Abstract
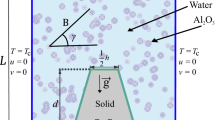
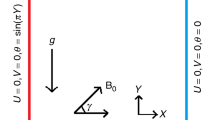
Thermal and flow behaviors of sensible heat energy storage unit subjected to uniform and nonuniform magnetic field effects and to double time dependent heat sources were numerically investigated. The sensible heat energy storage unit is occupied with the nanofluid consisting in Cu nanoparticles dispersed into water and subjected to two variable magnetic sources. The dimensionless governing equations are established and solved via finite element numerical approach. An excellent consistency with published data has been observed during validation of the results. The influence of a certain range of key nondimensional parameters on the transient problem including the frequency of sinusoidal time-dependent temperature imposed from heat sources (λ = 0.1–50), temperature-dependent amplitude of sinusoidal fluctuations (Λ = 0–1), the magnetic number (Mn = 0–5000) and Hartmann number (Ha = 0–50) for two separate Rayleigh number (Ra = 104 and 106) was considered. According to the findings, temperature-varying boundaries affect convective flow, heat exchange, thermal stratification, and total heat content. The oscillations amplitudes for the average time-dependent Nusselt number grow as Ra, Λ and λ increase and Ha decreases. Total heat content in the storage unit is found to have higher mean values at steady development for higher Ra values when Ha = 0. Mn values slightly enhance the mean values of heat content.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.]
Abbreviations
- g:
-
Gravitational acceleration (m s−2)
- Cp :
-
Specific heat (J kg−1 K−1)
- D:
-
Cavity size (m)
- V :
-
Velocity vector (m s−1)
- Ec:
-
Eckert number
- x, y:
-
Cartesian coordinates (m)
- u, v:
-
Components of velocity in x and y directions, respectively (m s−1)
- T:
-
Temperature (k)
- B :
-
Magnetic induction vector
- H * :
-
Magnetic field vector
- M :
-
Magnetization vector
- Da :
-
Darcy number
- Ha :
-
Hartmann number
- a :
-
Dimensional amplitude
- a i, b i :
-
Coordinates of the magnetic sources
- f :
-
Dimensional frequency
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- n :
-
Normal direction to the semi-cylinders
- Nu a :
-
Average Nusselt number
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- \(\dot{r}\) :
-
Distance to the magnetic source
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- Mn :
-
Magnetism Numbers
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number
- K′:
-
Constant
- T c′:
-
Curie temperature
- S :
-
Thermal stratification
- Q:
-
Total heat content
- t:
-
Dimensional time (s)
- λ :
-
Frequency of sinusoidal time-dependant temperature imposed from heat sources
- Λ:
-
Temperature-dependent amplitude of sinusoidal fluctuations
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity coefficient, m−2 s−1
- β :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient (1/K)
- Ω:
-
Strength of the magnetic source
- Ωr :
-
Strength ratio of the two magnetic sources #1 and #2
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- μ 0 :
-
Permeability of vacuum
- φ :
-
Volume fraction of nanoparticles
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- σ :
-
Electrical conductivity (S m−1)
- θ :
-
Non-dimensional temperature
- τ:
-
Non-dimensional time
- ff :
-
Ferro fluid
- r :
-
The relative properties of the ferrofluid to the base fluid
- x, y:
-
In x and y directions
- 1, 2:
-
Refer to the magnetic sources #1 and #2, respectively
- i:
-
Initial
- -:
-
Dimensionless variables
- ~ :
-
Dimensional variables
References
Suri ARS, Kumar A, Maithani R. Convective heat transfer enhancement techniques of heat exchanger tubes: A review. Int J Ambient Energy. 2018;39:649–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2017.1324816.
Singh H, Eames PC. Correlations for natural convective heat exchange in CPC solar collector cavities determined from experimental measurements. Sol Energy. 2012;86:2443–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2012.05.014.
Laguerre O, Ben Amara S, Flick D. Experimental study of heat transfer by natural convection in a closed cavity: Application in a domestic refrigerator. J Food Eng. 2005;70:523–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2004.10.007.
