Abstract
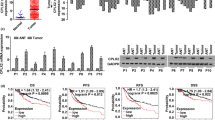
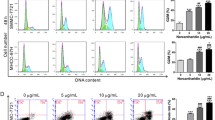
FOXM1 is a crucial oncogenic transcription factor involved in almost all cancer hallmark pathways across all cancer types. Our previous work had found that FOXM1 targeted peptide P201 can strongly inhibit the growth of cancer cells including the liver cancer HCCLM3 cells. In addition, by RNA-seq of HCCLM3 cells treated with MCP-1, an anticancer peptide optimized from P201, ALOXE3, a key feature of ferroptosis was significantly elevated while FOXM1 was down-regulated, we wonder if the cell death of HCCLM3 induced by MCP-1 was associated with ferroptosis. Also, the relationship between FOXM1 and ferroptosis was less understood. Hence, in this study, we explore the effect of MCP-1 on ferroptosis and establish the associations among MCP-1, FOXM1 and ALOXE3 in HCCLM3 cells. The results showed that MCP-1 can significantly induce the elevated expression of ALOXE3, while the other important ferroptosis features including GSH, GPX4,ROS and total iron in HCCLM3 cells were all expectedly regulated. Also, ferrostatin-1, a specific inhibitor for ferroptosis, can reverse the cell death of HCCLM3 cells when co-administrated with MCP-1. TCGA database hepatocellular carcinoma gene expression analysis showed that FOXM1 was negative-related to ALOXE3 and further confirmed by the results of siRNA knockdown of FOXM1 in HCCLM3 cells. Moreover, the co-expressed genes analysis for FOXM1 and ALOXE3 revealed that many of them were closely involved in the regulation of ferroptosis. Taken together, we discovered and confirmed the induction of ferroptosis by MCP-1 in liver cancer HCCLM3 cells and primarily established the associations among MCP-1, FOXM1 and ALOXE3.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Barger CJ, Branick C, Chee L, Karpf AR (2019) Pan-cancer analyses reveal genomic features of FOXM1 overexpression in Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 11(2):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020251
Bella L, Zona S, Nestal de Moraes G, Lam EW-F (2014) FOXM1: a key oncofoetal transcription factor in health and disease. Semin Cancer Biol 29:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.07.008
Bi Z, Liu W, Ding R, Wu Y, Dou R, Zhang W, Yuan X, Liu X, Xiong L, Guo Z, Mao C (2017) A novel peptide, 9R-P201, strongly inhibits the viability, proliferation and migration of liver cancer HepG2 cells and induces apoptosis by down-regulation of FoxM1 expression. Eur J Pharmacol 796:175–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.12.029
Chen Y, Li H (2022) Prognostic and predictive models for left- and right- colorectal Cancer patients: a Bioinformatics Analysis based on ferroptosis-related genes. Front Oncol 12:833834. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.833834
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D (2021) Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 18(5):280–296. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-020-00462-0
Dixon SJ, Pratt DA (2023) Ferroptosis: a flexible constellation of related biochemical mechanisms. Mol Cell 83(7):1030–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2023.03.005
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS et al (2012) Ferroptosis: An Iron-Dependent form of non-apoptotic cell death. Cell 149(5):1060–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Gan B (2021) Mitochondrial regulation of ferroptosis. J Cell Biol 220(9):202105043. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202105043
Halasi M, Gartel AL (2013) Targeting FOXM1 in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 85(5):644–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2012.10.013
Hao X, Zheng Z, Liu H, Zhang Y, Kang J, Kong X, Rong D, Sun Guangshun S, Guoqiang, Liu L et al (2022) Inhibition of APOC1 promotes the transformation of M2 into M1 macrophages via the ferroptosis pathway and enhances anti-PD1 immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma based on single-cell RNA sequencing. Redox Biol 56:102463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2022.102463
Hassannia B, Vandenabeele P, Vanden Berghe T (2019) Targeting ferroptosis to Iron Out Cancer. Cancer Cell 35(6):830–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2019.04.002
Kalathil D, John S, Nair AS (2020) FOXM1 and Cancer: Faulty Cellular Signaling derails Homeostasis. Front Oncol 10:626836. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.626836
Kuang F, Liu J, Tang D, Kang R (2020) Oxidative damage and antioxidant defense in Ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:586578. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.586578
Lei G, Zhuang L, Gan B (2022) Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 22(7):381–396. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-022-00459-0
Li C, Zhang Y, Liu J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D (2020a) Mitochondrial DNA stress triggers autophagy-dependent ferroptotic death. Autophagy 17(4):948–960. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1739447
Li X, Huang Weimei, Huang Wenbin, Wei T, Zhu W, Chen G, Zhang J (2020b) Kinesin family members KIF2C/4A/10/11/14/18B/20A/23 predict poor prognosis and promote cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl Res 12(5):1614–1639
Lin Z, Liu J, Long F, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D, Yang M (2022) The lipid flippase SLC47A1 blocks metabolic vulnerability to ferroptosis. Nat Commun 13(1):7965. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35707-2
Liu W, Ding R, Zhang Y, Mao C, Kang R, Meng J, Huang Q, Xiong L, Guo Z (2017) Transcriptome profiling analysis of differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs in HepG2 cells treated with peptide 9R-P201. Biotechnol Lett 39(11):1639–1647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2407-1
