Abstract
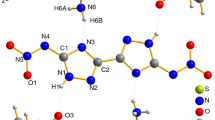
Thermogravimetry coupled with mass spectrometry (TG-MS) and ReaxFF molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are firstly applied to study the thermal decomposition mechanism of 5,5ʹ-dinitramino-3,3ʹ-bi[1,2,4-triazolate] carbohydrazide salt (CBNT). ReaxFF MD simulations are applied to investigate the primary chemical reactions, decomposition products and decomposition rate, respectively. Experimentally, TG-MS techniques are adopted to identify the final gaseous products decomposed by CBNT. Both TG-MS measured results and ReaxFF MD simulated results show that the final stable gaseous products are mainly NH3, H2O, N2 and CO2. The main intermediates and chemical reactions during the decomposition process are obtained by ReaxFF MD simulations as well. According to the simulation and experimental results, the most probable thermal decomposition path of CBNT is obtained. The initial decomposition step of CBNT is the dissociation of N−NO2 and N−NH3 bonds to generate NO2 and NH3, followed by the cleavage of the C−N bonds, and resulting in the formulation of the ring structure. After the main reactions of carbazide cations and bistriazole anions, high-frequency reactions primarily occur between the unstable intermediate products and finally produces small stable molecules such as NH3, H2O, N2 and CO2.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang RH, Xu HY, Guo Y, Sa RJ, Shreeve JM. Bis[3-(5-nitroimino-1,2,4-triazolate)]-based energetic salts: synthesis and promising properties of a new family of high-density insensitive materials. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:11904–5.
Li J, Jin SH, Lan GC, Chen K, Liu W, Zhang XP, Chen SS, Li LJ. A molecular dynamics study and detonation parameters calculation of 5,5’-dinitramino-3,3’-bi[1,2,4-triazolate] carbohydrazide salt (CBNT) and its PBXs. J Energ Mater. 2020;38:283–94.
Li J, Jin SH, Lan GC, Zhang XP, Wang J, Chen SS, Lu BP, Chen K. Measurement and correlation of solubilities of 5,5′-dinitramino-3,3′-bi[1,2,4-triazolate] carbohydrazide salt (CBNT) in various pure solvents and a binary mixture (dimethyl sulfoxide + water) from 298.15 to 343.15 K. J Chem Eng Data. 2019;64:3874–81.
Hiskey MA, Chavez DE (2001) Insensitive high nitrogen compounds. DE20012776133, 2001–56–168
Lei YP, Xu SL, Yang SQ. New research progress in application of high-nitrogen energetic compound. Chem Propell Polymer Mater. 2007;5:1–7.
He P, Yang JQ, Li T, Zhang JG. Overview on the quantum chemical methods for energetic materials. Chin J Energ Mater. 2018;26:34–45.
Zhang YF. Studies on synthesis of energetic compounds derived from azoles. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology; 2016.
Chen ZY, Wang XJ, Guo RJ, Li ZH, He YY, Zhang SH. Molecular dynamics simulation on the interface interactions of CBNT and polymers. Chin J Explos Propell. 2018;41:479–505.
Wang XJ, Zhang XP, Lu ZY, Wang X, Jin SH, Chen SS. Synthesis and properties of 5,5’-dinitramino-3,3’-bi[1,2,4-triazolate] carbohydrazide salt. Chin J Energ Mater. 2016;24:353–6.
Huang XC, Guo T, Liu M, Wang ZJ, Qiu SJ, Ge ZX. Review on bis-azoles and its energetic ion derivatives. Chin J Energ Mater. 2015;23:291–301.
Yang SQ, Xu SL, Huang HJ, Zhang W, Zhang XG. High nitrogen compounds and their energy materials. Prog Chem. 2008;20:526–37.
Klapotke TM, Stierstorfer J, Wallek AU. Nitrogen-rich salts of 1-methyl-5-nitriminotetrazolate: an auspicious class of thermally stable energetic materials. Chem Mater. 2008;20:4519–30.
Klapotke TM, Sabate CM. Bistetrazoles: nitrogen-rich, high-performing, insensitive energetic compounds. Chem Mater. 2008;20:3629–37.
Chavez DE, Hiskey MA, Naud DL. Tetrazine explosives. Propell Explos Pyrot. 2004;29:209–15.
Huang YG, Gao HX, Twamley B, Shreeve JM. Synthesis and characterization of new energetic nitroformate salts. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2007;16:2560–8.
