Abstract
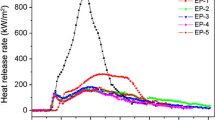
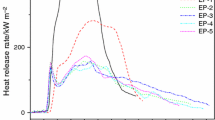
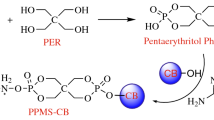
Generally, pentaerythritol (PER) and melamine are, respectively, used as charring agent and blowing agent to combine with ammonium polyphosphate (APP) to establish an intumescent flame retardant (IFR). As for IFR system, the intumescent volume and compactness of char residues are the keys to enhance the flame retardancy of polymers. In this work, hydroxylated melamine (MOH) was synthesized and used as both charring agent and blowing agent to replace pentaerythritol and melamine simultaneously, and it was combined with APP to develop an excellent intumescent flame retardant for epoxy resin. This APP/MOH intumescent flame retardant at the mass ratio of 3:1 significantly improved the LOI value of epoxy resin to 32.5% and reached UL 94 V-0 by 15 mass% loading contents. However, both APP and APP/PER system failed to pass UL-94 vertical burning test and lower LOI was obtained. Additionally, the peak of heat release rate and peak of smoke production rate of APP/MOH based epoxy resin were reduced by 68.3% and 39.0%, respectively, compared with those of neat epoxy resin. After analysis of the pyrolysis products from the gaseous and condensed phases, it was found that APP/MOH system produced higher intumescent volume and better compactness of char, which is a good barrier to hinder the transfer of fuels and heats.









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 September 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12497-3
References
Capricho JC, Fox B, Hameed N. Multifunctionality in epoxy resins. Polym Rev. 2019;60(1):1–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2019.1650063.
Mi X, Liang N, Xu H, Wu J, Jiang Y, Nie B, et al. Toughness and its mechanisms in epoxy resins. Prog Mater Sci. 2022;130:100977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2022.100977.
Ma T, Li L, Liu T, Guo C. Synthesis of a caged bicyclic phosphates derived anhydride and its performance as a flame-retardant curing agent for epoxy resins. Polyme Advan Technol. 2019;30(5):1314–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.4565.
Wang X, Guo W, Song L, Hu Y. Intrinsically flame retardant bio-based epoxy thermosets: a review. Compos Part B-Eng. 2019;179:107487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107487.
Rao W, Zhao P, Yu C, Zhao H-B, Wang Y-Z. High strength, low flammability, and smoke suppression for epoxy thermoset enabled by a low-loading phosphorus-nitrogen-silicon compound. Compos Part B-Eng. 2021;211:108640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108640.
Jiang G, Xiao Y, Qian Z, Yang Y, Jia P, Song L, et al. A novel phosphorus-, nitrogen- and sulfur-containing macromolecule flame retardant for constructing high-performance epoxy resin composites. Chem Eng J. 2022;451:137823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137823.
Yan L, Xu Z, Deng N, Chu Z. Synergistic effects of mono-component intumescent flame retardant grafted with carbon black on flame retardancy and smoke suppression properties of epoxy resins. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138(2):915–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08298-2.
Wang A, Zhang F, Xing L, Zhu Y, Xie W, Chen X, et al. Effect of aluminum diethylphosphinate and its synergist on flame-retardant effects of epoxy resin. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;147(13):7277–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-11045-1.
Chang LN, Jaafar M, Chow WS. Thermal behavior and flammability of epoxy/glass fiber composites containing clay and decabromodiphenyl oxide. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;112(3):1157–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2681-z.
Mauerer O. New reactive, halogen-free flame retardant system for epoxy resins. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2005;88(1):70–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2004.01.027.
Zhang J, Mi X, Chen S, Xu Z, Zhang D, Miao M, et al. A bio-based hyperbranched flame retardant for epoxy resins. Chem Eng J. 2020;381:122719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122719.
Liu S, Yu B, Feng Y, Yang Z, Yin B. Synthesis of a multifunctional bisphosphate and its flame retardant application in epoxy resin. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2019;165:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.04.022.
Pourchet S, Sonnier R, Ben-Abdelkader M, Gaillard Y, Ruiz Q, Placet V, et al. New reactive isoeugenol based phosphate flame retardant: toward green epoxy resins. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2019;7(16):14074–88. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02629.
Bifulco A, Parida D, Salmeia KA, Nazir R, Lehner S, Stämpfli R, et al. Fire and mechanical properties of DGEBA-based epoxy resin cured with a cycloaliphatic hardener: combined action of silica, melamine and DOPO-derivative. Mater Des. 2020;193:108862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108862.
He L, Chen T, Zhang Y, Hu L, Wang T, Han R, et al. Imide-DOPO derivative endows epoxy resin with excellent flame retardancy and fluorescence without losing glass transition temperature. Compos Part B-Eng. 2022;230:109553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109553.
