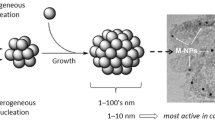
Abstract
In this work, our research group developed usable low-cost superparamagnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@NTA) that behave as an excellent energetic material to accelerate the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate (AP). As a synthetic strategy, magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4) were coated with nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) by a simple preparation method. Based on High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) results, Fe3O4@NTA presents a mean diameter of 7.4 nm and superparamagnetic behavior. Chemical characterization by Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) provided enough evidence for the presence of a carboxylic acid group and magnetite in the sample. The Fe3O4@NTA catalyst diminishes AP high-temperature decomposition (HTD) to 342 °C and shows a low activation energy (98.02 kJ mol−1). In addition, after the burning rate test, it was observed that these resulting nanoparticles showed an adequate magnetic response against an external magnet. These results are promising for future research, as the opportunity opens to reuse this functional magnetic material in successive catalytic cycles, thus contributing soon to the recycling of raw materials necessary for interplanetary travel.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal JP. High energy materials [Internet]. Hoboken: Wiley WILEY-VCH; 2010. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527628803.
Boldyrev VV. Thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate Thermochim. Acta. 2006;443:1–36.
Amin BU, Yu H, Wang L, Nazir A, Fahad S, Haq F, et al. Recent advances on ferrocene-based compounds and polymers as a burning rate catalysts for propellants. J Organomet Chem. 2020;921:121368.
Arroyo JL, Norambuena A, Reyes H, Valdebenito C, Abarca G, Carey DM, et al. Heterobimetallic catalysts for the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate: efficient burning rate catalysts for solid rocket motors and missiles. Inorg Chem. 2021;60:1436–48.
Escobar MA, Morales-Verdejo C, Arroyo JL, Dreyse P, González I, Brito I, et al. Burning rate performance study of ammonium perchlorate catalyzed by heteroleptic copper(i) complexes with pyrazino[2,3-f][1,10]phenanthroline-based ligands. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2021;2021:1632–9.
Abarca G, Ríos PL, Povea P, Cerda-Cavieres C, Morales-Verdejo C, Arroyo JL, et al. Nanohybrids of reduced graphene oxide and cobalt hydroxide (Co(OH)2|rGO) for the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. RSC Adv. 2020;10:23165–72.
Mahdavian AR, Mirrahimi MAS. Efficient separation of heavy metal cations by anchoring polyacrylic acid on superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles through surface modification. Chem Eng J. 2010;159:264–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.02.041.
Wan J, Li H, Chen K. Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4@ZnO core-shell structured nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys. 2009;114:30–2.
Maity D, Agrawal DC. Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles under oxidizing environment and their stabilization in aqueous and non-aqueous media. J Magn Magn Mater. 2007;308:46–55.
Characteristics PB. Plateau burning characteristics of AP based azide composite. Propellants. 1995;55:150–5.
Arun Chandru R, Patel RP, Oommen C, Raghunandan BN. Initial studies on development of high-performance nano-structured Fe2O3 catalysts for solid rocket propellants. J Mater Eng Perform. 2019;28:810–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3812-x.
Chang YC, Chen DH. Preparation and adsorption properties of monodisperse chitosan-bound Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for removal of Cu(II) ions. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;283:446–51.
Ngomsik AF, Bee A, Talbot D, Cote G. Magnetic solid-liquid extraction of Eu(III), La(III), Ni(II) and Co(II) with maghemite nanoparticles. Sep Purif Technol. 2012;86:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.10.013.
Masur S, Zingsem B, Marzi T, Meckenstock R, Farle M. Characterization of the oleic acid/iron oxide nanoparticle interface by magnetic resonance. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;415:8–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.03.045.
Feitoza NC, Gonçalves TD, Mesquita JJ, Menegucci JS, Santos M-KMS, Chaker JA, et al. Fabrication of glycine-functionalized maghemite nanoparticles for magnetic removal of copper from wastewater. J Hazard Mater. 2014;264:153–60.
Lin S, Liu L, Yang Y, Lin K. Study on preferential adsorption of cationic-style heavy metals using amine-functionalized magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MIONPs-NH2) as efficient adsorbents. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;407:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.173.
Vestal CR, Zhang ZJ. Atom transfer radical polymerization synthesis and magnetic characterization of MnFe2O4 /Polystyrene Core/Shell Nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:14312–3. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0274709.
Wu Z, Yang S, Wu W. Shape control of inorganic nanoparticles from solution Nanoscale. Royal Soc Chem. 2016;8:1237–59.
Singh D, Verma S, Gautam RK, Krishna V. Copper adsorption onto synthesized nitrilotriacetic acid functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Chem Eng. 2016;3:2161–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.07.020.
