Abstract
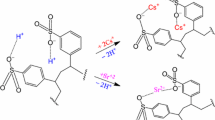
The safe disposal of large irradiated cation exchange resin waste in nuclear power plant has drawn worldwide attention. The kinetic characteristics and product characteristics of the simulated spent cation exchange resin in the pyrolysis and gasification were evaluated based on thermogravimetric analysis as well as TG-FTIR and TG-GC/MS. The temperature ranges at different decomposition stages of the resins were determined. In nitrogen atmosphere, the metal nuclides would hinder the reaction of waste resin in the first stage and promote the reaction in the second stage. The second-order reaction model was the best one to describe the kinetic mechanism in the first and second stages of the spent resins in different atmospheres, while Mample Power model (n = 1) and two-dimensional shrinking cylinder model were for the third gasification stage of the waste resins in 10 % oxygen atmosphere and 10 % steam atmosphere, respectively. The average mass loss ratio of the waste resin in 10 % oxygen atmosphere almost reached to 90 % that was higher than in 10 % steam atmosphere (80 %) and much higher than in nitrogen atmosphere (55 %). The initial reaction temperature in the third stage in 10 % oxygen was about 100 °C earlier than that in 10 % steam atmosphere, indicating that the sulfur bond would easily break due to the strong oxidization action of the oxygen. In the nitrogen atmosphere, the sulfur bond broke at 700 °C, which would lead to low mass loss ratio of the waste resin since the copolymer matrix is difficult to decompose. This work could supply basic data for the pyrolysis and gasification treatment of irradiated spent cation exchange resin in nuclear power plant.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hassan M, Lee S, Mehran MT, Shahzad F, Husnain SM, Ryu HJ. Post-decontamination treatment of MXene after adsorbing Cs from contaminated water with the enhanced thermal stability to form a stable radioactive waste matrix. J Nucl Mater. 2021;543:152566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2020.152566.
Murukutti MK, Jena H. Synthesis of nano-crystalline zeolite-A and zeolite-X from Indian coal fly ash, its characterization and performance evaluation for the removal of Cs+ and Sr2+ from simulated nuclear waste. J Hazard Mater. 2022;423:127085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127085.
Gonçalves MFS, Petraconi Filho G, Couto AA, Silva Sobrinho ASD, Miranda FS, Massi M. Evaluation of thermal plasma process for treatment disposal of solid radioactive waste. J Environ Manag. 2022;311:114895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114895.
Xu L, Meng X, Li M, Li W, Sui Z, Wang J, et al. Dissolution and degradation of nuclear grade cationic exchange resin by Fenton oxidation combining experimental results and DFT calculations. Chem Eng J. 2019;361:1511–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.169.
Micari M, Cipollina A, Tamburini A, Moser M, Bertsch V, Micale G. Combined membrane and thermal desalination processes for the treatment of ion exchange resins spent brine. Appl Energy. 2019;254:113699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113699.
Palamarchuk M, Egorin A, Tokar E, Tutov M, Marinin D, Avramenko V. Decontamination of spent ion-exchangers contaminated with cesium radionuclides using resorcinol-formaldehyde resins. J Hazard Mater. 2017;321:326–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.005.
Wan Z, Xu L, Wang J. Disintegration and dissolution of spent radioactive cationic exchange resins using Fenton-like oxidation process. Nucl Eng Des. 2015;291:101–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucengdes.2015.05.009.
Hafeez MA, Singh BK, Yang SH, Kim J, Kim B, Shin Y, et al. Recent advances in Fenton-like treatment of radioactive ion exchange resins. Chem Eng J Adv. 2023;14:100461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2023.100461.
Antonetti P, Claire Y, Massit H, Lessart P, Pham Van Cang C, Perichaud A. Pyrolysis of cobalt and caesium doped cationic ion-exchange resin. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2000;55(1):81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-2370(99)00075-3.
Yang HC, Lee SY, Choi YC, Yang IH, Chung DY. Thermokinetic analysis of spent ion-exchange resins for the optimization of carbonization reactor condition. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127(1):587–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5817-8.
