Abstract
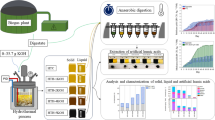
Pyrolysis non-isothermal kinetics, thermodynamics and products compositional characteristics of kitchen wastes fermentation residues (KWFR) were investigated to explore the bioenergy potential by thermogravimetric analysis and pyrolysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS) methods. The results showed that pyrolysis process can be divided into four common stages. The kinetics results deduced from FWO, KAS and Popescu methods showed that reaction activation energy (E) was 170.56, 168.98 and 172.10 kJ mol−1 and pre-exponential factor (A) was 1.22E + 17, 5.04E + 10 and 1.80E + 15 min−1, respectively, while the optimal mechanism function was G(α) = [1 − (1 − α)1/3]2(n = 2). The calculated thermodynamic parameters included ΔH (163.77–166.90 kJ mol−1), ΔS (− 62.25–61.28 J mol−1 K−1) and ΔG (145.41–184.02 kJ mol−1). The Py-GC/MS results showed mainly produced nitrogen-containing compounds, acidic alcohol compounds, aldehydes, ketones, esters, benzenes and hydrocarbons. This study highlights KWFR can be considered as an attractive feedstock for bioenergy and bio-based chemicals and meanwhile may help to solve the problem of kitchen wastes digestion tailings.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Y, Xing P, Liu J. Environmental performance evaluation of different municipal solid waste management scenarios in China. Res Conserv Recycl. 2017;125:98–106.
Pham T, Kaushik R, Parshetti G, Mahmood R, Balasubramanian R. Food waste-to-energy conversion technologies: current status and future directions. Waste Manag. 2015;38:399–408.
Liu W, Dong Z, Sun D, Chen Y, Wang S, Zhu J, Liu C. Bioconversion of kitchen waste into bioflocculant and its pilot-scale application in treating iron mineral processing wastewater. Bioresour Technol. 2019;288:121505.
Eriksson M, Osowski C, Malefors C, Björkman J, Eriksson E. Quantification of food waste in public catering services-a case study from a Swedish municipality. Waste Manag. 2017;61:415–22.
Pan F, Liu S, Xu Q, Chen X, Cheng J. Bioconversion of kitchen waste to surfactin via simultaneous enzymolysis and fermentation using mixed-culture of enzyme-producing fungi and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HM618. Biochem Eng J. 2021;172:108036.
Xu F, Wang B, Yang D, Ming X, Jiang Y, Hao J, Qiao Y, Tian Y. TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS study on pyrolysis mechanism and products distribution of waste bicycle tire. Energy Convers Manag. 2018;175:288–97.
Banerjee A, Vithusha T, Krishna B, Kumar J, Bhaskar T, Ghosh D. Pyrolysis of de-oiled yeast biomass of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa IIPL32: kinetics and thermodynamic parameters using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2021;340:125534.
Sharma A, Mohanty B. Non-isothermal TG/DTG-FTIR kinetic study for devolatilization of Dalbergia sissoo wood under nitrogen atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;146:865–79.
Liu J, Huang S, Chen K, Wang T, Mei M, Li J. Preparation of biochar from food waste digestate: pyrolysis behavior and product properties. Bioresour Technol. 2020;302:122841.
Opatokun S, Strezov V, Kan T. Product based evaluation of pyrolysis of food waste and its digestate. Energy. 2015;92:349–54.
Suriapparao D, Vinu R. Recovery of renewable carbon resources from the household kitchen waste via char induced microwave pyrolysis. Renew Energy. 2021;179:370–8.
Striūgas N, Skvorčinskienė R, Paulauskas R, Zakarauskas K, Vorotinskienė L. Evaluation of straw with absorbed glycerol thermal degradation during pyrolysis and combustion by TG-FTIR and TG-GC/MS. Fuel. 2017;204:227–35.
Jiang Y, Zong P, Tian B, Xu F, Tian Y, Qiao Y, Zhang J. Pyrolysis behaviors and product distribution of Shenmu coal at high heating rate: a study using TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS. Energy Convers Manag. 2019;179:72–80.
Wang S, Wang D, Tang Y, Sun Y, Jiang D, Su T. Study of pyrolysis behavior of hydrogen-rich bark coal by TGA and Py-GC/MS. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2017;128:136–42.
