Abstract
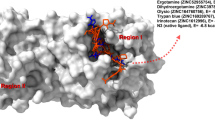
Subtractive cell surface panning from phage random peptide library and molecular docking were used to select and find binding peptides dual-targeting MMP14 and metal ions on MG-63 cells. Phages were abundantly enriched and totally 22 different peptide sequences were obtained. We demonstrated that the affinity phage peptides were not only targeted to MMP14 but also had affinities for zinc and nickel ions. Four possible peptide consensus sequences were identified as: AHQ/SLH/P, L/I/EPLL/I, T/Q/DARH/FQ, MK/PSR. The representative peptides were found to dock well to MMP14 at the sites around aa. 120–125 which were also the catalytic region of zinc binding sites on MMP14 by MVD molecular docking. The selected monoclonal phages could efficiently bind to the MMP14 expressed MG-63 cells and this again confirmed the targeting binding of the peptides to MMP14. In vitro study revealed that the selected monoclonal phages could greatly inhibit the viability of MG-63 cells. Also, the four synthetic representative consensus peptides inhibited the viability of MG-63 and HepG2 cells at μg levels. The consensus sequences identified in our study were newly reported and relatively specific to MMP14 and this may be further used for MMP14 based peptide drug development and/or diagnostic analyses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Thiennu HV, Takeshi I, Tamaki K, Tanzawa K, Thorpe P, Itohara S, Werb Z, Hanahan D (2000) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 2:737–744
Devel L, Rogakos V, David A, Makaritis A, Beau F, Cuniasse P, Yiotakis A, Dive V (2006) Development of selective inhibitors and substrate of matrix metalloproteinase-12. J Biol Chem 281:11152–11160
Devy L, Huang L, Naa L, Yanamandra N, Pieters H, Frans N, Chang E, Tao Q, Vanhove M, Lejeune A, Gool R, Sexton DJ, Kuang G, Rank D, Hogan S, Pazmany C, Ma Y, Schoonbroodt S, Nixon AE, Ladner RC, Hoet R, Henderikx P, TenHoor C, Rabbani SA, Valentino ML, Wood CR, Dransfield DT (2009) Selective inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-14 blocks tumor growth, invasion, and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 69:1517–1526
Dong J, Liu C, Zhang J, Xin ZT, Yang G, Gao B, Mao CQ, Liu NL, Wang F, Shao NS, Fan M, Xue YN (2006) Selection of novel nickel-binding peptides from flagella displayed secondary peptide library. Chem Biol Drug Des 68:107–112
Engel CK, Pirard B, Schimanski SKR, Habermann J, Klingler O, Schlotte V, Weithmann KU, Wendt KU (2005) Structural basis for the highly selective inhibition of MMP-13. Chem Biol 12:181–189
Holmbeck K, Bianco P, Caterina J, Yamada S, Kromer M, Kuznetsov SA, Mankani M, Robey PG, Poole AR, Pidoux I, Ward JM, Hansen HB (1999) MMP14-deficient mice develop disease due to inadequate collagen turnover. Cell 99:81–92
Hu J, Van den Steen PE, Sang QXA, Opdenakker G (2007) Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors as therapy for inflammatory and vascular diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:480–498
Jacobsen JA, Jourden JLM, Miller MT, Cohen SM (2010) To bind zinc or not to bind zinc: a examination of innovative approaches to improved metalloproteinase inhibition. Biochim et Biophys Acta 1803:72–94
Konstantinopoulos PA, Karamouzis MV, Papatsoris AG, Papavassiliou AG (2008) Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors as anticancer agents. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:1156–1168
Kridel SJ, Sawai H, Ratnikov BI, Chen EI, Li W, Godzik A, Strongin AY, Smith JW (2002) A unique substrate binding mode discriminates membrane Type-1 matrix metalloproteinase from other matrix metalloproteinase. J Biol Chem 2707:23788–23793
Kuhnast B, Bodenstein C, Haubner R, Wester HJ, Senekowitsch SR, Schwaiger M, Weber WA (2004) Targeting of gelatinase activity with a radiolabeled cyclic HWGF peptide. Nuclear Med Biol 31:337–344
Liang ZJ, Huang JS, Cui J, Xiong LL, Mao CQ (2011) Selection and molecular simulation of binding peptides dual-targeting MMP-14 and metal ions. Chinese J Biochem Mol Biol 27:341–349
Luo XH, Liao EY, Su X, Wu XP (2004) Parathyroid hormone inhibits the expression of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP14) in osteoblast-like MG-63 cells. J Bon Min Met 22:19–25
Moll GN, Kuipers A, Vries LD, Bosma T, Rink R (2009) A biological stabilization technology for peptide drugs: enzymatic introduction of thioether-bridges. Drug Discov Today 6:13–18
Morrison CJ, Butler GS, Rodriguez D, Overall CM (2009) Matrix metalloproteinase proteomics: substrate, targets and therapy. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:645–653
Murphy G, Nagase H (2008) Progress in matrix metalloproteinase research. Mol Asp Med 29:290–308
Ohkubo S, Miyadera K, Sugimoto Y, Matsuo K, Wierzba K, Yamada Y (1999) Identification of substrate sequences for membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase using bacteriophage peptide display library. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 266:308–313
Pan W, Arnone M, Kendall M, Grafstrom RH, Seitz SP, Wasserman ZR, Albright CF (2003) Identification of peptide substrates for human MMP-11 (stromelysin-3) using phage display. J Biol Chem 278:27820–27827
Sato H, Takino T, Okada Y, Cao J, Shinagawa A, Yamamoto E, Seiki M (1994) A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumor cell. Nature 370:61–65
Somerville RP, Oblander SA, Apte SS (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases: old dogs with new tricks. Genome Biol 4:216
Sounni NE, Noel A (2005) Membrane type-matrix metalloproteinases and tumor progression. Biochimie 87:329–342
Tallant C, Marrero A, Rüth FXG (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases: fold and function of their catalytic domains. Biochim et Biophy Acta 1803:20–28
Vlieghe P, Lisowski V, Martinez J, Khrestchatisky M (2010) Synthetic therapeutic peptides: science and market. Drug Discov Today 15:40–56
Yi ZL, Tong X, Ma CY, Huang JS, Mao CQ (2006) Selection and interaction of Ni2+ metal-binding peptides. Acta Microbiol Sinica 46:745–748
Zhu L, Wang HL, Wang L, Wang Y, Jiang K, Cheng Li, Ma Q, Gao S, Wang LP, Li W, Cai MJ, Wang HD, Niu G, Lee SK, Yang W, Fang XX, Chen XY (2011) High-affinity peptide against MT1-MMP for in vivo tumor imaging. J Control Release 150:248–255
Acknowledgments
The work was financially supported by the Program of the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (SWJTU09ZT28 to Canquan Mao) and National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (National 863, 2006AAZ353 to Canquan Mao).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
First two authors contributed equally to this work and are joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Z., Huang, J., Huang, T. et al. Selection and Finding of Lead Peptides Dual-targeting MMP14 and Metal Ions by Subtractive Cell Surface Panning and Molecular Docking. Int J Pept Res Ther 18, 31–40 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-011-9276-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-011-9276-6