Abstract
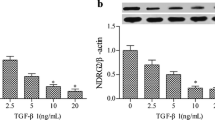
Prohibitin (PHB), a potential tumor suppressor, has been shown to inhibit cell proliferation by repressing E2F-mediated transcription. But little is known about the role of PHB involved in tubulointerstitial fibrosis (TIF). Here, for the first time, we found PHB protein was positively expressed at normal renal tissues, strongly down-regulated in renal biopsy specimens, and negatively correlated with the expression of alpha-smooth-muscle actin (α-SMA) and with the degrees of tubulointerstitial lesions. Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) is the most important profibrotic cytokine in the process of TIF and capable of inducing cell phenotypic change of interstitial fibroblasts characterized by the de novo expression of α-SMA. Confocal microscopy showed majority of PHB is located at cytoplasm as well as at nucleus in rat kidney fibroblasts cell (NRK-49F). As we found that PHB protein and mRNA expression were down-regulated in NRK-49F cells following TGF-β1 stimulation. We used transient transfection to over-express PHB protein and found that cells with increased PHB levels had a significant reduction in the percentage entering cell cycle and abolished de novo expression of α-SMA following TGF-β1 stimulation. Therefore, over-expression of PHB suppresses renal interstitial fibroblasts proliferation and cell phenotypic change induced by TGF-β1, which indicates PHB as a potential therapeutic target to halt the progression of TIF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strutz F, Muller GA (1995) On the progression of chronic renal disease Nephron 69: 371–379
Bohle A, Muller GA, Wehrmann M, Mackensen-Haen S, Xiao JC (1996) Pathogenesis of chronic renal failure in the primary glomerulopathies, renal vasculopathies, and chronic interstitial nephritides Kidney Int 54: S2–S9
Eddy AA (2000) Molecular basis of renal fibrosis Pediatr Nephrol 15:290–301
Negri AL (2004) Prevention of progressive fibrosis in chronic renal diseases: Antifibrotic agents J Nephrol 17: 496–503
Kaneto H, Morrissey J, Klahr S (1993) Increased expression of TGF-b1 mRNA in the obstructed kidney of rats with unilateral uretheral ligation Kidney Int 44: 313–321
Yamamoto T, Noble NA, Miller DE, Border WA (1994) Sustained expression of TGF-b1 underlies development of progressive kidney fibrosis Kidney Int 45: 916–927
Yamamotto T, Nakamura T, Noble NA, Ruoslahti E, Border WA (1993) Expression of transforming growth factor-b is elevated in human and experimental diabetic nephropathy Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 1814–1818
Cuhaci B, Kumar MS, Bloom RD, Pratt B, Haussman G, Laskow DA, Alidoost M, Grotkowski C, Cahill K, Butani L, Sturgill BC, Pankewycz OG (1999) Transforming growth factor-b levels in human allograft chronic fibrosis correlate with the rate of decline in renal function Transplantation 68: 785–790
Badid C, Vincent M, Fouque D, Laville M, Desmouliere A (2001) Myofibroblast: a prognosticmarker and target cell in progressive renal disease Ren Fail 23: 543–549
el Nahas AM, Muchaneta-Kubara EC, Zhang G, Adam A, Goumenos D (1996) Phenotypic modulation of renal cells during experimental and clinical renal scarring Kidney Int 54: S23–S27
Klahr S, Morrissey J (2002) Obstructive nephropathy and renal fibrosis Am J Physiol 283: F861–F875
De Heer E, Sijpkens YW, Verkade M, den Dulk M, Langers A, Schutrups J, Bruijn JA, van Es LA (2000) Morphometry of interstitial fibrosis Nephrol Dial Transpl 15:72–73
Huang WY, Sun H, Pan XQ, Guo M, Zhang AH, Wu YJ, Huang SM, Chen RH (2003) Screening of genes involved in renal interstitial fibrosis in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction Chin J Pediatr 41: 855–856
Mishra S, Murphy LC, Nyomba BL, Murphy LJ (2005) PHB: a potential target for new therapeutics TRENDS Mol Med 11: 192–197