Madhi H, Lee J, Choi YE, Li Y, Kim MH, Choi Y, Goh S (2022) FOXM1 inhibition enhances the therapeutic outcome of Lung Cancer Immunotherapy by modulating PD-L1 expression and cell proliferation. Adv Sci (Weinh) 9(29):2202702. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202202702
Miotto G, Rossetto M, Di Paolo ML, Orian L, Venerando R, Roveri A, Vučković A-M, Bosello Travain V, Zaccarin M, Zennaro L et al (2019) Insight into the mechanism of ferroptosis inhibition by ferrostatin-1. Redox Biol 28:101328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101328
Nandi D, Cheema PS, Jaiswal N, Nag A (2018) FoxM1: repurposing an oncogene as a biomarker. Semin Cancer Biol 52(Pt 1):74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.08.009
Ouyang S, Li H, Lou L, Huang Q, Zhang Z, Mo J, Li M, Lu J, Zhu K, Chu Y et al (2022) Inhibition of STAT3-ferroptosis negative regulatory axis suppresses tumor growth and alleviates chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Redox Biol 52:102317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2022.102317
Peng M, Hu Q, Wu Z, Wang B, Wang C, Yu F (2023) Mutation of tp53 confers ferroptosis resistance in lung cancer through the foxm1/mef2c axis. Am J Pathol 193(10):1587–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.05.003
Qin Y, Pei Z, Feng Z, Lin P, Wang S, Li Y, Huo F, Wang Q, Wang Z, Chen Z-N et al (2021) Oncogenic activation of YAP Signaling Sensitizes Ferroptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via ALOXE3-Mediated lipid peroxidation Accumulation. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:751593. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.751593
Radhakrishnan SK, Gartel AL (2008) FOXM1: the Achilles’ heel of cancer? Nat Rev Cancer 8(3). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2223-c1. c1; author reply c2
Raghuwanshi S, Gartel AL (2023) Small-molecule inhibitors targeting FOXM1: current challenges and future perspectives in cancer treatments. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1878(6):189015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189015
Triska M, Ivliev A, Nikolsky Y, Tatarinova TV (2017) Analysis of cis-Regulatory elements in gene co-expression networks in Cancer. Methods Mol Biol 1613:291–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7027-8_11
van Dam S, Võsa U, van der Graaf A, Franke L, de Magalhães JP (2017) Gene co-expression analysis for functional classification and gene–disease predictions. Brief Bioinform 19(4):575–592. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbw139
Vasaikar SV, Straub P, Wang J, Zhang B (2018) LinkedOmics: analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D956–D963. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1090
Wang Y, Wu X, Ren Z, Li Y, Zou W, Chen J, Wang H (2023) Overcoming cancer chemotherapy resistance by the induction of ferroptosis. Drug Resist Updat 66:100916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drup.2022.100916
Wei G, Yang X, Lu H, Zhang L, Wei Y, Li H, Zhu M, Zhou X (2022) Prognostic value and immunological role of FOXM1 in human solid tumors. Aging 14(22):9128–9148. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204394
Xia Y, Liu S, Li C, Ai Z, Shen W, Ren W, Yang X (2020) Discovery of a novel ferroptosis inducer-talaroconvolutin A-killing colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis 11(11):988. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03194-2
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun X, Kang R, Tang D (2016) Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ 23(3):369–379. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2015.158
Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M, Shchepinov MS, Stockwell BR (2016) Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(34):E4966–E4975. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1603244113
Yang X, Liu J, Wang C, Cheng KK-Y, Xu H, Li Q, Hua T, Jiang X, Sheng L, Mao J, Liu Z (2021) miR-18a promotes glioblastoma development by down-regulating ALOXE3-mediated ferroptotic and anti-migration activities. Oncogenesis 10(2):15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-021-00304-3
Zhao Y, Yu Y, Zhao W, You S, Feng M, Xie C, Chi X, Zhang Y, Wang X (2019) As a downstream target of the AKT pathway, NPTX1 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Rep 39(6):BSR20181662. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20181662
Zhao L, Zhou X, Xie F, Zhang L, Yan H, Huang J, Zhang C, Zhou F, Chen J, Zhang L (2022) Ferroptosis in cancer and cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun (Lond) 42(2):88–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/cac2.12250
Zheng X, Chen W, Yi J, Li W, Liu J, Fu W, Ren L, Li S, Ge B, Yang Y et al (2022) Apolipoprotein C1 promotes glioblastoma tumorigenesis by reducing KEAP1/NRF2 and CBS-regulated ferroptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43(11):2977–2992. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00917-3
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81872789); the Key Research and Development Project of Chengdu (No. 2018-YF05-00004-SN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The draft paper was written by my graduate student FZ and revised by CM and Mrs YJ. The main work was finished by FZ. Coauthors of ZS, SJ, YJ, MC, AL and XH joined parts of the work and analyses. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, F., Shang, Z., Jia, S. et al. Anticancer Peptide MCP-1 Induces Ferroptosis in Liver Cancer HCCLM3 Cells by Targeting FOXM1/ALOXE3 Signal Pathway. Int J Pept Res Ther 30, 37 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-024-10614-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-024-10614-w