Li J, Wang J. Advances in cement solidification technology for waste radioactive ion exchange resins: a review. J Hazard Mater. 2006;135(1–3):443–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.053.
Sercombe J, Gwinner B, Tiffreau C, Simondi-Teisseire B, Adenot F. Modelling of bituminized radioactive waste leaching. Part I: Constitutive equations. J Nucl Mater. 2006;349(1):96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2005.10.014.
Moriyama N, Dojiri S, Emura S, Sugo T, Machi S. Incorporation of radioactive spent ion exchange resins in plastics. J Nucl Sci Technol. 1975;12(6):362–9. https://doi.org/10.3327/jnst.12.362.
Li CT, Lee WJ, Wu CH, Wang YT. PAH emission from waste ion-exchange resin incineration. Sci Total Environ. 1994;155(3):253–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(94)90504-5.
Matsuda M, Funabashi K, Yusa H, Kikuchi M. Influence of functional sulfonic acid group on pyrolysis characteristics for cation exchange resin. J Nucl Sci Technol. 1987;24(2):124–8. https://doi.org/10.3327/jnst.24.124.
Wang L, Yi L, Wang G, Li L, Lu L, Guo L. Experimental investigation on gasification of cationic ion exchange resin used in nuclear power plants by supercritical water. J Hazard Mater. 2021;419:126437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126437.
Nezu A, Moro K, Watanabe T. Thermal plasma treatment of waste ion exchange resins by CO2 injection. Thin Solid Films. 2006;506–507:432–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2005.08.033.
Luca V, Bianchi HL, Allevatto F, Vaccaro JO, Alvarado A. Low temperature pyrolysis of simulated spent anion exchange resins. J Environ Chem Eng. 2017;5(4):4165–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.064.
Juang RS, Lee TS. Oxidative pyrolysis of organic ion exchange resins in the presence of metal oxide catalysts. J Hazard Mater. 2002;92(3):301–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00025-0.
Foong SY, Liew RK, Yang Y, Cheng YW, Yek PNY, Wan Mahari WA, et al. Valorization of biomass waste to engineered activated biochar by microwave pyrolysis: progress, challenges, and future directions. Chem Eng J. 2020;389:124401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124401.
Liang F, Zhang T, Xiang HZ, Yang XM, Hu WH, Mi BB, et al. Pyrolysis characteristics of cellulose derived from moso bamboo and poplar. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132(2):1359–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6920-1.
Xu F, Wang B, Yang D, Qiao Y, Tian Y. The steam gasification reactivity and kinetics of municipal solid waste chars derived from rapid pyrolysis. Waste Manag. 2018;80:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.09.006.
Widjaya ER, Chen G, Bowtell L, Hills C. Gasification of non-woody biomass: a literature review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;89:184–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.023.
Starink MJ. The determination of activation energy from linear heating rate experiments: a comparison of the accuracy of isoconversion methods. Thermochim Acta. 2003;404(1–2):163–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-6031(03)00144-8.
Bridgwater AV. Review of fast pyrolysis of biomass and product upgrading. Biomass Bioenerg. 2012;38:68–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.01.048.
Wu PK, Chen MQ, Wang HW, Wei SH, Zhong XB. Steam gasification characteristics of char pellets of typical technical solid wastes. Thermochim Acta. 2021;699:178907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2021.178907.
Hu DH, Chen MQ, Huang YW, Wei SH, Zhong XB. Evaluation on isothermal pyrolysis characteristics of typical technical solid wastes. Thermochim Acta. 2020;688:178604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2020.178604.
Wang HW, Chen MQ, Fu K, Wei SH, Zhong XB. Evaluation on migration and transformation of trace nuclides in thermal degradation for low-level radioactive waste. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2022;161:105420.
Saad JM, Williams PT, Zhang YS, Yao D, Yang H, Zhou H. Comparison of waste plastics pyrolysis under nitrogen and carbon dioxide atmospheres: a thermogravimetric and kinetic study. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2021;156:105135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105135.