El Omari K, Kousksou T, Le Guer Y. Impact of shape of container on natural convection and melting inside enclosures used for passive cooling of electronic devices. Appl Therm Eng. 2011;31:3022–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2011.05.036.
Choi, S. E. J. In: Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles CONF-951135-29 (1995).
Izadi S, Armaghani T, Ghasemiasl R, Chamkha AJ, Molana M. A comprehensive review on mixed convection of nanofluids in various shapes of enclosures. Powder Technol. 2019;343:880–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.11.006.
Basak T, Chamkha AJ. Heatline analysis on natural convection for nanofluids confined within square cavities with various thermal boundary conditions. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55:5526–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.05.025.
Khanafer K, Vafai K, Lightstone M. Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2003;46:3639–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0017-9310(03)00156-X.
Sadeghi MS, Anadalibkhah N, Ghasemiasl R, Armaghani T, Dogonchi AS, Chamkha AJ, Ali H, Asadi A. On the natural convection of nanofluids in diverse shapes of enclosures: An exhaustive review. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2022;147:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10222-y.
Giwa SO, Sharifpur M, Ahmadi MH, Meyer JP. A review of magnetic field influence on natural convection heat transfer performance of nanofluids in square cavities. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;145:2581–623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09832-3.
Rostami S, Aghakhani S, Hajatzadeh Pordanjani A, Afrand M, Cheraghian G, Oztop HF, Shadloo MS. A review on the control parameters of natural convection in different shaped cavities with and without nanofluid. Processes. 2020;8:1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8091011.
Abouali O, Ahmadi G. Computer simulations of natural convection of single phase nanofluids in simple enclosures: A critical review. Appl Therm Eng. 2012;36:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2011.11.065.
Haddad Z, Oztop HF, Abu-Nada E, Mataoui A. A review on natural convective heat transfer of nanofluids. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2012;16:5363–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.04.003.
Saha A, Chakravarty A, Ghosh K, Biswas N, Manna NK. Role of obstructing block on enhanced heat transfer in a concentric annulus. Waves Random Complex Media. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2022.2106386.
Saha A, Manna NK, Ghosh K, Biswas N. Analysis of geometrical shape impact on thermal management of practical fluids using square and circular cavities. Eur Phys J Spec Top. 2022;231:2509–37. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00593-8.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Alizadeh A. An experimental study of Cu–water nanofluid flow inside serpentine tubes with variable straight-section lengths. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2015;61:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2014.09.014.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Davoudi S, Dibaei MH. Performance of agitated-vessel U tube heat exchanger using spiky twisted tapes and water based metallic nanofluids. Chem Eng Res Des. 2018;133:26–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2018.02.030.
M’hamed B, Sidik NAC, Yazid MNAWM, Mamat R, Najafi G, Kefayati GHR. A review on why researchers apply external magnetic field on nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;78:60–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2016.08.023.
Nkurikiyimfura I, Wang Y, Pan Z. Heat transfer enhancement by magnetic nanofluids—A review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2013;21:548–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.12.039.
Manna NK, Biswas N. Magnetic force vectors as a new visualization tool for magnetohydrodynamic convection. Int J Therm Sci. 2021;167:107004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2021.107004.
Hemmat Esfe M, Afrand M, Esfandeh S. Investigation of the effects of various parameters on the natural convection of nanofluids in various cavities exposed to magnetic fields: A comprehensive review. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;140:2055–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08939-6.
Ghasemi B, Aminossadati SM, Raisi A. Magnetic field effect on natural convection in a nanofluid-filled square enclosure. Int J Therm Sci. 2011;50:1748–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2011.04.010.
Kefayati GR. Effect of a magnetic field on natural convection in an open cavity subjugated to water/alumina nanofluid using Lattice Boltzmann method. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2013;40:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2012.10.024.
Mahmoudi AH, Pop I, Shahi M. Effect of magnetic field on natural convection in a triangular enclosure filled with nanofluid. Int J Therm Sci. 2012;59:126–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2012.04.006.
Sheikholeslami M, Bandpy MG, Ellahi R, Zeeshan A. Simulation of MHD CuO–water nanofluid flow and convective heat transfer considering Lorentz forces. J Magn Magn Mater. 2014;369:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.06.017.
