Abstract
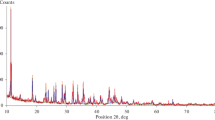
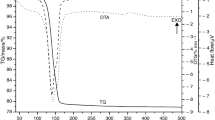
Dehydration of halloysite (Hly) to metahalloysite (m-Hly) was examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The Hly samples heated in temperature range of 80–400 ℃. The heating time (t) at each temperature was changed up to 420 min. The peak intensities (I) for the basal spacing (d001) of Hly (1.0 nm) and m-Hly (0.7 nm) were determined. The variation of the intensities with the heating time was evaluated for each temperature. The full heating time (tf) for each completed crystal transformation was determined graphically and used as kinetic variable. The rate constant (k) was evaluated as \(k=1/{t}_\text{f}\) for the crystal transformation assumed from the zeroth order (n = 0). It has been observed that the drawn lnk-1/T graph conforms to the Arrhenius equation in the form of \(\mathrm{ln}k=-3247.2/T+3.4215\). The activation energy was calculated as E# = 27 kJ mol−1 from the slope of this line equation, and the frequency factor from its intercept was calculated as A = 31 min−1.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergaya MF, Theng BKG, Lagaly G. Handbook of clay Science. Oxford: Elsevier; 2006.
Moore DM, Reynolds RC Jr. X-ray diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press; 1997.
Warr LN. Recommended abbreviations for the names of clay minerals and associated phases. Clay Miner. 2020;55:261–4.
Singh B. Why does halloysite roll? A new model. Clay Clay Miner. 1996;44:191–6.
Adamo P, Violante P, Wilson MJ. Tubular and spheroidal halloysite in pyroclastic deposits in the area of the Roccamonfina volcano (Southern Italy). Geoderma. 2001;99:295–316.
Joussein E, Petit S, Churchman J, Theng B, Righi D, Delvaux B. Halloysite clay minerals- a review. Clay Miner. 2005;40:383–426.
Lvov Y, Price R, Gaber B, Ichinose I. Thin film nanofabrication via layer-by-layer adsorption of tubule halloysite, spherical silica, proteins and polycations. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng. 2002;198–200:375–82.
Kamble R, Ghang M, Gaikaward S, Panda BK. Halloysite nanotubes and applications: a review. J Adv Sci Res. 2012;3(2):25–9.
Yuan P, Tan D, Annabi-Bergaya F. Properties and applications of halloysite nanotubes: recent research advances and future prospects. Appl Clay Sci. 2015;112–113:75–93.
Wilson IR. Kaolin and halloysite deposits of China. Clay Miner. 2004;39:1–15.
Zhao M, Liu P. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on halloysite nanotubes. Micropor Mesopor Mat. 2008;112:24–41.
Luo P, Zhao Y, Zhang B, Liu J, Yang Y, Liu J. Study on the adsorption of Neutral Red from aqueous solution onto halloysite nanotubes. Water Res. 2010;44:1489–97.
Rong T-L, Xiao J-K. The catalytic cracking activity of the kaolin-group minerals. Mater Lett. 2002;57:297–301.
Barrientos-Ramírez S, Ramos-Fernández EV, Silvestre-Albero J, Sepúlveda-Escribano A, Pastor-Blas MM, González-Montiel A. Use of nanotubes of natural halloysite as catalyst support in the atom transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate. Micropor Mesopor Mat. 2009;120:132–40.
Zatta L, da Costa Gardolinski JEF, Wypych F. Raw halloysite as reusable heterogeneous catalyst for esterification of lauric acid. Appl Clay Sci. 2011;51:165–9.
Kumar AP, Depan D, Tomer NS, Singh RP. Nanoscale particles for polymer degradation and stabilization-trends and future perspectives. Prog Polym Sci. 2009;34:479–515.
Eser N, Önal M, Çelik M, Pekdemir AD, Sarıkaya Y. Preparation and characterization of polymethacrylamide/halloysite composites. Polym Compos. 2020;41:893–9.
Eser N, Önal M, Çelik M, Pekdemir AD, Sarıkaya Y. Synthesis, characterization and some physicochemical properties of polypyrrole/halloysite composites. J Macromol Sci Pure Appl. 2020;57(3):222–8.
Kaze CR, Alomayri T, Hasan A, Lecomte-Nana GL, Nemaleu JGD, Tchakoute HK, Kamseu E, Melo UC, Hubert R. Reaction kinetics and rheological behaviour of meta-halloysite based geopolymer cured at room temperature: Effect of thermal activation on physicochemical and microstructural properties. Appl Clay Sci. 2020;196: 105773.
Mohamed H, Deutou JGN, Kaze CR, Moungam LMB, Kamseu E, Melo UC, Leonelli C. Mechanical and microstructural properties of geopolymer mortars from meta-halloysite: effect of titanium dioxide TiO2 (anatase and rutile) content. SN Appl Sci. 2020;2:1573.
