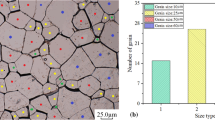
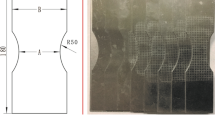
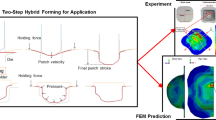
Abstract
Low frequency vibration assisted forming characterized with high excitation force can reduce the forming load and improve the surface quality, and has been proven to have a promising application in forming processes of high-strength metals. In this work, the plastic deformation behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy sheets under low frequency vibration was studied. The low frequency vibration assisted tension (LFVT) tests were performed on 7075-WT and 7075-T6 sheets. The obvious stress oscillation (called the stress superposition effect) and stress softening/hardening effect were observed in the experimental stress–strain relation under LFVT. After explaining the effects with the thermal activation theory, a physical constitutive model was developed by introducing the mechanical work done by low frequency vibration, a critical vibration energy value, and Hooke’s law into the thermal activation framework. The VUHARD user-subroutine was used to embed the developed model into ABAQUS/Explicit to perform the finite element (FE) analysis of the LFVT tests. The comparison of the predicted load through the FE simulation with the experimental one demonstrated the developed model could precisely describe the stress–strain relation under LFVT. The simulation result with different vibration modes also showed that the vibration softening effect gradually increased as the amplitude or frequency increased. The influence of the amplitude on vibration softening stress was much greater than that of the frequency.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Areias, P.: One-step semi-implicit integration of general finite-strain plasticity models. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 17, 73–87 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-020-09510-0
Behrens, B., Hübner, S., Müller, P., Besserer, H., Gerstein, G., Koch, S., Rosenbusch, D.: New multistage sheet-bulk metal forming process using oscillating tools. Metals 10, 617 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050617
Blaha, F., Langenecker, B.: Elongation of zinc monocrystals under ultrasonic action. Naturwissenschaften 42, 556 (1955)
Campbell, J.D., Ferguson, W.G.: The temperature and strain-rate dependence of the shear strength of mild steel. Philos. Mag. 21, 63–82 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1080/14786437008238397
Choi, I.C., Brandl, C., Schwaiger, R.: Thermally activated dislocation plasticity in body-centered cubic chromium studied by high-temperature nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 140, 107–115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.08.026
Choi, Y., Lee, J., Panicker, S.S., Jin, H.-K., Panda, S.K., Lee, M.-G.: Mechanical properties, springback, and formability of W-temper and peak aged 7075 aluminum alloy sheets: experiments and modeling. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 170, 105344 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105344
Daud, Y., Lucas, M., Huang, Z.: Modelling the effects of superimposed ultrasonic vibrations on tension and compression tests of aluminium. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 186, 179–190 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.12.032
Follansbee, P.S., Kocks, U.F.: A constitutive description of the deformation of copper based on the use of the mechanical threshold stress as an internal state variable. Acta Metall. 36, 81–93 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(88)90030-2
François, D., Pineau, A., Zaoui, A.: Mechanical Behaviour of Materials. Springer, Netherlands (1998)
Frost, H., Ashby, M.: Deformation Mechanism Maps: the Plasticity and Creep of Metals and Ceramics. Pergamon press (1982)
Gao, C.Y., Zhang, L.C.: A constitutive model for dynamic plasticity of FCC metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 3138–3143 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.01.083
Gao, C.Y., Zhang, L.C.: Constitutive modelling of plasticity of fcc metals under extremely high strain rates. Int. J. Plast. 32–33, 121–133 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2011.12.001
Haasen, P., Hassen, P., Mordike, B.: Physical Metallurgy. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1996)
Kocks, U.F.: Termodynamics and kinetics of slip. Prog. Mater. Sci. 19, 1–291 (1975)
Kocks, U.F.: Constitutive behavior based on crystal plasticity. In: Unified Constitutive Equations for Creep and Plasticity. Springer, Dordrecht (1987)
Kumari, M., Ray, K.K.: Effect of the mode of deformation on activation volume of a material. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 650, 335–344 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.10.060
Kuykendall, K.: An evaluation of constitutive laws and their ability to predict flow stress over large variations in temperature, strain, and strain rate characteristic of friction stir welding, (2011)
Lin, J., Li, J., Liu, T., Zhu, L., Chu, X., Zhao, G., Guan, Y.: Evaluation of friction reduction and frictionless stress in ultrasonic vibration forming process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 288, 116881 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116881
Lin, J., Pruncu, C., Zhu, L., Li, J., Zhai, Y., Chen, L., Guan, Y., Zhao, G.: Deformation behavior and microstructure in the low-frequency vibration upsetting of titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 299, 117360 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117360
Liu, B., Vu-Bac, N., Zhuang, X., Rabczuk, T.: Stochastic multiscale modeling of heat conductivity of polymeric clay nanocomposites. Mech. Mater. 142, 103280 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2019.103280
Liu, B., Vu-Bac, N., Zhuang, X., Fu, X., Rabczuk, T.: Stochastic full-range multiscale modeling of thermal conductivity of Polymeric carbon nanotubes composites: a machine learning approach. Compos. Struct. 289, 115393 (2022a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115393
Liu, B., Vu-Bac, N., Zhuang, X., Fu, X., Rabczuk, T.: Stochastic integrated machine learning based multiscale approach for the prediction of the thermal conductivity in carbon nanotube reinforced polymeric composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 224, 109425 (2022b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2022.109425
Ma, P., Shi, C., Ye, B.: Experimental study on the forming process of spline by frequency and amplitude modulated axial vibration extrusion. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 107, 1649–1657 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-04998-4
