Abstract
We approach the problem of identifying the stratigraphic markers using seismic data in automated mode. This automation would be achieved through the application of correlation exponent and its double derivative for the first time. Prominent contrasts derived from correlation exponents from seismic trace are associated with the different stratigraphic layers that help to isolate these layers. Further explicit analysis of double derivative of correlation exponent aids to segregate the un-compacted and compacted sediments. The feasibility and reliability of the proposed technique were tested over the seismic traces of Taranaki Basin. 48 seismic traces traversing the various geological features identified by earlier researchers in the field were selected. The combined interpretation of the anomalous value of correlation exponent and their double derivative for the seismic traces indicate the prominent geological features: progradation surfaces, bright spots, sedimentary packages and faults. This study presents a tool for automated seismic interpretation and reservoir characterization. The overall success in identification of various features by correlation exponent is about 77.3%.

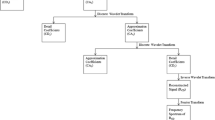
(modified after Chenrai 2016)

OpendTect (interpreted)









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacon M, Simm R, Redshaw T (2004) 3-D seismic interpretation. Geol Mag 141:245–246. https://doi.org/10.1017/S001675680422917X
Bai C, Kennett BLN (2000) Automatic phase-detection and identification by full use of a single three-component broadband seismogram. Bull Seismol Soc Am 90:187–198. https://doi.org/10.1785/0119990070
Camastra F (2003) Data dimensionality estimation methods: a survey. Pattern Recogn 36:2945–2954. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(03)00176-6
Chang X, Liu Y, Wang H et al (2002) 3-D tomographic static correction. Geophysics 67:1275–1285. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1500390
Chenrai P (2016) Seismic stratigraphy and fluid flow in the Taranaki and Great South Basins offshore New Zealand. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Manchester
Eckmann J-P, Ruelle D (1992) Fundamental limitations for estimating dimensions and Lyapunov exponents in dynamical systems. Physica D 56:185–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2789(92)90023-G
Ezekiel S, Barrick MJ, Lang M (2003) Seismic signal analysis using correlation dimension. In: IASTED International Multi-Conference. Applied Informatics, pp 179–182
Gee MJR, Gawthorpe RL, Bakke K, Friedmann SJ (2007) Seismic geomorphology and evolution of submarine channels from the angolan continental margin. J Sediment Res 77:433–446. https://doi.org/10.2110/jsr.2007.042
Goryainov PM, Ivanyuk GYu, Sharov NV (1997) Fractal analysis of seismic and geological data. Tectonophysics 269:247–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(96)00162-X
Grassberger P, Procaccia I (1983a) Characterization of strange attractors. Phys Rev Lett 50:346–349. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.50.346
Grassberger P, Procaccia I (1983b) Measuring the strangeness of strange attractors. Physica D 9:189–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2789(83)90298-1
Hami-Eddine K, Klein P, Richard L, Furniss A (2012) Anomaly detection using dynamic Neural Networks, classification of prestack data. In: SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2012. Society of Exploration Geophysicists, pp 1–5
Hilarov VL (1998) Self-similar crack-generation effects in the fracture process in brittle materials. Modelling Simul Mater Sci Eng 6:337–342. https://doi.org/10.1088/0965-0393/6/4/002
Illidge E, Camargo J, Pinto J (2016) Turbidites characterization from seismic stratigraphy analysis: application to the Netherlands offshore F3 block. In: AAPG/SEG 2016 international conference & exhibition. Cancun, Mexico, pp 6–9
Johnston AG (2014) Interactions between the prograding Giant Foresets Formation and a subsiding depocentre: insights from the Parihaka 3D & ES89 2D seismic surveys. M.Sc. Thesis, Victoria University of Wellington
Kalantan Z, Einbeck J (2012) On the computation of the correlation integral for fractal dimension estimation. 2012 International conference on statistics in science, business and engineering (ICSSBE). IEEE, Langkawi, pp 1–6
King PR, Thrasher GP (1996) Cretaceous-Cenozoic geology and petroleum systems of the Taranaki Basin, New Zealand. Inst Geol Nucl Sci Monogr 13:243
Kumar PC (2016) Application of geometric attributes for interpreting faults from seismic data: an example from Taranaki Basin, New Zealand. SEG technical program expanded abstracts 2016. Society of Exploration Geophysicists, Tulsa, pp 2077–2081