Sheikholeslami M, Vajravelu K. Nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a cavity with variable magnetic field. Appl Math Comput. 2017;298:272–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2016.11.025.
Sreedevi P, Sudarsana Reddy P. Effect of magnetic field and thermal radiation on natural convection in a square cavity filled with TiO2 nanoparticles using Tiwari–Das nanofluid model. Alex Eng J. 2022;61:1529–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.06.055.
Bondareva NS, Sheremet MA, Pop I. Magnetic field effect on the unsteady natural convection in a right-angle trapezoidal cavity filled with a nanofluid. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2015;25:1924–46. https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-07-2014-0236.
Al-Zamily AMJ. Effect of magnetic field on natural convection in a nanofluid-filled semi-circular enclosure with heat flux source. Comput Fluids. 2014;103:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2014.07.013.
Sheremet MA, Pop I, Roşca NC. Magnetic field effect on the unsteady natural convection in a wavy-walled cavity filled with a nanofluid: Buongiorno’s mathematical model. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2016;61:211–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.12.015.
Manna NK, Biswas N, Mandal DK, Sarkar UK, Öztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. Impacts of heater-cooler position and Lorentz force on heat transfer and entropy generation of hybrid nanofluid convection in quarter-circular cavity. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2023;33:1249–86. https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-07-2022-0402.
Chatterjee D, Biswas N, Manna NK, Sarkar S. Effect of discrete heating-cooling on magneto-thermal-hybrid nanofluidic convection in cylindrical system. Int J Mech Sci. 2023;238:107852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107852.
Alsabery AI, Tayebi T, Chamkha AJ, Hashim I. Effects of two-phase nanofluid model on natural convection in a square cavity in the presence of an adiabatic inner block and magnetic field. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2018;28:1613–47. https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-10-2017-0425.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Nanofluid two phase model analysis in existence of induced magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;107:288–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.10.130.
Loenko DS, Shenoy A, Sheremet MA. Effect of time-dependent wall temperature on natural convection of a non-Newtonian fluid in an enclosure. Int J Therm Sci. 2021;166:106973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2021.106973.
Hussam WK, Khanafer K, Salem HJ, Sheard GJ. Natural convection heat transfer utilizing nanofluid in a cavity with a periodic side-wall temperature in the presence of a magnetic field. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2019;104:127–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2019.02.018.
Biswas N, Sarkar UK, Chamkha AJ, Manna NK. Magneto-hydrodynamic thermal convection of Cu–Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid saturated with porous media subjected to half-sinusoidal nonuniform heating. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;143:1727–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10123-0.
Biswas N, Manna NK, Chamkha AJ. Effects of half-sinusoidal nonuniform heating during MHD thermal convection in Cu–Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid saturated with porous media. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;143:1665–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10109-y.
Mondal MK, Biswas N, Datta A, Mandal DK, Manna NK. Magneto-hydrothermal convective dynamics of hybrid nanofluid-packed partially cooled porous cavity: Effect of half-sinusoidal heating. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-11959-y.
Tzirtzilakis EE. A mathematical model for blood flow in magnetic field. Phys Fluids. 2005;17:77103.
Tzirtzilakis EE, Xenos MA. Biomagnetic fluid flow in a driven cavity. Meccanica. 2013;48:187–200.
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD. Ferrohydrodynamic and magnetohydrodynamic effects on ferrofluid flow and convective heat transfer. Energy. 2014;75:400–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.07.089.
Kargarsharifabad H. Experimental and numerical study of natural convection of Cu-water nanofluid in a cubic enclosure under constant and alternating magnetic fields. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2020;119:104957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2020.104957.
Corvaro F, Paroncini M. Experimental analysis of natural convection in square cavities heated from below with 2D-PIV and holographic interferometry techniques. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2007;31:721–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Izadi, M., Tayebi, T., Alshehri, H.M. et al. Transient magneto-buoyant convection of a magnetizable nanofluid inside a circle sensible storage subjected to double time-dependent thermal sources. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 8511–8531 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12242-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12242-w