Gao HX, Shreeve JM. Azole-based energetic salts. Chem Rev. 2011;111:7377–436.
Guo YY, Ye ZW. Progress in synthesis of energetic ionic salts of triazole and tetrazole compounds. Chin J Appl Chem. 2013;30:489–99.
Huang HF, Zhou ZM. Progress of study on organic anion based energetic salts. Chin J Explos Propell. 2012;35:1–10.
Lan G, Zhang G, Chao H, Li Z, Wang J, Li J. Ameliorating the performances of 3,4-bis(4′-nitrofurazano-3′-yl)furoxan (DNTF) by establishing tannic acid (TA) interface layer on DNTF surface. Chem Eng J. 2022;434:134513.
Zhang L, Zybin SV, Duin ACT, Dasgupta S, Goddard WA, Kober EM. Carbon cluster formation during thermal decomposition of octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine and 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene high explosives from ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics simulations. J Phys Chem A. 2009;113:10619–40.
Lan G, Li J, Zhang G, Ruan J, Lu Z, Jin S, Cao D, Wang J. Thermal decomposition mechanism study of 3-nitro-1,2,4-triazol-5-one (NTO): Combined TG-FTIR-MS techniques and ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics simulations. Fuel. 2021;295:120655.
Wen YS, Zhang CY, Xue XG, Long XP. Cluster evolution during the early stages of heating explosives and its relationship to sensitivity: a comparative study of TATB, beta-HMX and PETN by molecular reactive force field simulations. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015;17:12013–22.
Liu Y, Li F, Sun H. Thermal decomposition of FOX-7 studied by ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. Theor Chem Acc. 2014;133:1567.
Zhang M, Li CF, Zhao FQ, Xu SY, Ju XH. Reactive molecular dynamics simulation of thermal decomposition for nano-AlH3/TNT and nano-AlH3/CL-20 composites. J Mater Sci. 2019;54:7016–27.
Li J, Jin SH, Lan GC, Chen SS, Shu QH, Li LJ, Chen K. Reactive molecular dynamics simulations on the thermal decompositions and oxidations of TKX-50 and twinned TKX-50. CrystEngComm. 2020;22:2593–600.
Wang FP, Chen L, Geng DS, Wu JY, Lu JY, Wang C. Thermal decomposition mechanism of CL-20 at different temperatures by ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics simulations. J Phys Chem A. 2018;122:3971–9.
Xie W, Heltsley R, Cai XH, Deng FQ, Liu JM, Lee C, Pan WP. Study of stability of high-temperature polyimides using TG/MS technique. J Appl Polym Sci. 2002;83:1219–27.
Perng LH. Thermal decomposition characteristics of poly(ether imide) by TG/MS. J Polym Res. 2000;7:185–93.
Dong LM, Li XD, Yang RJ. Thermal decomposition study of HNIW by synchrotron photoionization mass spectrometry. Propell Explos Pyrot. 2011;36:493–8.
Liang B, Wang JB, Hu JH, Li CF, Li RK, Liu Y, Zeng K. TG-MS-FTIR study on pyrolysis behavior of phthalonitrile resin. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2019;169:108954.
Lisa G, Yoshitake Y, Michinobu T. Thermal degradation of some ferrocene-containing poly(aryleneethynylene)s. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2016;120:399–408.
Liu LC, Liu Y, Zybin SV, Sun H, Goddard WA. ReaxFF-lg: Correction of the ReaxFF reactive force field for london dispersion, with applications to the equations of state for energetic materials. J Phys Chem A. 2011;115:11016–22.
Strachan A, Duin ACT, Chakraborty D, Dasgupta S, Goddard WA. Shock waves in high-energy materials: The initial chemical events in nitramine RDX. Phys Rev Lett. 2003;91:098301.
Rom N, Zybin SV, Duin ACT, Goddard WA, Zeiri Y, Katz G, Kosloff R. Density-dependent liquid nitromethane decomposition: molecular dynamics simulations based on ReaxFF. J Phys Chem A. 2011;115:10181–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., she, C., Yang, C. et al. A combined ReaxFF simulation and TG-MS study on the thermal decomposition mechanism of 5,5ʹ-dinitramino-3,3ʹ-bi[1,2,4-triazolate] carbohydrazide salt (CBNT). J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 10885–10896 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12432-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12432-6