Maeno, T., Mori, K., Ichikawa, Y., Sugawara, M.: Use of liquid lubricant for backward extrusion of cup with internal splines using pulsating motion. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 244, 273–281 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.02.001
Meng, B., Cao, B.N., Wan, M., Wang, C.J., Shan, D.B.: Constitutive behavior and microstructural evolution in ultrasonic vibration assisted deformation of ultrathin superalloy sheet. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 157–158, 609–618 (2019a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.05.009
Meng, D., Zhao, X., Zhao, S., Han, Q.: Effects of vibration direction on the mechanical behavior and microstructure of a metal sheet undergoing vibration-assisted uniaxial tension. Mater. Sci. Eng. a. 743, 472–481 (2019b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.11.115
Meng, D., Ma, J., Zhao, X., Guo, Y., Zhu, C., Yu, M.: Mechanical behavior and material property of low-carbon steel undergoing low-frequency vibration-assisted upsetting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 16, 1846–1855 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.12.113
Pohlman, R., Lehfeldt, E.: Influence of ultrasonic vibration on metallic friction. Ultrasonics 4, 178–185 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-624X(66)90244-7
Prabhakar, A., Verma, G.C., Krishnasamy, H., Pandey, P.M., Lee, M.G., Suwas, S.: Dislocation density based constitutive model for ultrasonic assisted deformation. Mech. Res. Commun. 85, 76–80 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechrescom.2017.08.003
Rabizadeh, E., Bagherzadeh, A.S., Anitescu, C., Alajlan, N., Rabczuk, T.: Pointwise dual weighted residual based goal-oriented a posteriori error estimation and adaptive mesh refinement in 2D/3D thermo-mechanical multifield problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 359, 112666 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2019.112666
Samigullina, A.A., Mukhametgalina, A.A., Sergeyev, S.N., Zhilyaev, A.P., Nazarov, A.A., Zagidullina, Y.R., Parkhimovich, N.Y., Rubanik, V.V., Tsarenko, Y.V.: Microstructure changes in ultrafine-grained nickel processed by high pressure torsion under ultrasonic treatment. Ultrasonics 82, 313–321 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2017.09.005
Sedaghat, H., Xu, W., Zhang, L.: Ultrasonic vibration-assisted metal forming: constitutive modelling of acoustoplasticity and applications. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 265, 122–129 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.10.012
Skripnyak, V.A., Skripnyak, V.V., Skripnyak, E.G., Skripnyak, N.V.: Modelling of the mechanical response of Zr–Nb and Ti–Nb alloys in a wide temperature range. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 16, 215–224 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-019-09447-z
Taylor, G.I.: Plastic strain in metal. J. Inst. Met. 62, 307–324 (1938)
Tello, K.E., Gerlich, A.P., Mendez, P.F.: Constants for hot deformation constitutive models for recent experimental data. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 15, 260–266 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1179/136217110X12665778348380
Wang, X., Qi, Z., Chen, W.: Investigation of mechanical and microstructural characteristics of Ti–45Nb undergoing transversal ultrasonic vibration-assisted upsetting. Mater. Sci. Eng. a. 813, 141169 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141169
Xie, Z., Guan, Y., Zhu, L., Zhai, J., Lin, J., Yu, X.: Investigations on the surface effect of ultrasonic vibration-assisted 6063 aluminum alloy ring upsetting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 96, 4407–4421 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1611-z
Xie, Z., Guan, Y., Lin, J., Zhai, J., Zhu, L.: Constitutive model of 6063 aluminum alloy under the ultrasonic vibration upsetting based on Johnson-Cook model. Ultrasonics 96, 1–9 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2019.03.017
Xu, Y., Zhuang, X., Zhang, W., Li, Q., Zhao, Z.: Mechanical behaviors and microstructure characteristics of W-tempered and peak-aged 7075 alloy sheets under low frequency vibration–assisted tension. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 833, 142338 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.142338
Yao, Z., Kim, G.Y., Wang, Z., Faidley, L.A., Zou, Q., Mei, D., Chen, Z.: Acoustic softening and residual hardening in aluminum: modeling and experiments. Int. J. Plast. 39, 75–87 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2012.06.003
Zain-ul-abdein, M., Nélias, D.: Effect of coherent and incoherent precipitates upon the stress and strain fields of 6xxx aluminium alloys: a numerical analysis. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 12, 255–271 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-015-9298-x
Zener, C., Hollomon, J.H.: Effect of strain rate upon plastic flow of steel. J. Appl. Phys. 15, 22–32 (1944). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1707363
Zhang, Q., Ben, N., Yang, K.: Effect of variational friction and elastic deformation of die on oscillating cold forging for spline shaft. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 244, 166–177 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.01.001
Zhao, W., Wu, C.: Constitutive equation including acoustic stress work and plastic strain for modeling ultrasonic vibration assisted friction stir welding process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 145, 103434 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2019.103434
Zohrevand, M., Aghaie-Khafri, M., Forouzan, F., Vuorinen, E.: Internal stress relief and microstructural evolution by ultrasonic treatment of austeno-ferritic 2205 duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. a. 815, 141290 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141290
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51875351) and Shanghai Outstanding Academic Leaders Plan (21XD1422000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WZ: Investigation, methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft. YX: Investigation, formal analysis, data curation, visualization. QL: Data curation, Validation. XZ: writing—review and editing, conceptualization, funding acquisition. ZZ: Supervision, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Xu, Y., Li, Q. et al. Constitutive modeling and deformation analysis of W-temper and peak aged 7075 alloy sheets under low frequency vibration assisted tension. Int J Mech Mater Des 19, 583–604 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-023-09647-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-023-09647-8