Yang C, Liu P, Zhao Y. Preparation and characterization of coaxial halloysite/polypyrrole tubular nanocomposites for electrochemical energy storage. Electrochim Acta. 2010;55:6857–64.
Mei D, Zhang B, Liu R, Zhang Y, Liu J. Preparation of capric acid/halloysite nanotube composite as form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol. 2011;95:2772–7.
Deng S, Zhang J, Ye L, Wu J. Toughening epoxies with halloysite nanotubes. Polymer. 2008;49:5119–27.
Chen Q-Z, Liang S-L, Wang J, Simon GP. Manipulation of mechanical compliance of elastomeric PGS by incorporation of halloysite nanotubes for soft tissue engineering applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4:1805–18.
Wada K. Intercalation of water in kaolin minerals. Am Mineral. 1965;50:924–41.
Churchman GJ, Carr RM. Stability fields of hydration states of an halloysite. The Am Min. 1972;57:914–23.
Churchman GJ, Davy TJ, Aylmore LAG, Gilkes RJ, Self PG. Characteristics of fine pores in some halloysites. Clay Miner. 1995;30:89–98.
Yuan P, Tan D, Annabi-Bergaya F, Yan W, Fan M, Liu D, He H. Changes in structure, morphology, porosity, and surface activity of mesoporous halloysite nanotubes under heating. Clay Clay Miner. 2012;60(6):561–73.
Liu T, Zhang J, Ouyang P, Fu L, Yang H. The relation between nanotube diameter, length and surface area and pore volume of multi-walled spiral halloysite nanotubes: A theoretical study. Appl Clay Sci. 2021;215: 106303.
Weber JN, Roy R. Dehydroxylation of kaolinite, dickite and halloysite:heats of reaction and kinetics of dehydration at PH2O: 15 psi. Am Min. 1965;50:1038–45.
Kaze CR, Nana A, Lecomte-Nana GL, Deutou JGN, Kamseu E, Melo UC, Andreola F, Leonelli C. Thermal behaviour and microstructural evolution of metakaolin and meta-halloysite-based geopolymer binders: a comparative study. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2022;147:2055–71.
Joussein E, Petit S, Fialips C-I, Vieillard P, Righi D. Differences in the dehydration-rehydration behavior of halloysites: new evidence and interpretations. Clay Clay Miner. 2006;54(4):473–84.
Ouyang J, Zhou Z, Zhang Y, Yang H. High morphological stability and structural transition of halloysite (Hunan, China) in heat treatment. Appl Clay Sci. 2014;101:16–22.
Duce C, Ciprioti SV, Ghezzi L, Ierardi V, Tiné MR. Thermal behavior study of pristine and modified halloysite nanotubes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;121:1011–9.
Yuan P. Thermal-treatment-induced deformations and modifications of halloysite. Developments in Clay Science. Elsevier; 2016. pp.137–66.
Kautz CQ, Ryan PC. The 10A to 7A halloysite transition in a tropical soil sequence, costa rica. Clays Clay Miner. 2003;51(3):252–63.
Du R, Wu K, Zhang L, She Y, Xu D, Chao C, Qin X, Zhang B. Thermal behavior and kinetic study on the pyrolysis of Shenfu coal by sectioning method. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;125:959–66.
Pekdemir AD, Sarıkaya Y, Önal M. Thermal transformation kinetics of a kaolinitic clay. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123:767–72.
Noyan H, Önal M, Sarıkaya Y. A model developed for acid dissolution thermodynamics of a Turkish bentonite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;94:591–6.
Sarıkaya Y, Önal M. An indirect model for sintering thermodynamics. Turk J Chem. 2016;40:841–5.
Sarıkaya Y, Ceylan H, Önal M, Pekdemir AD. Thermal deactivation kinetics and thermodynamics of a silica gel using surface area data. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;146:1505–10.
Sarıkaya Y, Önal M, Pekdemir AD. Thermal degradation kinetics of sepiolite. Clay Miner. 2020;55:96–100.
Sarıkaya Y, Önal M, Pekdemir AD. Kinetic and thermodynamic approaches on thermal degradation of sepiolite crystal using XRD-analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;140:2667–72.
Dağlar S, Kahya ND, Ustunisik G, Onal M, Sarikaya Y. Thermal crystallization kinetics of an opal-like biogenic silica. Silicon. 2022;14:7214–7.
Ece ÖI, Schroeder PA. Clay mineralogy and chemistry of halloysite and alunite deposits in the Turplu area, Balıkesir. Turkey Clay Clay Miner. 2007;55(1):18–36.
Acknowledgements
This work received financial support from Ankara University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (19L0430007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors participated equally in the design, experimental, theoretical and writing studies of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Önal, M., Sarıkaya, Y. Irreversible thermal transformation kinetics of halloysite to metahalloysite using XRD analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 13457–13462 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12640-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12640-0