Basualto C, Gaete J, Molina L, Valenzuela F, Yañez C, Marco JF. Lanthanide sorbent based on magnetite nanoparticles functionalized with organophosphorus extractants. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2015;16:35010. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/16/3/035010.
Calorimeters S: Standard test method for arrhenius kinetic constants for thermally unstable materials using differential scanning calorimetry and the FLYNN/Wall/Ozawa Method. ASTM Inst West Cons. 2016;i:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1520/e0698-01
Ghosh K, Behera S, Kumar A, Padale BG, Deshpande DG, Kumar A, et al. Studies on aluminized, high burning rate, Butacene® based, composite propellants. Cent Eur J Energ Mater. 2014;11:323–34.
Povea P, Arroyo JL, Carreño G, Norambuena Á, Rios PL, Camarada MB, et al. Catalytic effects of p-phenylene-bridged methylated binuclear ferrocenes on thermal decomposition of the main component of composite solid propellants. Thermochim Acta. 2018;666:181–9.
Gaete J, Molina L, Alfaro I, Yañez J, Valenzuela F, Basualto C. Recovery and separation of rhenium and molybdenum from aqueous solutions that simulate mine waters using magnetite nanoparticles functionalized with amine-derivative groups. Miner Eng. 2019;136:66–76.
Silva VAJ, Andrade PL, Silva MPC, Bustamante AD, De Los Santos VL, Albino AJ. Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with fucan polysaccharides. J Magn Magn Mater. 2013;343:138–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.04.062.
Melo JP, Ríos PL, Povea P, Morales-Verdejo C, Camarada MB. Graphene oxide quantum dots as the support for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their applications as new catalysts for the decomposition of composite solid propellants. ACS Omega. 2018;3:7278–87.
Paulina LR, Povea P, Cerda-cavieres C, Arroyo JL, Morales-Verdejo C, Abarca G, et al. RSC Advances Novel in situ synthesis of copper nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide and its application as a new catalyst for the decomposition of composite solid propellants †. RSC Adv. 2019;9:8480–9.
Wang W, Yao J. Catalytic activity of magnetite with different shapes for the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Chem Lett. 2014;43:1554–6.
Zhiliang S, Yulei T, Yan X. Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanowires and their catalytic activity towards thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Russ J Gen Chem. 2015;85:926–9.
Joshi SS, Patil PR, Krishnamurthy VN. Thermal Decomposition of ammonium perchlorate in the presence of nanosized ferric oxide. Def Sci J. 2008;58:721–7.
Ghosh K, Chimurkar D, Kumar G, Kumar A, Banerjee S, Gupta M. HTPB-clay nanocomposites (HCN): an efficient burning rate catalyst for composite propellant. Propellants, Explos Pyrotech. 2019;44:1–11.
Chaturvedi S, Dave PN. Solid propellants: AP/HTPB composite propellants. Arab J Chem. 2019;12:2061–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.12.033.
Chmielarek M, Maksimowski P, Gołofit T, Cieślak K, Pawłowski W, Tomaszewski W. Modification of HTPB (α, ω-dihydroxypolybutadiene) by esterification, silanization, epoxidation and hydrogenation. Mater Wysokoenergetyczne / High Energy Mater. 2020;12:203–20.
Gaete J, Arroyo JL, Norambuena Á, Abarca G, Morales-Verdejo C. Mechanistic insights into the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate: the role of amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Inorg Chem. 2022;61:1447–55.
Budhwar AS, Gautam A, More PV, Pant CS, Banerjee S, Khanna PK. Modified iron oxide nanoparticles as burn rate enhancer in composite solid propellants. Vacuum. 2018;156:483–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.08.013.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by FONDECYT grants 1210827 and 11170879 and FONDECYT postdoctoral grant 3220124.
Funding
Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico, 1210827, Cesar Morales Verdejo, Agencia Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo, 11170879, Gabriel Abarca, 3220124, José Gaete.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JG contributed to Formal analysis, Methodology, TEM measurements analysis, Writing, review & editing, Investigation. CV contributed to Software, Formal analysis, Investigation. YD contributed to Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing. JLA: Resources, Formal analysis, Investigation. AN contributed to Resources, Formal analysis, Investigation. FV contributed to Resources, Formal analysis, Investigation. CB contributed to Resources, Formal analysis, Investigation. GA contributed to Conceptualization, Methodology, TEM measurements analysis, Writing, review & editing, Investigation, Supervision. CM-V contributed to Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing, review & editing, Investigation, Supervision. All the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 2780 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MOV 12760 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gaete, J., Valdebenito, C., Dibdalli, Y. et al. Superparamagnetic energetic nanoparticles: a surface self-propagation pathway for the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 2313–2321 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11885-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11885-5