Thompson WE, Branch A, Whittaker JA, Lyn D, Zilberstein M, Mayo KE, Thomas K (2001) Characterization of PHB in a newly established rat ovarian granulosa cell line Endocrinology 142: 4076–4085
Nijtmans LG, Artal SM, Grivell LA, Coates PJ (2002) The mitochondrial PHB complex: roles in mitochondrial respiratory complex assembly, ageing and degenerative disease Cell Mol Life Sci 59: 143–155
Artal-Sanz M, Tsang WY, Willems EM, Grivell LA, Lemire BD, van der Spek H, Nijtmans LG (2003) The mitochondrial prohibitin complex is essential for embryonic viability and germline function in Caenorhabditis elegans J Biol Chem 278: 32091–32099
Thompson WE, Ramalho-Santos J, Sutovsky P (2003) Ubiquitination of prohibitin in mammalian sperm mitochondria: possible roles in the regulation of mitochondrial inheritance and sperm quality control Biol Reprod 69: 254–260
Jupe ER, Liu XT, Kiehlbauch JL, McClung JK, Dell’Orco TT (1996) The 3′ untranslated region of PHB and cellular immortalization Exp Cell Res 224: 128–135
Wang S, Fusaro G, Paddmanabhan J, Chellappan SP (2002) PHB co-localizes with Rb in the nucleus and recruits N-CoR and HDAC1 for transcriptional repression Oncogene 21: 8388–8396
Joshi B, Ko D, Ordonez-Ercan D, Chellappan SP (2003) A putative coiled-coil domain of prohibitin is sufficient to repress E2F1-mediated transcription and induce apoptosis Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312: 459–466
Fusaro G, Wang S, Chellappan S (2002) Differential regulation of Rb family proteins and prohibitin during camptothecin-induced apoptosis Oncogene 21: 4539–4548
Churg J, Bernstein J, Glassock RJ: In: Renal Disease Classification and atlas of glomerular disease, 2nd edn. Ikagu Shoin, New York, pp. 541–553, 1995
The Chinese Society of Pediatric Nephrology (2001) Clinical classification, diagnosis and treatment of glomerular diseases in children Chin J Pediatr 39: 746–749
Thomas SE, Anderson S, Gordon KL, Oyama TT, Shankland SJ, Johnson RJ (1988) Tubulointerstitial disease in aging: Evidence of underlying peritubular capillary damage, potential role for renal ischemia J Am Soc Nephrol 9: 231–242
Coates PJ, Nenutil R, McGregor A, Picksley SM, Crouch DH, Hall PA, Wright EG (2001) Mammalian PHB proteins respond to mitochondrial stress and decrease during cellular senescence Exp Cell Res 265: 262–273
Gamble SC, Odontiadis M, Waxman J (2004) Androgens target PHB to regulate proliferation of prostate cancer cells Oncogene 23: 2996–3004
Zeisberg M, Strutz F, Muller GA (2001) Renal fibrosis: an update Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 10: 315–320
Andrew L, David JA (2004) TGF-β1 signaling and the fibrotic response FASEB 18: 816–827
Bottinger EP, Bitzer M (2002) TGF-β1 signaling in renal disease J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 2600–2610
Moustakas A, Heldin CH (2005) Non-Smad TGF-β1 signals J Cel Sci 118: 3573–3584
Wang S, Nath N, Adlam M (1999) PHB, a potential tumor suppressor, interacts with RB and regulates E2F function Oncogene 18: 3501–3510
Shinae KK, Nobutake A, Hiroto O (2000) Role of TGF-β in EGF-induced transformation of NRK cells is sustaining high-level EGF-signaling FEBS Lett 466: 160–164
Satoshi O, Shinae KK, Yuko H (1998) Constitutive Association of EGF Receptor with the CrkII-23 Mutant that Inhibits Transformation of NRK Cells by EGF and TGF-β Cell Signal 10: 283–290
Wang S, Nath N, Fusaro G, Chellappan S (1999) Rb and PHB target distinct regions of E2F1for repression and respond to different upstream signals Mol Cell Biol 19: 7447–7460
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the grant from National Nature Science Foundation of China (No: 30270619).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Xu, H., Chen, J. et al. Prohibitin suppresses renal interstitial fibroblasts proliferation and phenotypic change induced by transforming growth factor-β1. Mol Cell Biochem 295, 167–177 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9286-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9286-4