Xiao Y, Jiang G, Ma C, Zhou X, Wang C, Xu Z, et al. Construction of multifunctional linear polyphosphazene and molybdenum diselenide hybrids for efficient fire retardant and toughening epoxy resins. Chem Eng J. 2021;426:131839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131839.
Jian RK, Ai YF, Xia L, Zhao LJ, Zhao HB. Single component phosphamide-based intumescent flame retardant with potential reactivity towards low flammability and smoke epoxy resins. J Hazard Mater. 2019;371:529–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.045.
Liu J, He Z, Wu G, Zhang X, Zhao C, Lei C. Synthesis of a novel nonflammable eugenol-based phosphazene epoxy resin with unique burned intumescent char. Chem Eng J. 2020;390:124620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124620.
Shi T, Zhang S, Shi X. Oxidized regenerated celluloses to fabricate high fire safety for epoxy resin with super expansion char layer. Cellulose. 2021;28(5):2995–3015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03723-y.
Zhang J, Li Z, Yin G-Z, Wang D-Y. Construction of a novel three-in-one biomass based intumescent fire retardant through phosphorus functionalized metal-organic framework and β-cyclodextrin hybrids in achieving fire safe epoxy. Compos Commun. 2021;23:100594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.100594.
Chen M-J, Lin Y-C, Wang X-N, Zhong L, Li Q-L, Liu Z-G. Influence of cuprous oxide on enhancing the flame retardancy and smoke suppression of epoxy resins containing microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2015;54(51):12705–13. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03877.
Chen M-J, Wang X, Li X-L, Liu X-Y, Zhong L, Wang H-Z, et al. The synergistic effect of cuprous oxide on an intumescent flame-retardant epoxy resin system. RSC Adv. 2017;7(57):35619–28. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA05482C.
Sui Y, Sima H, Shao W, Zhang C. Novel bioderived cross-linked polyphosphazene microspheres decorated with FeCo-layered double hydroxide as an all-in-one intumescent flame retardant for epoxy resin. Compos Part B-Eng. 2022;229:109463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109463.
Liang D, Zhu X, Dai P, Lu X, Guo H, Que H, et al. Preparation of a novel lignin-based flame retardant for epoxy resin. Mater Chem Phys. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.124101.
Ye T-P, Liao S-F, Zhang Y, Chen M-J, Xiao Y, Liu X-Y, et al. Cu(0) and Cu(II) decorated graphene hybrid on improving fireproof efficiency of intumescent flame-retardant epoxy resins. Compos Part B-Eng. 2019;175:107189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107189.
Xu Z, Chu Z, Yan L, Chen H, Jia H, Tang W. Effect of chicken eggshell on the flame-retardant and smoke suppression properties of an epoxy-based traditional APP-PER-MEL system. Polym Compos. 2018;40(7):2712–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25077.
Xu X, Wang S, Ma S, Yuan W, Li Q, Feng J, et al. Vanillin-derived phosphorus-containing compounds and ammonium polyphosphate as green fire-resistant systems for epoxy resins with balanced properties. Polym Advan Technol. 2019;30(2):264–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.4461.
Wang W, Liu Y, Wen H, Wang Q. Synthesis of a hyperbranched polyamide charring agent and its flame-retarding and toughening behavior in epoxy resin. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2021;184:109479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109479.
Qiu S, Ma C, Wang X, Zhou X, Feng X, Yuen RKK, et al. Melamine-containing polyphosphazene wrapped ammonium polyphosphate: a novel multifunctional organic-inorganic hybrid flame retardant. J Hazard Mater. 2018;344:839–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.018.
Kim M, Ko H, Park S-M. Synergistic effects of amine-modified ammonium polyphosphate on curing behaviors and flame retardation properties of epoxy composites. Compos Part B-Eng. 2019;170:19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.04.016.
Shao Z-B, Cui J, Li X-L, Díaz Palencia JL, Wang D-Y. Chemically inorganic modified ammonium polyphosphate as eco-friendly flame retardant and its high fire safety for epoxy resin. Compos Commun. 2021;28:100959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2021.100959.
Li X-L, Zhang F-H, Jian R-K, Ai Y-F, Ma J-L, Hui G-J, et al. Influence of eco-friendly calcium gluconate on the intumescent flame-retardant epoxy resin: flame retardancy, smoke suppression and mechanical properties. Compos Part B-Eng. 2019;176:107200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107200.
Wang J-S, Liu Y, Zhao H-B, Liu J, Wang D-Y, Song Y-P, et al. Metal compound-enhanced flame retardancy of intumescent epoxy resins containing ammonium polyphosphate. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2009;94(4):625–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2009.01.006.
Gérard C, Fontaine G, Bourbigot S. Synergistic and antagonistic effects in flame retardancy of an intumescent epoxy resin. Polyme Advan Technol. 2011;22(7):1085–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1996.
Ren Y, Yuan D, Li W, Cai X. Flame retardant efficiency of KH-550 modified urea-formaldehyde resin cooperating with ammonium polyphosphate on polypropylene. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2018;151:160–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.03.014.