Li B, Chen M. Estimation of radionuclides migration mechanism in thermal decomposition of spent ion exchange resin in nuclear power plant. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2023;173:106089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2023.106089.
Chun U-K, Choi K, Yang K-H, Park J-K, Song M-J. Waste minimization pretreatment via pyrolysis and oxidative pyroylsis of organic ion exchange resin. Waste Manag. 1998;18(3):183–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(98)00020-8.
Luo J, Hu WR, Suo ZL, Wang YB, Zhang YK. Co-pyrolysis of spent radioactive ion exchange resin and manganese dioxide: decrease the decomposition temperatures of functional groups. J Hazard Mater. 2021;418:126275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126275.
Zheng YH, Yan YD, Xu WD, Xue Y, Wang YL, Liu X, et al. Thermal decomposition and oxidation of cation exchange resins with and without Na2CO3-K2CO3 salt. Environ Technol Innov. 2022;28:102601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2022.102601.
Dubois MA, Dozol JF, Nicotra C, Serose J, Massiani C. Pyrolysis and incineration of cationic and anionic ion-exchange resins—identification of volatile degradation compounds. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 1995;31:129–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-2370(94)00817-K.
Castro HA, Rodríguez RA, Luca V, Bianchi HL. Pyrolysis and high performance plasma treatment applied to spent ion exchange resins. J Nucl Eng Radiat Sci. 2019;5(2):020901. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4042193.
Brodda B-G, Dix S, Fachinger J. Investigation of the pyrolytic degradation of ion exchange resins by means of foil pulse pyrolysis coupled with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Sep Sci Technol. 1993;28(1–3):653–73.
Chambre D, Iditoiu C, Segal E. Non-isothermal dehydration kinetics of acrylic ion-exchange resins. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;88(3):673–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-006-8042-z.
Yang HC, Lee MW, Hwang HS, Moon JK, Chung DY. Study on thermal decomposition and oxidation kinetics of cation exchange resins using non-isothermal TG analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;118(2):1073–83.
Huang YJ, Wang HP, Chao CC, Liu HH, Hsiao MC, Liu SH. Oxidation kinetics of spent low-level radioactive resins. Nucl Sci Eng. 2005;151(3):355–60. https://doi.org/10.13182/NSE05-A2555.
Zhang J, Li CY, Gu J, Yuan HR, Chen Y. Synergistic effects for fast co-pyrolysis of strong-acid cation exchange resin and cellulose using Py-GC/MS. Fuel. 2021;302:121232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121232.
Scheithauer D, Heschel W, Meyer B, Krzack S. Pyrolysis of undoped and multi-element doped ion exchange resins with regard to storage properties. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2017;124:276–84.
Martin-Lara MA, Blazquez G, Zamora MC, Calero M. Kinetic modelling of torrefaction of olive tree pruning. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;113:1410–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.11.147.
Criado JM, Málek J, Ortega A. Applicability of the master plots in kinetic analysis of non-isothermal data. Thermochim Acta. 1989;147(2):377–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6031(89)85192-5.
Senum G, Yang R. Rational approximations of the integral of the Arrhenius function. J Therm Anal Calorim. 1977;11(3):445–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01903696.
Li Y, Chen MQ, Li QH, Huang YW. Effect of microwave pretreatment on the combustion behavior of lignite/solid waste briquettes. Energy. 2018;149:730–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.02.087.
Zhang L, Duan F, Huang Y. Thermogravimetric investigation on characteristic of biomass combustion under the effect of organic calcium compounds. Biores Technol. 2015;175:174–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.077.
Eun HC, Yang HC, Cho YZ, Lee HS. Study on a stable destruction method of radioactive waste ion exchange resins. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2009;281(3):585–90.
Kim K, Kim K, Choi M, Son SH, Han JH. Treatment of ion exchange resins used in nuclear power plants by super- and sub-critical water oxidation—a road to commercial plant from bench-scale facility. Chem Eng J. 2012;189:213–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.02.060.