Mattos NH, Alves TM, Scully A (2019) Structural and depositional controls on Plio-Pleistocene submarine channel geometry (Taranaki Basin, New Zealand). Basin Res 31:136–154. https://doi.org/10.1111/bre.12312
Mela K, Louie JN (2001) Correlation length and fractal dimension interpretation from seismic data using variograms and power spectra. Geophysics 66:1372–1378. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1487083
Mondal D, Roy PNS (2019) Fractal and seismic b-value study during dynamic roof displacements (roof fall and surface blasting) for enhancing safety in the longwall coal mines. Eng Geol 253:184–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.03.018
Mondal D, Roy PNS, Behera PK (2017) Use of correlation fractal dimension signatures for understanding the overlying strata dynamics in longwall coal mines. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 91:210–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.11.019
Pham N, Fomel S, Dunlap D (2019) Automatic channel detection using deep learning. Interpretation 7:SE43–SE50. https://doi.org/10.1190/INT-2018-0202.1
Pilaar WFH, Wakefield LL (1978) Structural and stratigraphic evolution of the Taranaki Basin, offshore North Island, New Zealand. APPEA J 18:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1071/AJ77011
Posamentier HW, Kolla V (2003) Seismic geomorphology and stratigraphy of depositional elements in deep-water settings. J Sediment Res 73:367–388. https://doi.org/10.1306/111302730367
Posamentier HW (2000) Seismic stratigraphy into the next millennium; a focus on 3D seismic data. In: American Association of Petroleum Geologists Annual Conference. New Orleans, pp 16–19
Qayyum F, Betzler C, Catuneanu O (2018) Space-time continuum in seismic stratigraphy: principles and norms. Interpretation 6:T97–T108
Roy PNS, Gupta DK (2015) Fractal analyzer: a MATLAB application for multifractal seismicity analysis. Seismol Res Lett 86:1424–1431. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220150013
Roy PNS, Padhi A (2007) Multifractal analysis of earthquakes in the southeastern Iran-Bam region. Pure Appl Geophys 164:2271–2290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-007-0272-x
Roy PNS, Ram A (2006) A correlation integral approach to the study of 26 January 2001 Bhuj earthquake, Gujarat, India. J Geodyn 41:385–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2005.10.003
Sabbione JI, Velis D (2010) Automatic first-breaks picking: new strategies and algorithms. Geophysics 75:V67–V76. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.3463703
Scully A (2016) A seismic investigation into structural controls on submarine channel distribution in the Taranaki Basin, New Zealand. University College Cork, Cork
Shumaker L (2016) Sedimentology, Seismic Geomorphology, and Provenance Investigations of deep-water deposits: Taranaki Basin, New Zealand. Dissertation, Stanford University
Silva RM, Baroni L, Ferreira RS, et al (2019) Netherlands Dataset: a New Public Dataset for Machine Learning in Seismic Interpretation. In: arXiv:1904.00770. http://arxiv.org/abs/1904.00770
Smith LA (1988) Intrinsic limits on dimension calculations. Phys Lett A 133:283–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9601(88)90445-8
Taner MT (2001) Seismic attributes. CSEG Recorder 26:48–56
Wu X (2017) Directional structure-tensor-based coherence to detect seismic faults and channels. Geophysics 82:A13–A17. https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2016-0473.1
Zhou C, Ouyang J, Ming W et al (2019) A stratigraphic prediction method based on machine learning. Appl Sci 9:3553–3582. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173553
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the Society of Exploration Geophysicist for making the seismic data freely available (https://wiki.seg.org). We are grateful to the dGB Earth Sciences for providing an academic license of OpendTect software. We are also thankful to New Zealand Petroleum and Minerals Online Exploration Database for providing information and data for Arawa-1 well. Authors also acknowledge IIT, Kharagpur ISIRD sponsored project (code ERG) for providing the computing facility. Authors acknowledge the Editor in Chief Prof. Claudio Lo Iacono and anonymous reviewers for their valuable constructive suggestions that improved the manuscript substantially.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karmanov, P., Roy, P.N.S., Rangarajan, S. et al. Automated seismic horizon recognition from seismic data using correlation exponent and its double derivative: a case study of Parihaka field, Offshore Taranaki Basin, New Zealand. Mar Geophys Res 42, 37 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-021-09462-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-021-09462-w