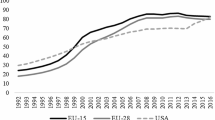
Abstract
The telecommunications sector has undergone the most drastic changes in terms of market liberalization and has dominated the privatisation process in most countries in terms of the size of its assets and because this industry is the flagship of public services. The purpose of this study is to conduct a comparative analysis of the efficiency of eleven European privatised Public Telecommunications Operators PTOs from 1997 to 2005 and to determine whether privatisation, liberalisation and investment in infrastructure have increased their efficiency or not. We make use of the DEA methodology to analyse the efficiency of PTOs, as this model is especially appropriate to analyse organisations whose production process does not result in the obtaining of a product but in the delivery of a public service. In spite of the technological progress, our results do not show that the comparative performance of PTOs has grown significantly during the period analysed. Therefore, we must take into account other factors such as privatisation, state regulation and organisational changes to determine their performance. From our study, we can conclude that not all companies have been able to adapt equally to the competitive market. The non-efficient companies have traditionally operated in a protectionist market and they continue in a monopolistic situation in spite of market liberalization.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This assertion is coherent with the Public Choice Theory (Buchanan 1972).
References
Aivazian, V., Ge, Y., & Qui, J. (2005). Can corporatization improve the performance of SOEs even without privatization? Journal of Corporate Finance, 11, 791–808.
Andersson, P., & Mölleryd, B. (1997). Telecommunication services in context: Distribution consequences of technological change and convergence. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 8(5), 453–473.
Banker, R. D., Charnes, A., & Cooper, W. (1984). Some models for estimating technical and scale efficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Management Science, 30(9), 1078–1092.
Banker, R., Charnes, A., Cooper, W., Swarts, J., & Thomas, D. (1989). An introduction to data envelopment analysis with some of its models and their uses. Research in Governmental and Non-profit Accounting, 5, 125–163.
Berggren, C., & Laestadius, S. (2003). Co-development and composite clusters—the secular strength of Nordic Telecommunications. Industrial and Corporate Change, 12(1), 91–114.
Berne, M., & Pogorel, G. (2004, May). Privatisation experiences in France. Cesifo Working Paper No. 1195, Category 9: Industrial Organisation.
Bortolotti, B., D’Souza, J., Fantini, M., & Megginson, L. W. (2002). Privatization and the sources of performance improvement in the global telecommunications industry. Telecommunications Policy, 26, 243–268.
Brennan, T. J. (2005). Regulation and competition as complements. In M. A. Crew & M. Spiegel (Eds.), Obtaining the best from regulation and competition. US: Springer.
Buchanan, J. M. (1972). Theory of public choice. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
Charnes, A., & Cooper, W. W. (1962). Programming with linear fractional functional. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 9, 181–186.
Charnes, A., Cooper, W. W., Lewin, A. Y., Morey, R. C., & Rousseau, J. (1985). Sensitivity and stability analysis in DEA. Annals of Operations Research, 2, 139–156.
Charnes, A. W., Cooper, W. W., & Rhodes, E. (1978). Measuring efficiency of decision making units. European Journal of Operational Research, 2(6), 429–444.
Chong, A., & Galdo, V. (2006). Streamlining and privatization prices in the telecommunications industry. Economica, 73, 461–484.
Coelli, T., Estache, A., Perelman, S., & Trujillo, L. (2003). A primer on efficiency measurement for utilities and transport regulators. World Bank Institute Development Studies. Washington, DC: World Bank.
Cohen, S., & Thatcher, M. (2005). The new governance of markets and non-majoritarian regulators. Governance: An International Journal of Policy, Administration, and Institutions, 18(3), 329–346.
Cooper, W. W., Seiford, L. M., & Tone, K. (2000). Data envelopment analysis: A comprehensive text with models, applications, references and DEA-Solver software. London: Kluwer.
De Bijl, P., & Peitz, M. (2002). Regulation and entry into telecommunications markets. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Domberger, S., Meadowcroft, S. A., & Thompson, D. J. (1986). Competitive tendering and efficiency: The case of refuse collection. Fiscal Studies, 7, 69–87.
Dornisch, D. (2001). Competitive dynamics in Polish telecommunications, 1990–2000: Growth, regulation, and privatization of an infrastructural multi-network. Telecommunications Policy, 25(6), 381–407.
Haar, L. N., & Jones, T. (2008). Misreading liberalisation and privatisation: The case of the US energy utilities in Europe. Energy Policy, 36(7), 2610–2619.
Hartley, K., & Huby, M. (1985). Contracting-out in health and local authorities: Prospects, progress and pitfalls. Public Money, 5, 23–26.
Helm, D. (2006). Regulatory reform, capture, and the regulatory burden. Oxford Review of Economic Policy, 22(2), 169–185.
Hodge, G. A. (2000). Privatisation: An international review of performance. Westview Press.
International Organization of Supreme Audit Institutions (INTOSAI). (1995). Working Group on the Audit of Privatisation, Ankara.
Jensen, M. C., & Meckling W. H. (1976). Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics, 3, 303–360.
Johnsen, A., Nørreklit, H., & Vakkuri, J. (2006). Introducing a nordic perspective on public sector performance measurement. Financial Accountability & Management, 22(2), 207–212.
