Abstract
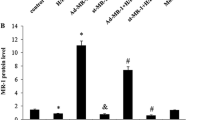
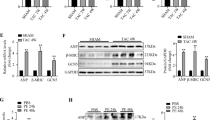
Ischemia/reperfusion injury causes cardiomyocyte apoptosis, ventricular remodeling, leading to a dilated heart. Hypoxia is one of the causes involved in ischemia damage, and BNIP3 is a hypoxia-inducible marker and also a sensor to induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Recent reports discussed ablating BNIP3 can restrain cardiomyocytes apoptosis and post-infarction remodeling. BNIP3 is a crucial therapeutic target. However, the BNIP3-induced hypertrophy aspect is rarely investigated. Here, we transiently transfected BNIP3 plasmids into H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells to evaluate the molecular signaling and hypertrophy markers using Western blot. We measured the cell size change using actin staining. We disclose that BNIP3 overexpression induced an increase in cell size, activated the pathological-related hypertrophy signaling pathways, such as IL6-MEK5-ERK5, IL6-JAK2-STAT1/3, calcineurin/NFAT3 and p38β MAPK resulting in the fetal genes, ANP and BNP expressing. Concluding above, BNIP3 acts as a pathological hypertrophy inducer, which might be a potential therapeutic target for heart damage prevention.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANP:
-
Atrial natriuretic peptide
- BNP:
-
B-type natriuretic peptide
- ERK5:
-
Extracellular-regulated kinase 5
- IL6:
-
Interleukin-6
- JAK2:
-
Janus kinase 2
- β-MHC:
-
β-Myosin heavy chain
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NFAT3:
-
Nuclear factor of activated T cells 3
- STAT1/3:
-
Signal transducers and activators of transcription-1,-3
References
Whelan RS, Mani K, Kitsis RN (2007) Nipping at cardiac remodeling. J Clin Invest 117:2751–2753
Drazner MH, Rame JE, Marino EK, Gottdiener JS, Kitzman DW, Gardin JM, Manolio TA, Dries DL, Siscovick DS (2004) Increased left ventricular mass is a risk factor for the development of a depressed left ventricular ejection fraction within five years: the Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:2207–2215
Olson EN, Schneider MD (2003) Sizing up the heart: development redux in disease. Genes Dev 17:1937–1956
Dorn GW 2, Force T (2005) Protein kinase cascades in the regulation of cardiac hypertrophy. J Clin Invest 115:527–537
Molkentin JD, Dorn GW 2 (2001) Cytoplasmic signaling pathways that regulate cardiac hypertrophy. Annu Rev Physiol 63:391–426
Chu CH, Tzang BS, Chen LM, Kuo CH, Cheng YC, Chen LY, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Kuo WW, Huang CY (2008) IGF-II/mannose-6-phosphate receptor signaling induced cell hypertrophy and atrial natriuretic peptide/BNP expression via Galphaq interaction and protein kinase C-alpha/CaMKII activation in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. J Endocrinol 197:381–390
Molkentin JD, Lu JR, Antos CL, Markham B, Richardson J, Robbins J, Grant SR, Olson EN (1998) A calcineurin-dependent transcriptional pathway for cardiac hypertrophy. Cell 93:215–228
Molkentin JD, Olson EN (1997) GATA4: a novel transcriptional regulator of cardiac hypertrophy? Circulation 96:3833–3835
Kanda T, Takahashi T (2004) Interleukin-6 and cardiovascular diseases. Jpn Heart J 45:183–193
Pan J, Fukuda K, Kodama H, Sano M, Takahashi T, Makino S, Kato T, Manabe T, Hori S, Ogawa S (1998) Involvement of gp130-mediated signaling in pressure overload-induced activation of the JAK/STAT pathway in rodent heart. Heart Vessel 13:199–208
Pan J, Fukuda K, Saito M, Matsuzaki J, Kodama H, Sano M, Takahashi T, Kato T, Ogawa S (1999) Mechanical stretch activates the JAK/STAT pathway in rat cardiomyocytes. Circ Res 84:1127–1136
Ng DC, Court NW, dos Remedios CG, Bogoyevitch MA (2003) Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathways in failing human hearts. Cardiovasc Res 57:333–346
Kunisada K, Tone E, Fujio Y, Matsui H, Yamauchi-Takihara K, Kishimoto T (1998) Activation of gp130 transduces hypertrophic signals via STAT3 in cardiac myocytes. Circulation 98:346–352
Nicol RL, Frey N, Pearson G, Cobb M, Richardson J, Olson EN (2001) Activated MEK5 induces serial assembly of sarcomeres and eccentric cardiac hypertrophy. EMBO J 20:2757–2767
Wang Y, Huang S, Sah VP, Ross J Jr, Brown JH, Han J, Chien KR (1998) Cardiac muscle hypertrophy and apoptosis induced by distinct members of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase family. J Biol Chem 273:2161–2168
Zechner D, Thuerauf DJ, Hanford DS, McDonough PM, Glembotski CC (1997) A role for the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in myocardial cell growth, sarcomeric organization, and cardiac-specific gene expression. J Cell Biol 139:115–127
Boyd JM, Malstrom S, Subramanian T, Venkatesh LK, Schaeper U, Elangovan B, D’Sa-Eipper C, Chinnadurai G (1994) Adenovirus E1B 19 kDa and Bcl-2 proteins interact with a common set of cellular proteins. Cell 79:341–351
Bruick RK (2000) Expression of the gene encoding the proapoptotic Nip3 protein is induced by hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9082–9087
Chen G, Ray R, Dubik D, Shi L, Cizeau J, Bleackley RC, Saxena S, Gietz RD, Greenberg AH (1997) The E1B19K/Bcl-2-binding protein Nip3 is a dimeric mitochondrial protein that activates apoptosis. J Exp Med 186:1975–1983
