Abstract
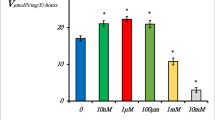
The linear pentadecapeptide gramicidin A forms an ion channel in the lipid bilayer to selectively transport monovalent cations. Nevertheless, we have surprisingly found that gramicidin A directly inhibits mammalian Na+/K+-ATPase. Gramicidin A inhibited ATP hydrolysis by Na+/K+-ATPase from porcine cerebral cortex at the IC50 value of 8.1 μM, while gramicidin S was approximately fivefold less active. The synthetic gramicidin A analog lacking N-terminal formylation and C-terminal ethanolamine exhibited a weaker inhibitory effect on the ATP-hydrolyzing activity of Na+/K+-ATPase than gramicidin A, indicating that these end modifications are necessary for gramicidin A to inhibit Na+/K+-ATPase activity. Moreover, Lineweaver–Burk analysis showed that gramicidin A exhibits a mixed type of inhibition. In addition to the most well-studied ionophore activity, our present study has disclosed a novel biological function of gramicidin A as a direct inhibitor of mammalian Na+/K+-ATPase activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen OS, Koeppe RE II, Roux B (2005) Gramicidin channels. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 4:10–20. doi:10.1109/TNB.2004.842470
Kelkar DA, Chattopadhyay A (2007) The gramicidin ion channel: a model membrane protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:2011–2025. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.05.011
Sarges R, Witkop B (1965) Gramicidin A. V. The structure of valine- and isoleucine-gramicidin A. J Am Chem Soc 87:2011–2020. doi:10.1021/ja01087a027
Bamberg E, Apell HJ, Alpes H (1977) Structure of the gramicidin A channel: discrimination between the πL, D and the β helix by electrical measurements with lipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74:2402–2406. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.6.2402
Urry DW (1971) The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed π(L, D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 68:672–676. doi:10.1073/pnas.68.3.672
Urry DW, Goodall MC, Glickson JD, Mayers DF (1971) The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: characteristics of head-to-head dimerized π(L, D) helices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 68:1907–1911. doi:10.1073/pnas.68.8.1907
Hayashi Y, Mimura K, Matsui H, Takagi T (1989) Minimum enzyme unit for Na+/K+-ATPase is the αβ-protomer. Determination by low-angle laser light scattering photometry coupled with high-performance gel chromatography for substantially simultaneous measurement of ATPase activity and molecular weight. Biochim Biophys Acta 983:217–229. doi:10.1016/0005-2736(89)90237-X
Kobayashi T, Tahara Y, Takenaka H, Mimura K, Hayashi Y (2007) Na+- and K+-dependent oligomeric interconversion among αβ-protomers, diprotomers and higher oligomers in solubilized Na+/K+-ATPase. J Biochem 142:157–173. doi:10.1093/jb/mvm150
Kielley WW (1955) Mg-activated muscle ATPases. Methods Enzymol 2:588–591. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(55)02259-3
Komatsu Y, Fujii T (1971) Effects of calcium ions on the adenosine-triphosphatase activities of erythrocyte membrane. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 19:1943–1948
Hoenig M, Lee RJ, Ferguson DC (1989) A microtiter plate assay for inorganic phosphate. J Biochem Biophys Methods 19:249–252. doi:10.1016/0165-022X(89)90031-6
Chan WC, White PD (2000) In: Chan WC, White PD (eds) Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis: a practical approach. Oxford University Press, Inc., New York, pp 41–76
Miyanishi H, Takahashi T, Mihara H (2004) De novo design of peptides with l-α-nucleobase amino acids and their binding properties to the P22 boxB RNA and its mutants. Bioconjug Chem 15:694–698. doi:10.1021/bc034210n
Riddell FG (2002) Structure, conformation, and mechanism in the membrane transport of alkali methal ions by ionophoric antibiotics. Chirality 14:121–125. doi:10.1002/chir.10052
Sarkar N, Langrey D, Paulus H (1977) Biological function of gramicidin: selective inhibition of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74:1478–1482. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.4.1478
Zhao DY, Dhalla NS (1989) Influence of gramicidin S on cardiac membrane Ca2+/Mg2+ ATPase activities and contractile force development. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 67:546–552
Zhao D, Dhalla NS (1991) Purification and composition of Ca2+/Mg2+ ATPase from rat heart plasma membrane. Mol Cell Biochem 107:135–149
Meghji P, Burnstock G (1995) Inhibition of extracellular ATP degradation in endothelial cells. Life Sci 57:763–771. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(95)02004-3
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Drs. Yoshikazu Tahara and Yutaro Hayashi for the gift of Na+/K+-ATPase. We thank Drs. Hisakazu Mihara and Tsuyoshi Takahashi for synthesizing gramicidin A analog and critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takada, Y., Matsuo, K. & Kataoka, T. Gramicidin A directly inhibits mammalian Na+/K+-ATPase. Mol Cell Biochem 319, 99–103 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9882-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9882-6