Hu J, Jiang B, Wang J, Qiao Y, Zuo T, Sun Y, Jiang X. Physicochemical characteristics and pyrolysis performance of corn stalk torrefied in aqueous ammonia by microwave heating. Bioresour Technol. 2019;274:83–8.
Liaw S, Perez V, Zhou S, Rodriguez-Justo O, Garcia-Perez M. Py-GC/MS studies and principal component analysis to evaluate the impact of feedstock and temperature on the distribution of products during fast pyrolysis. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2014;109:140–51.
Yan H, Hou F, Zhao H, Wang H, Gao S, Wu M, Yu P, Liu J, Li N, Sun Y, Jiang W, Fan K, He T, Qin S. Pyrolysis kinetics of invasive coastal plant Spartina anglica using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Sources Part A. 2016;38:2867–75.
Han Z, Zhuang D, Zhao H, Yan H, Mao G, Yao C, Wang J, Bi Z, Shan G, Pan J, Sun X, Zhao Y, Yang Y. Comparative study on thermal behaviors between micrites and thrombolites using thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139:1229–42.
Vyazovkin S, Burnham A, Criado J, Pérez-Maqueda L, Popescu C, Sbirrazzuoli N. ICTAC kinetics committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim Acta. 2011;520:1–19.
Maia A, Morais L. Kinetic parameters of red pepper waste as biomass to solid biofuel. Bioresour Technol. 2016;204:157–63.
Kumar M, Shukla S, Upadhyay S, Mishra P. Analysis of thermal degradation of banana (Musa balbisiana) trunk biomass waste using iso-conversional models. Bioresour Technol. 2020;310:123393.
Xu Y, Chen B. Investigation of thermodynamic parameters in the pyrolysis conversion of biomass and manure to biochars using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2013;146:485–93.
Chen L, Yu Z, Liang J, Liao Y, Ma X. Co-pyrolysis of Chlorella vulgaris and kitchen waste with different additives using TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS. Energy Convers Manag. 2018;177:582–91.
Giwa A, Xu H, Chang F, Zhang X, Ali N, Yuan J, Wang K. Pyrolysis coupled anaerobic digestion process for food waste and recalcitrant residues: fundamentals, challenges, and considerations. Energy Sci Eng. 2019;7:2250–64.
Alghashm S, Qian S, Hua Y, Wu J, Zhang H, Chen W, Shen G. Properties of biochar from anaerobically digested food waste and its potential use in phosphorus recovery and soil amendment. Sustainability. 2018;10:4692.
Ahmad M, Mehmood M, Al-Ayed O, Ye G, Luo H, Ibrahim M, Rashid U, Nehdi I, Qadir G. Kinetic analyses and pyrolytic behavior of para grass (Urochloa mutica) for its bioenergy potential. Bioresour Technol. 2017;224:708–13.
Mishra R, Mohanty K. Pyrolysis kinetics and thermal behavior of waste sawdust biomass using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2018;251:63–74.
Guo K, Wells S, Han F, Arslan Z, Sun H, Zhang J. Trace elements and heavy metals in Asian rice-derived food products. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017;228:76.
Kim L, Traistaru G, Covaliu C, Pascu L, Cristea I, Serbanescu A, Cernica G. Characterization of different types of biomass wastes using thermogravimetric and ICP-MS analyses. Rev Chim. 2019;70(12):4584–90.
Jo J, Kim S, Shim J, Lee Y, Yoo Y. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of food wastes. Energies. 2017;10:1191.
Ma Z, Chen D, Gu J, Bao B, Zhang Q. Determination of pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of palm kernel shell using TGA-FTIR and model-free integral methods. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;89:251–9.
Monlau F, Francavilla M, Sambusiti C, Antoniou N, Solhy A, Libutti A, Zabaniotou A, Barakat A, Monteleone M. Toward a functional integration of anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis for a sustainable resource management, Comparison between solid-digestate and its derived pyrochar as soil amendment. Appl Energy. 2016;169:652–62.
Sfakiotakis S, Vamvuka D. Study of co-pyrolysis of olive kernel with waste biomass using TGA/DTG/MS. Thermochim Acta. 2018;670:44–54.
