Abstract
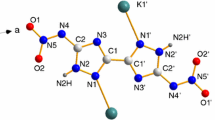
The systematical thermal behaviors of 3⁃azido⁃1,3⁃dinitroazetidine (ADNAZ) was investigated in this research and compared with those of 1,3,3-trinitroazetidine (TNAZ). The results showed that ADNAZ has a low melting temperature at 78 °C. The final mass loss of ADNAZ under atmospheric pressure is 88.2%. Compared to TNAZ, the replacement of gem-dinitro group with gemazidonitro group makes greatly reduce vapor pressure, melting point as well as the thermal decomposition temperature. The in-situ FTIR spectroscopy of ADNAZ proved the strength of nitro group decreases faster than that of azide group, and a carbonyl group (C=O) was formed at the quaternary carbon center on the azetidine skeleton during heating process. TG/DSC–FTIR–MS quadruple technology was applied, finding small molecular fragments from ADNAZ’s thermolysis includes H2 (m/z = 2), H2O (m/z = 18), CN (m/z = 26), HCN (m/z = 27), N2 (m/z = 28), NO (m/z = 30), C2H2O (m/z = 42), HN3 (m/z = 43), CO2 (m/z = 44), and NO2 (m/z = 46). A detailed decomposition mechanism was proposed based on the experimental results.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Viswanath DS, Ghosh TK, Boddu VM. Emerging energetic materials: synthesis, physicochemical, and detonation properties. Dordrecht: Springer; 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1201-7.
Shukla MK, Boddu VM, Steevens JA, et al. Energetic materials: from cradle to grave. Cham: Springer; 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59208-4.
Klapötke TM. Chemistry of high-energy materials. Berlin: De Gruyter; 2015.
Dalinger IL, Shakhnes AK, Monogarov KA, et al. Novel high energetic pyrazoles: N-fluorodinitromethyl and N-(difluoroamino)dinitromethyl derivatives. Mendeleev Commun. 2015;25:429–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mencom.2015.11.010.
Agrawal JP, Hodgson RD. Organic chemistry of explosives. Chichester: Wiley; 2007. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470059364.
Politzar PA, Murray JS. Energetic materials, path 2: detonation, combustion. Netherlands: Elsevier; 2003.
Pepekin VI, Matyushin YN, Khisamutdinov GH, et al. Thermochemical properties of α-azidopolynitroalkanes and the dissociation energy of C–N3 bonds in organic azides. Khim Fiz. 1993;12:1399–403.
Zhou J, Zhang JL, Wang BZ, et al. Recent synthetic efforts towards high energy density materials: How to design high-performance energetic structures? FirePhysChem. 2022;2:83–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpc.2021.09.005.
Khisamutdinov GK, Slovetsky VI, Golub YM, et al. α-Azidopolynitroalkanes. synthesis and vibrational spectra. Russ Chem Bull. 1997;46:324–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02494372.
Xue Q, Bi FQ, Zhai LJ, et al. Synthesis, characterization and performance of promising energetic materials based on 1,3-oxazinane. ChemPlusChem. 2019;84:913–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/cplu.201900322.
Liu ZR. Review and prospect of thermal analysis technology applied to study thermal properties of energetic materials. FirePhysChem. 2021;1:129–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpc.2021.05.002.
Sućeska M, Rajić M, Zeman S, et al. 1,3,3-trinitroazetidine (TNAZ). Study of thermal behaviour. Part II. J Energ Mater. 2001;19:241–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/07370650108216128.
Nedel’ko V, Korsunskii B, Makhova N, et al. Thermal decomposition of 1,3,3-trinitroazetidine in the gas phase, solution, and melt. Russ Chem Bull. 2010;58:2028–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11172-009-0277-y.
Li JZ, Zhang GF, Fan XZ, et al. Thermal behavior of 1,3,3-trinitroazetidine. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2006;76:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2005.04.008.
Zhang GQ. Technological Synthesis and application advance of 1,3,3-trinitroazetidine (TNAZ). Chin J Energ Mater. 2022;10:174–7.
Katorov DV, Rudakov GF, Ladonin AV. Preparation of low-melting compositions based on 1,3,3-trinitroazetideine. Cent Eur J Energ Mater. 2007;4:125–33.
Jia SY, Zhang HH, Zhang JR, et al. A melt-cast explosive 3-azido-1,3-dinitroazetidine (AzDNAZ) with gem-azidonitro of novel energetic group: synthesis and performance. Chin J Energ Mater. 2020;28:685–9. https://doi.org/10.11943/CJEM2019231.
Liu ZR. Thermal analysis of energetic materials (Chinese Edition). Beijing: Defense Industry Press; 2008.
Sikder N, Sikder AK, Bulakh NR, et al. 1,3,3-Trinitroazetidine (TNAZ), a melt-cast explosive: synthesis, characterization and thermal behaviour. J Hazard Mater. 2004;113:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.06.002.
Huang H, Shi Y, Yang J. Thermal characterization of the promising energetic material TKX-50. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;121:705–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4472-9.
Chen GJ, Fu XY, Tang AQ. Ab initio studies on the thermolysis of azetidine. Chin J Chem. 1992;10:193–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.19920100301.
Oyumi Y, Brill TB. Thermal decomposition of energetic materials 4. High-rate, in situ, thermolysis of the four, six, and eight membered, oxygen-rich, gem-dinitroalkyl cyclic nitramines, TNAZ, DNNC, and HNDZ. Combust Flame. 1985;62:225–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-2180(85)90148-8.
Klaeboe P, Nielsen CJ, Priebe H, et al. The vibrational spectra, molecular structure and conformations of organic azides. I A survey J Mol Struct. 1986;141:161–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2860(86)80320-9.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21805226 and No.21805223).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ, JZ and BZ designed and carried out the thermal research. SJ prepared the ADNAZ sample. LQ and ZM carried out the analysis of the gaseous thermal decomposition products. QP carried out the in-situ FTIR spectroscopy analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Zhang, J., Jia, S. et al. Thermal research on the melt⁃cast explosive of 3-azido-1,3-dinitroazetidine (ADNAZ). J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 7661–7668 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12246-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12246-6