Zheng YH, Yan YD, Xue Y, Wang YL, Liu X, Mi WS, et al. Catalytic effect of cesium on the oxidation behavior of cation exchange resins in Li2CO3–Na2CO3–K2CO3 melt. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2022;29(42):64215–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22158-x.
Karlstrom O, Hupa L. Energy conversion of biomass char: Oxidation rates in mixtures of O2/CO2/H2O. Energy. 2019;181:615–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.05.192.
Zheng F, Ren Z, Xu B, Wan K, Cai J, Yang J, et al. Elucidating multiple-scale reaction behaviors of phenolic resin pyrolysis via TG-FTIR and ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulations. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2021;157:105222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105222.
Ge L, Li X, Feng H, Xu C, Lu Y, Chen B, et al. Analysis of the pyrolysis process, kinetics and products of the base components of waste wind turbine blades (epoxy resin and carbon fiber). J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2023;170:105919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2023.105919.
Zhou W, Zhu G, Cheng H, Xia Z, Wang X, Wu Y, et al. Investigation of EPET, EPEI, and EPU pyrolysis characteristics: Thermal decomposition behaviours, pyrolysis products and mechanism. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2023;175:106203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2023.106203.
Biedermann M, Grob K. Phenolic resins for can coatings: I. phenol-based resole analysed by GC–MS, GC×GC, NPLC–GC and SEC. LWT-Food Sci Technol. 2006;39(6):633–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2005.04.008.
Fu Z, Ma Z, Liu J, Li C, Liu C, Wang Q, et al. Phosphorus-containing active esters modified dicyclopentadiene epoxy resins with simultaneously improved flame retardancy, thermal stability, and dielectric properties. Chem Eng J. 2024;482:148998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.148998.
Liang B, Wang JB, Hu JH, Li CF, Li RK, Liu Y, et al. TG-MS-FTIR study on pyrolysis behavior of phthalonitrile resin. Polym Degrad Stab. 2019;169:108954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.108954.
Yousef S, Eimontas J, Stasiulaitiene I, Zakarauskas K, Striūgas N. Recovery of energy and carbon fibre from wind turbine blades waste (carbon fibre/unsaturated polyester resin) using pyrolysis process and its life-cycle assessment. Environ Res. 2024;245:118016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.118016.
Zhou T, Xiao H, Peng W, Liang B, Liu Y, Lv J, et al. Study on pyrolysis behaviors of L-tyrosine-based phthalonitrile resin. Polym Testing. 2020;86:106506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106506.
Hamodi N, Papadopoulou K, Lowe T, Abram T. Thermal analysis and immobilisation of spent ion exchange resin in borosilicate glass. New J Glass Ceram. 2012;2(3):111–20.
Luo J, Zhou X, Tong W, Du X, Li P, Zhang Y. Oxidative pyrolysis of ion exchange resin in the presence of manganese dioxide: Product analysis, conversion and simplification mechanism. J Environ Chem Eng. 2023;11(5):110695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.110695.
Luca V, Bianchi HL, Manzini AC. Cation immobilization in pyrolyzed simulated spent ion exchange resins. J Nucl Mater. 2012;424(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2012.01.004.
Wang J, Wan Z. Treatment and disposal of spent radioactive ion-exchange resins produced in the nuclear industry. Prog Nucl Energy. 2015;78:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2014.08.003.
Zhou G, Low Z-X, Feng S, Zhang F, Zhong Z, Xing W. Effect of relative humidity and dust moisture content on filtration performance of bag filter. Sep Purif Technol. 2023;308:122952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122952.
Wang C, Li P, Zong Y, Zhang Y, Li S, Wei F. A high efficiency particulate air filter based on agglomerated carbon nanotube fluidized bed. Carbon. 2014;79:424–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.07.086.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under No U21B2095.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Chen, M. & Li, B. Experimental evaluation on pyrolysis and gasification characteristics of simulated waste cation exchange resin. J Therm Anal Calorim (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13060-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13060-4