigen presentation functions. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous regulators of gene expression, and they can control immune responses. To dissect the complex nature of ROS-mediated effects in macrophages, we sought to characterize miRNAs that are responsive to oxidative stress-induced with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the mouse macrophage cell line, RAW 264.7. We have identified a set of unique miRNAs that are differentially expressed in response to H2O2. These include miR-27a*, miR-27b*, miR-29b*, miR-24-2*, and miR-21*, all of which were downregulated except for miR-21*. By using luciferase reporter vector containing nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB) response elements, we demonstrate that overexpression of miR-27b* suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of NF-kB in RAW 264.7 cells. Our data suggest that macrophage functions can be regulated by oxidative stress-responsive miRNAs by modulating the NF-kB pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mogensen TH (2009) Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:240–273 Table of Contents
Kohchi C, Inagawa H, Nishizawa T, Soma G (2009) ROS and innate immunity. Anticancer Res 29:817–821
Donepudi M, Jovasevic VM, Raychaudhuri P, Mokyr MB (2003) Melphalan-induced up-regulation of B7-1 surface expression on normal splenic B cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 52:162–170
Tse HM, Milton MJ, Schreiner S, Profozich JL, Trucco M, Piganelli JD (2007) Disruption of innate-mediated proinflammatory cytokine and reactive oxygen species third signal leads to antigen-specific hyporesponsiveness. J Immunol 178:908–917
Murata Y, Yamashita A, Saito T, Sugamura K, Hamuro J (2002) The conversion of redox status of peritoneal macrophages during pathological progression of spontaneous inflammatory bowel disease in Janus family tyrosine kinase 3(−/−) and IL-2 receptor gamma(−/−) mice. Int Immunol 14:627–636
Haddad JJ, Fahlman CS (2002) Redox- and oxidant-mediated regulation of interleukin-10: an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant cytokine? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 297:163–176
Xiao C, Rajewsky K (2009) MicroRNA control in the immune system: basic principles. Cell 136:26–36
Baltimore D, Boldin MP, O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Taganov KD (2008) MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat Immunol 9:839–845
Li QJ, Chau J, Ebert PJ, Sylvester G, Min H, Liu G, Braich R, Manoharan M, Soutschek J, Skare P, Klein LO, Davis MM, Chen CZ (2007) miR-181a is an intrinsic modulator of T cell sensitivity and selection. Cell 129:147–161
Xiao C, Srinivasan L, Calado DP, Patterson HC, Zhang B, Wang J, Henderson JM, Kutok JL, Rajewsky K (2008) Lymphoproliferative disease and autoimmunity in mice with increased miR-17-92 expression in lymphocytes. Nat Immunol 9:405–414
Xiao C, Calado DP, Galler G, Thai TH, Patterson HC, Wang J, Rajewsky N, Bender TP, Rajewsky K (2007) MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the transcription factor c-Myb. Cell 131:146–159
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, Baltimore D (2006) NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12481–12486
O’Connell RM, Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Cheng G, Baltimore D (2007) MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:1604–1609
Lin Y, Liu X, Cheng Y, Yang J, Huo Y, Zhang C (2009) Involvement of MicroRNAs in hydrogen peroxide-mediated gene regulation and cellular injury response in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 284:7903–7913
Cheng Y, Liu X, Zhang S, Lin Y, Yang J, Zhang C (2009) MicroRNA-21 protects against the H(2)O(2)-induced injury on cardiac myocytes via its target gene PDCD4. J Mol Cell Cardiol 47:5–14
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Bilitewski U (2008) Determination of immunomodulatory effects: focus on functional analysis of phagocytes as representatives of the innate immune system. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1545–1554
Wang GM, Wu F, Raghavachari N, Reddan JR (1998) Thioltransferase is present in the lens epithelial cells as a highly oxidative stress-resistant enzyme. Exp Eye Res 66:477–485
Stenvang J, Lindow M, Kauppinen S (2008) Targeting of microRNAs for therapeutics. Biochem Soc Trans 36:1197–1200
Li G, Barnes D, Butz D, Bjorling D, Cook ME (2005) 10t, 12c-conjugated linoleic acid inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase expression in vitro and in vivo. J Lipid Res 46:2134–2142