Yasuda M, Theodorakis P, Subramanian T, Chinnadurai G (1998) Adenovirus E1B-19K/BCL-2 interacting protein BNIP3 contains a BH3 domain and a mitochondrial targeting sequence. J Biol Chem 273:12415–12421
Ray R, Chen G, Vande VC, Cizeau J, Park JH, Reed JC, Gietz RD, Greenberg AH (2000) BNIP3 heterodimerizes with Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L) and induces cell death independent of a Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3) domain at both mitochondrial and nonmitochondrial sites. J Biol Chem 275:1439–1448
Dorn GW 2, Kirshenbaum LA (2009) Cardiac reanimation: targeting cardiomyocyte death by BNIP3 and NIX/BNIP3L. Oncogene 27:S158–S167
Diwan A, Matkovich SJ, Yuan Q, Zhao W, Yatani A, Brown JH, Molkentin JD, Kranias EG, Dorn GW 2 (2009) Endoplasmic reticular–mitochondrial crosstalk in Nix-mediated cell death. J Clin Invest 119:203–212
Nakayama H, Chen X, Baines CP, Klevitsky R, Zhang X, Zhang H, Jaleel N, Chua BH, Hewett TE, Robbins J, Houser SR, Molkentin JD (2007) Ca2+- and mitochondrial-dependent cardiomyocyte necrosis as a primary mediator of heart failure. J Clin Invest 117:2431–2444
Daido S, Kanzawa T, Yamamoto A, Takeuchi H, Kondo Y, Kondo S (2004) Pivotal role of the cell death factor BNIP3 in ceramide-induced autophagic cell death in malignant glioma cells. Cancer Res 64:4286–4293
Kanzawa T, Zhang L, Xiao L, Germano IM, Kondo Y, Kondo S (2005) Arsenic trioxide induces autophagic cell death in malignant glioma cells by upregulation of mitochondrial cell death protein BNIP3. Oncogene 24:980–991
Diwan A, Krenz M, Syed FM, Wansapura J, Ren X, Koesters AG, Li H, Kirshenbaum LA, Hahn HS, Robbins J, Jones WK, Dorn GW (2007) Inhibition of ischemic cardiomyocyte apoptosis through targeted ablation of Bnip3 restrains postinfarction remodeling in mice. J Clin Invest 117:2825–2833
Schwartz K, de la Bastie D, Bouveret P, Oliviéro P, Alonso S, Buckingham M (1986) Alpha-skeletal muscle actin mRNAs accumulate in hypertrophied adult rat hearts. Circ Res 59:551–555
Izumo S, Nadal-Ginard B, Mahdavi V (1988) Protooncogene induction and reprogramming of cardiac gene expression produced by pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:339–343
Mercadier JJ, Samuel JL, Michel JB, Zongazo MA, de la Bastie D, Lompre AM, Wisnewsky C, Rappaport L, Levy B, Schwartz K (1989) Atrial natriuretic factor gene expression in rat ventricle during experimental hypertension. Am J Physiol 257:H979–H987
Molkentin JD (2004) Calcineurin-NFAT signaling regulates the cardiac hypertrophic response in coordination with the MAPKs. Cardiovasc Res 63:467–475
Zhang L, Li L, Liu H, Borowitz JL, Isom GE (2009) BNIP3 mediates cell death by different pathways following localization to endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrion. FASEB J 23:3405–3414
Wu HC, Yeh YL, Kuo WW, Huang SK, Kuo WH, Hsieh DJ, Wu CL, Tsai CH, Lee SD, Huang CY (2008) P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways are involved in the hypertrophy and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis conditioned medium. Cell Biochem Funct 26:246–255
Nemoto S, Sheng Z, Lin A (1998) Opposing effects of Jun kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases on cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biol 18:3518–3526
Liang Q, Molkentin JD (2002) Divergent signaling pathways converge on GATA4 to regulate cardiac hypertrophic gene expression. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:611–616
Mesri M, Altieri DC (1998) Endothelial cell activation by leukocyte microparticles. J Immunol 161:4382–4387
Loppnow H, Libby P (1990) Proliferating or interleukin 1-activated human vascular smooth muscle cells secrete copious interleukin 6. J Clin Invest 85:731–738
Gwechenberger M, Mendoza LH, Youker KA, Frangogiannis NG, Smith CW, Michael LH, Entman ML (1999) Cardiac myocytes produce interleukin-6 in culture and in viable border zone of reperfused infarctions. Circulation 99:546–551
Kaneko K, Kanda T, Yokoyama T, Nakazato Y, Iwasaki T, Kobayashi I, Nagai R (1997) Expression of interleukin-6 in the ventricles and coronary arteries of patients with myocardial infarction. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 97:3–12
Chen LM, Kuo WW, Yang JJ, Wang SG, Yeh YL, Tsai FJ, Ho YJ, Chang MH, Huang CY, Lee SD (2007) Eccentric cardiac hypertrophy was induced by long-term intermittent hypoxia in rats. Exp Physiol 92:409–416
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by Taiwan Department of Health Clinical Trial and Research Center of Excellence (DOH99-TD-B-111-004) and in part by Taiwan Department of Health Cancer Research Center of Excellence (DOH99-TD-C-111-005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dennis Jine-Yuan Hsieh, Chih-Yang Huang, and Jin-Ming Hwang share equal contribution.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, YJ., Kuo, WW., Kuo, CH. et al. BNIP3 induces IL6 and calcineurin/NFAT3 hypertrophic-related pathways in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. Mol Cell Biochem 345, 241–247 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0578-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0578-3