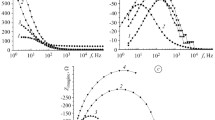
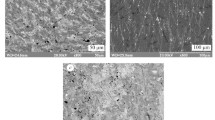
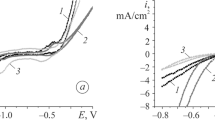
By the methods of chronopotentiometry, voltammetry, and scanning electron microscopy, we investigate the influence of modification of the Fe78.5Ni1.0Mo0.5Si6.0B14.0 and Fe73.1Cu1.0Nb3.0Si15.5B7.4 amorphous metallic alloys by heat treatment (373 and 473°K), holding in variable magnetic fields (50 Hz), and combined thermal and magnetic treatment of different durations on the corrosion rate of the surface of amorphous metallic alloys in a reference NaCl solution. It is shown that we can substantially increase the corrosion resistance of alloys using by applying variable magnetic fields for 3 h in the case of Fe78.5Ni1.0Mo0.5Si6.0B14.0 alloy and for 3 h with subsequent annealing at 473°K for 1 h in the case of Fe73.1Cu1.0Nb3.0Si15.5B7.4 alloy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Іnoue, “Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys,” Acta Mater., 48, 279–306 (2000).
O. Hertsyk, M. Kovbuz, and L. Bednars’ka, “Amorphization and elemental composition of metallic alloys as anticorrosion factors,” Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater., Special Issue, No. 2, 178–182 (2001).
O. M. Hertsyk, M. O. Kovbuz, O. A. Ezers’ka, and T. H. Pereverzeva, “Modification of the surface of soft magnetic amorphous alloys by oligomers for the formation of durable corrosion-resistant coatings,” Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater., 47, No. 3, 116–121 (2011); English translation: Mater. Sci., 47, No. 3, 401–407 (2011).
O. Ya. Tuzyak and V. Yu. Kurlyak, Fundamentals of Electron and Probe Microscopy [in Ukrainian], Franko Lviv National University, Lviv (2012).
O. M. Hertsyk, M. O. Kovbuz, A. М. Kostruba, and L. М. Boichyshyn, “Specific features of formation of the surface layers of oligoperoxides on the glass surface,” Khim., Fiz. Tekhnol. Poverkh., 1, No. 4, 431–435 (2010).
J. E. May, P. A. P. Nascente, and S. E. Kuri, “Corrosion processes and their influence on the magnetic flux density of FeNbCuSiB alloys,” Corr. Sci., 48, 1721–1732 (2006).
B. I. Bairachnyi, T. A. Il’yashenko, and T. M. Funduka, “Cathodic processes in chloride solutions of iron and copper,” Ukr. Khim. Zh., 61, No. 9, 34–37 (1995).
I. V. Zolotukhin, Progress in Physical Science [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1990).
O. M. Hertsyk, M. O. Kovbuz, L. M. Bednars’ka, et al., “Specific features of the electrochemical dissolution of the Fe73.7Cu1.0Nb2.4Si15.5B7.4 amorphous alloy,” Visn. L’viv. Univ. Ser. Khim., Issue 43, 205–208 (2003).
S. I. Mudryi, L. M. Bednars’ka, M. O. Kovbuz, et al., “Structural transformations caused by the thermal and thermomagnetic treatment of Co-based amorphous alloys,” Metallofiz. Noveish. Tekhnol., 27, No. 9, 1187–1191 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizyko-Khimichna Mekhanika Materialiv, Vol. 50, No. 3, pp. 128–134, May–June, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hertsyk, О.М., Kovbuz, М.О., Pereverzeva, T.H. et al. Influence of Heat Treatment and Variable Magnetic Fields on the Chemical Resistance of Amorphous Alloys Based on Iron. Mater Sci 50, 454–460 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-014-9742-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-014-9742-3