Sun J, Ramnath RD, Zhi L, Tamizhselvi R, Bhatia M (2008) Substance P enhances NF-kappaB transactivation and chemokine response in murine macrophages via ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 294:C1586–C1596
Barber RD, Harmer DW, Coleman RA, Clark BJ (2005) GAPDH as a housekeeping gene: analysis of GAPDH mRNA expression in a panel of 72 human tissues. Physiol Genomics 21:389–395
Bustin SA (2000) Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol 25:169–193
Smyth GK, Michaud J, Scott HS (2005) Use of within-array replicate spots for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Bioinformatics 21:2067–2075
Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N, Golani I (2001) Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behav Brain Res 125:279–284
Zhang Y, Fong CC, Wong MS, Tzang CH, Lai WP, Fong WF, Sui SF, Yang M (2005) Molecular mechanisms of survival and apoptosis in RAW 264.7 macrophages under oxidative stress. Apoptosis 10:545–556
Simone NL, Soule BP, Ly D, Saleh AD, Savage JE, Degraff W, Cook J, Harris CC, Gius D, Mitchell JB (2009) Ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress alters miRNA expression. PLoS One 4:e6377
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ (2008) miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D154–D158
Chen K, Rajewsky N (2007) The evolution of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet 8:93–103
Yu X, Zhou Q, Li SC, Luo Q, Cai Y, Lin WC, Chen H, Yang Y, Hu S, Yu J (2008) The silkworm (Bombyx mori) microRNAs and their expressions in multiple developmental stages. PLoS One 3:e2997
Ruby JG, Stark A, Johnston WK, Kellis M, Bartel DP, Lai EC (2007) Evolution, biogenesis, expression, and target predictions of a substantially expanded set of Drosophila microRNAs. Genome Res 17:1850–1864
Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M (2009) Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 27:693–733
Bowie A, O’Neill LA (2000) Oxidative stress and nuclear factor-kappaB activation: a reassessment of the evidence in the light of recent discoveries. Biochem Pharmacol 59:13–23
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801
Maemura K, Zheng Q, Wada T, Ozaki M, Takao S, Aikou T, Bulkley GB, Klein AS, Sun Z (2005) Reactive oxygen species are essential mediators in antigen presentation by Kupffer cells. Immunol Cell Biol 83:336–343
Perkins ND (2007) Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:49–62
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y (2000) Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev Immunol 18:621–663
Mercurio F, Manning AM (1999) NF-kappaB as a primary regulator of the stress response. Oncogene 18:6163–6171
Fan Z, Yang H, Bau B, Soder S, Aigner T (2006) Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NFkappaB on IL-1beta-induced effects on collagen type II, MMP-1 and 13 mRNA expression in normal articular human chondrocytes. Rheumatol Int 26:900–903
Fantuzzi L, Spadaro F, Purificato C, Cecchetti S, Podo F, Belardelli F, Gessani S, Ramoni C (2008) Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C activation is required for CCR5-dependent, NF-kB-driven CCL2 secretion elicited in response to HIV-1 gp120 in human primary macrophages. Blood 111:3355–3363
Remppis A, Bea F, Greten HJ, Buttler A, Wang H, Zhou Q, Preusch MR, Enk R, Ehehalt R, Katus H, Blessing E (2010) Rhizoma Coptidis inhibits LPS-induced MCP-1/CCL2 production in murine macrophages via an AP-1 and NFkappaB-dependent pathway. Mediators Inflamm 2010:194896
Sarada S, Himadri P, Mishra C, Geetali P, Ram MS, Ilavazhagan G (2008) Role of oxidative stress and NFkB in hypoxia-induced pulmonary edema. Exp Biol Med 233:1088–1098
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Gustavo Delhon for critically reading the manuscript. This work was supported by the COBRE Program from the National Center for Research Resources (P20-RR-17675, NIH), Redox Biology Center, University of Nebraska-Lincoln. The UNMC Microarray Core Facility receives partial support from the NIH grant number P20 RR016469 from the INBRE Program of the National Center for Research Resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sivasubramani Thulasingam and Chandirasegaran Massilamany contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thulasingam, S., Massilamany, C., Gangaplara, A. et al. miR-27b*, an oxidative stress-responsive microRNA modulates nuclear factor-kB pathway in RAW 264.7 cells. Mol Cell Biochem 352, 181–188 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0752-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0752-2