Jordana, J., & Sancho, D. (2005). Policy networks and market opening: Telecommunications liberalization in Spain. European Journal of Political Research, 44(3), 519–546.
Kay, J. A., & Thomson, D. J. (1986). Privatisation: A policy in search of a rationale. Economic Journal, 96, 18–32.
Kitching, J. (1967). Why do mergers miscarry? Harward Business Review, November–December, 84–101.
Kuusik, A., & Varblane, U. (2008). How to avoid customers leaving: the case of the Estonian telecommunication industry. Baltic Journal of Management, 4(1), 66–79.
La Porta, R., & López De Silanes, F. (1999). The benefits of privatization: Evidence from Mexico. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 114(4), 1193–1242.
Lane, J. E. (2000). New public management: An introduction. London: Routledge.
Lien, D., & Peng, Y. (2001). Competition and production efficiency: Telecommunications in OECD countries. Information Economics and Policy, 13(1), 51–76.
Majumdar, S. K. (1998). On the utilization of resources: perspectives from the US telecommunications industry. Strategic Management Journal, 19, 809–831.
Mansell, R., Davies, A., & Hulsink, W. (1996). The new telecommunications in the Netherlands: Strategy, policy and regulation. Telecommunications Policy, 20(2), 273–289.
Martin, S., & Parker, D. (1995). Privatization and economic performance throughout the UK business cycle. Managerial and Decision Economics, 16(3), 225–237.
Megginson, W. L. (2005). The financial economics of privatization. New York: Oxford University Press.
Megginson, W. L., Nash, R. C., & Van Randenbourgh, M. (1994). The financial and operating performance of newly privatised firms: An international empirical analysis. The Journal of Finance, 49(2), 403–452.
Newbery, D. M. (1997). Privatisation and liberalisation of networks utilities. European Economic Review, 41, 357–383.
Newbery, D., & Pollitt, M. (1997). The restructuring and privatization of Britain’s CEGB—was it worth it? Journal of Industrial Economics, 45, 269–303.
OECD. (2003). Communications outlook 2003. Paris: OECD.
OECD. (2005). Communications outlook 2005. Paris: OECD.
OECD. (2007). Communications outlook 2007. Paris: OECD.
Parker, D. (2003). Performance, risk and strategy in privatised, regulated industries. The UK’s experience. The International Journal of Public Sector Management, 16(1), 75–100.
Pentzaropoulos, G. C., & Giokas, D. I. (2002). Comparing the operational efficiency of the main European telecommunications organizations: A quantitative analysis. Telecommunications Policy, 26(11), 595–606.
Puxty, A. G. (1997). Accounting choice and a theory of crisis: The cases of post-privatization British Telecom and British Gas. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 22(7), 713–735.
Ros, A. (1999). Does ownership or competition matter? The effects of telecommunications reform on network expansion and efficiency. Journal of Regulatory Economics, 15, 65–92.
Ramanathan, R. (2003). An introduction to data envelopment analysis. New Delhi: Sage.
Seiford, L. (1996). Data envelopment analysis: The evolution of the state of the art (1978–1995). The Journal of the Productivity Analysis, 7, 99–137.
Sueyoshi, T. (1994). Stochastic frontier production analysis: measuring performance of public telecommunications in 24 OECD countries. European Journal of Operational Research, 74, 466–478.
Sueyoshi, T. (1997). Measuring efficiencies and returns to scale of Nippon telegraph & telephone in production and cost analysis. Management Sciences, 43(6), 779–796.
Sueyoshi, T. (1998). Privatization of Nippon telegraph and telephone: Was it a good policy decision? European Journal of Operational Research, 107(1), 45–61.
Thatcher, M. (2004). Winners and losers in Europeanisation: Reforming the national regulation of telecommunications. West European Politics, 27(2), 284–309.
Tsai, H. C., Chen, C. M., & Tzeng, G. H. (2006). The comparative productivity efficiency for global telecoms. International Journal of Production Economics, 103, 509–526.
Vakkuri, J. (2003). Research techniques and their use in managing non-profit organisations—an illustration of DEA analysis in NPO environments. Financial Accountability and Management, 19(3), 243–263.
Vergés, J. (2000). Privatisations in Spain: Process, policies and goals. European Journal of Law and Economics, 9(3), 255–280.
Vickers, J., & Yarrow, G. (1988). Privatization and economics analysis. Cambridge, Massachusset: The MIT Press.
Vickers, J., & Yarrow, G. (1991). Economic perspectives on privatization. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 5(2), 111–132.
Villalonga, B. (2000). Privatization and efficiency: Differentiating ownership effects from political, organizational, and dynamic effects. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 42, 43–74.
Yarrow, G. (1986). Privatization in theory and practice. Economic Policy, 2, 324–364.
Zhu, J. (2003). Efficiency evaluation with strong ordinal input and output measures. European Journal of Operational Research, 146(3), 477–485.
Zhu, J. (2000). Multi-factor performance measure model with an application to Fortune 500 companies. European Journal of Operational Research, 123(1), 105–124.
Acknowledgments
This study has been carried out with the financial support of the Spanish National R&D Plan through research project ECO2010-17463.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres, L., Bachiller, P. Efficiency of telecommunications companies in European countries. J Manag Gov 17, 863–886 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10997-011-9203-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10997-011-9203-4