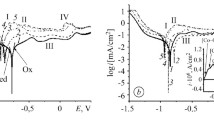
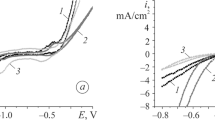
We estimate the electrochemical activity of specimens of the amorphous metallic alloys (АМA) Al87Ni8Y5, Al87Ni8Y4Gd1, and Al87Ni8Dy1Y4 in alkaline solutions of potassium hydroxide of different concentrations and the influence of partial substitution of 1 at. % Gd or Dy for Y. It is shown that all investigated specimens are corrosion-resistant in the course of cyclic polarization within the potential range from – 1.2 to + 1.0 V in aqueous KОН solutions of various concentrations (0.5–5.0) М. It is shown that AMA electrodes alloyed with 1 at.% Dy exhibit the highest catalytic activity in a 4 М KОН solution.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Eliaz and D. Eliezer, “An overview of hydrogen interaction with amorphous alloys,” Adv. Perform. Mater., 6, 5–31 (1999).
F. Rosalbino, S. Delsante, G. Borsone, and E. Angeline, “Electrocatalytic behavior of Co–Ni–R (R = Rare Earth Metal) crystalline alloys as electrode materials for hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline medium,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 33, 6696–6703 (2008).
L. M. Boichyshyn, O. M. Hertsyk, M. A. Kovbus, T. G. Pereverzeva, and B. Ya. Kotur, “Electrocatalytic evolution of hydrogen on amorphous Fe–Nb–B–rare-earth-metal electrodes from alkaline solutions,” Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 87, No. 1, 62–69 (2014).
S. Marini, P. Salvi, P. Nelli, R. Pesenti, M. Villa, and Y. Kiros, “Stable and inexpensive electrodes for the hydrogen evolution reaction,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 38, No. 26, 11484–11495 (2013).
M. A. Dominguez-Crespo, A. M. Torre-Huerta, B. Brachetti-Sibaja, and A. Flores-Vela, “Electrochemical performance of Ni–RE (RE = rare earth) as electrode material for hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline medium,” Corros. Sci., 36, 135–151 (2011).
L. Fan, H. Lu, and J. Leng, “Performance of fine structured aluminum anodes in neutral and alkaline electrolytes for Al-air batteries,” Electrochim. Acta, 165, 22–28 (2015).
C. Kjartansdóttir, M. Caspersen, S. Egelund, and P. Moller, “Electrochemical investigation of surface area effects on PVD Al–Ni as electrocatalyst for alkaline water electrolysis,” Electrochim. Acta, 142, 324–335 (2014).
N. R. Tailleart, R. Huang, T. Aburada, D. J. Horton, and J. R. Scully, “Effect of thermally induced relaxation on passivity and corrosion of an amorphous Al–Co–Ce alloy,” Corros. Sci., 59, 238–248 (2012).
J. G. Lin, W. W. Wang, X. Q. Wu, J. H. Lei, and S. Yin, “Crystallization and corrosion resistance of as-spun (Al86Ni9La5)98 Zr2 amorphous alloy,” J. Alloys Compound., 478, No. 1–2, 763–766 (2009).
L. M. Boichyshyn, O. M. Hertsyk, M. O. Kovbuz, T. H. Pereverzeva, and B. Ya. Kotur, “Properties of amorphous alloys of Al–REM–Ni and Al–REM–NI–Fe systems with nanocrystalline structure,” Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater., 48, No. 4, 127–131 (2012); English translation: Mater. Sci., 48, No. 4, 555–559 (2013).
E. Czech and T. Troczynski, “Hydrogen generation through massive corrosion of deformed aluminum in water,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 35, 1029–1037 (2010).
F. Rosalbino, E. Angelini, S. De Negri, A. Saccone, and S. Delfino, “Electrochemical behavior assessment of novel Mg-rich Mg–Al–RE alloys (RE = Ce, Er),” Intermetallics, 14, 1487–1492 (2006).
V. I. Lad’yanov, A. L. Bel’tykov, S. G. Men’shikova, V. V. Maslov, V. K. Nosenko, and V. A. Mashira, “Viscosity of glass forming Al86Ni8(La/Ce)6, Al86Ni6Co2Gd4 (Y/Tb)2 melts,” Phys. Chem. Liq., 46, No. 1, 71–77 (2008).
L. Boichyshyn, M. Kovbuz, O. Hertsyk, V. Nosenko, and B. Kotur, “Influence of structurization of amorphous metallic alloys Al87Y5−x Gd x Ni8−y (x = 0, 1, 5; y = 0, 4) on their mechanical properties,” Phys. Solid State, 55, No. 2, 243–246 (2013).
T. Mika, M. Karolus, G. Haneczok, L. Bednarska, E. Łagiewka, and B. Kotur, “Influence of Gd and Fe on crystallization of Al87Y5Ni8 amorphous alloy,” J. Non-Crystal. Solids, 354, No. 27, 3099–3106 (2008).
Y. Liu, S. L. Ye, B. An, Y. G. Wang, Y. J. Li, L. C. Zhang, and W. M. Wang, “Effects of mechanical compression and autoclave treatment on the backbone clusters in the Al86Ni9La5 amorphous alloy,” J. Alloys Compd., 587, 59–65 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizyko-Khimichna Mekhanika Materialiv, Vol. 51, No. 4, pp. 100–106, July–August, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boichyshyn, L.М., Hertsyk, О.М., Kovbuz, М.О. et al. Electrodes Based on Amorphous Metallic Aluminum Alloys in the Reactions of Hydrogen Release. Mater Sci 51, 548–554 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-016-9874-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-016-9874-8