Zhu Z, Lin P, Wang H, Wang L, Yu B, Yang F. A facile one-step synthesis of highly efficient melamine salt reactive flame retardant for epoxy resin. J Mater Sci. 2020;55(55):12836–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04935-6.
Shen D, Xu Y-J, Long J-W, Shi X-H, Chen L, Wang Y-Z. Epoxy resin flame-retarded via a novel melamine-organophosphinic acid salt: thermal stability, flame retardance and pyrolysis behavior. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2017;128:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2017.10.025.
Zhong L, Zhang K-X, Wang X, Chen M-J, Xin F, Liu Z-G. Synergistic effects and flame-retardant mechanism of aluminum diethyl phosphinate in combination with melamine polyphosphate and aluminum oxide in epoxy resin. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;134(3):1637–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7699-4.
Tiwari D, Goel C, Bhunia H, Bajpai PK. Melamine-formaldehyde derived porous carbons for adsorption of CO2 capture. J Environ Manag. 2017;197:415–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.013.
Lu Y, Ji C, Li Y, Qu R, Sun C, Zhang Y. Facile one-pot synthesis of C and g-C3N4 composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity using hydroxymethylated melamine as carbon source and soft template. Mater Lett. 2018;211:78–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.09.080.
Wang X, Hu Y, Song L, Xing W, Lu H, Lv P, et al. Effect of a triazine ring-containing charring agent on fire retardancy and thermal degradation of intumescent flame retardant epoxy resins. Polyme Adv Technol. 2011;22(12):2480–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1788.
Alongi J, Han Z, Bourbigot S. Intumescence: tradition versus novelty. Compr Rev Prog Polym Sci. 2015;51:28–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2015.04.010.
Sun Y, Zhong S, Luo Q, Yu B, Song J, Tan D. A vanillin-derived flame retardant based on 2-aminopyrimidine for enhanced flame retardancy and mechanical properties of epoxy resin. Polyme Advan Technol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5875.
Liu XY, Xie RY, Chen T, He L, Wang T, Liao W, et al. Improvement of polyurethane film strength by H-bonding crosslinking with hydroxylated melamine. J Appl Polym Sci. 2021;138(47):51411. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.51411.
Chen M-J, Shao Z-B, Wang X-L, Chen L, Wang Y-Z. Halogen-free flame-retardant flexible polyurethane foam with a novel nitrogen-phosphorus flame retardant. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2012;51(29):9769–76. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie301004d.
Wang T, Long M-C, Zhao H-B, An W-L, Xu S, Deng C, et al. Temperature-responsive intumescent chemistry toward fire resistance and super thermal insulation under extremely harsh conditions. Chem Mater. 2021;33(15):6018–28. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c01408.
Price D, Liu Y, Milnes GJ, Hull R, Kandola BK, Horrocks AR. An investigation into the mechanism of flame retardancy and smoke suppression by melamine in flexible polyurethane foam. Fire Mater. 2002;26(4–5):201–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.810.
Xu Q, Zhai H, Wang G. Mechanism of smoke suppression by melamine in rigid polyurethane foam. Fire Mater. 2015;39(3):271–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.2249.
Zhang W, Zhai X, Xiang T, Zhou M, Zang D, Gao Z, et al. Superhydrophobic melamine sponge with excellent surface selectivity and fire retardancy for oil absorption. J Mater Sci. 2016;52(1):73–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0235-7.
Fang Y, Miao J, Yang X, Zhu Y, Wang G. Fabrication of polyphosphazene covalent triazine polymer with excellent flame retardancy and smoke suppression for epoxy resin. Chem Eng J. 2020;385:123830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123830.
Tuinstra F, Koenig JL. Raman spectrum of graphite. J Chem Phys. 1970;53(3):1126–30. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1674108.
Huo S, Yang S, Wang J, Cheng J, Zhang Q, Hu Y, et al. A liquid phosphaphenanthrene-derived imidazole for improved flame retardancy and smoke suppression of epoxy resin. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2020;2(8):3566–75. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.0c00577.
Liu X-D, Zheng X-T, Dong Y-Q, He L-X, Chen F, Bai W-B, et al. A novel nitrogen-rich phosphinic amide towards flame-retardant, smoke suppression and mechanically strengthened epoxy resins. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2022;196:109840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2022.109840.
He L, Chen T, Wang T, Zhao H-B, Deng J-N, Li T-T, et al. Extra strong Cu2+-doped intumescent char to protect epoxy resin against fire. Compos Part B-Eng. 2023;253:110539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2023.110539.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21975208), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2020JDJQ0062), and Open and Innovative Fund of Hubei Three Gorges Laboratory (2022LF2021, SK213005), Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province for Outstanding Youth (2023NSFSC1955), and Science and Technology Program of Yibin (2022GY001) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: In this article, Jin-Nice Deng should have been denoted as a corresponding author.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Liu, XY., Wang, T. et al. An improved intumescent flame-retardant epoxy resin with hydroxylated melamine as both charring and blowing agent. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 10103–10114 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12361-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12361-4