Genieva S, Gonsalvesh L, Georgieva V, Tavlieva M, Vlaev L. Kinetic analysis and pyrolysis mechanism of raw and impregnated almond shells. Thermochim Acta. 2021;698:178877.
Wang B, Xu F, Zong P, Zhang J, Tian Y, Qiao Y. Effects of heating rate on fast pyrolysis behavior and product distribution of Jerusalem artichoke stalk by using TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS. Renew Energy. 2019;132:486–96.
Ekawa B, Stanford V, Vyazovkin S. Isoconversional kinetics of vaporization of nanoconfined liquids. J Mol Liq. 2021;327:114824.
Ma Z, Wang J, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Zhao C, Yu Y, Wang S. Comparison of the thermal degradation behaviors and kinetics of palm oil waste under nitrogen and air atmosphere in TGA-FTIR with a complementary use of model-free and model-fitting approaches. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2018;134:12–24.
Kumar M, Srivastava N, Upadhyay S, Mishra P. Thermal degradation of dry kitchen waste: kinetics and pyrolysis products. Biomass Convers Biorefin. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01309-z.
Vuppaladadiyam A, Zhao M, Memon M, Soomro A, Wei W. Solid waste as a renewable source of energy: a comparative study on thermal and kinetic behavior of three organic solid wastes. Energy Fuel. 2019;33:4378–88.
Han Z, Zhuang D, Yan H, Zhao H, Sun B, Li D, Sun Y, Hu W, Xuan Q, Chen J, Xiu Y. Thermogravimetric and kinetic analysis of thermal decomposition characteristics of microbial calcites induced by cyanobacteria Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127:1371–9.
Vikraman V, Boopathi G, Kumar D, Mythili R, Subramanian P. Non-isothermal pyrolytic kinetics of milk dust powder using thermogravimetric analysis. Renew Energy. 2021;180:838–49.
Biller P, Ross A. Pyrolysis GC–MS as a novel analysis technique to determine the biochemical composition of microalgae. Algal Res. 2014;6:91–7.
Chiavari G, Galletti G. Pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry of amino acids. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 1992;24:123–37.
Tsuge S, Matsubara H. High-resolution pyrolysis-gas chromatography of proteins and related materials. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 1985;8:49–64.
Yu Z, Dai M, Huang M, Fang S, Xu J, Lin Y, Ma X. Catalytic characteristics of the fast pyrolysis of microalgae over oil shale: analytical Py-GC/MS study. Renew Energy. 2018;125:465–71.
Paine J, Pithawalla Y, Naworal J. Carbohydrate pyrolysis mechanisms from isotopic labelling. Part 4. The pyrolysis of D-glucose: the formation of furans. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2008;83:37–63.
Syarif H, Bakar M, Yang Y, Neeranuch P. Characterisation and Py-GC/MS analysis of Imperata Cylindrica as potential biomass for bio-oil production in Brunei Darussalam. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2018;134:510–9.
Jeon M, Jeon J, Suh D, Park S, Sa Y, Joo S, Parka Y. Catalytic pyrolysis of biomass components over mesoporous catalysts using Py-GC/MS. Catal Today. 2013;204:170–8.
Binder J, Raines R. Simple chemical transformation of lignocellulosic biomass into furans for fuels and chemicals. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:1979–85.
Lv G, Wu S. Analytical pyrolysis studies of corn stalk and its three main components by TG-MS and Py-GC/MS. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2012;97:11–8.
Park H, Park K, Jeon J, Kim J, Ryoo R, Jeong K, Park S, Park Y. Production of phenolics and aromatics by pyrolysis of miscanthus. Fuel. 2012;97:379–84.
Hao J, Zong P, Tian Y, Zhang J, Qiao Y. Distribution and chemical structure characteristic of the fast thermal-cracking products of Buton oil sand bitumen by Py-GC/TOF-MS and a fluidized bed reactor. Energy Convers Manag. 2019;183:485–99.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China(42072136, 42106144); and Shandong Key Research and Development Program Major Science and technology innovation engineering projects (2019JZZY020808), and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019MD027, ZR2020QD089, ZR2020MC041, ZR2021QE125).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HZ, HZ and HY contributed to conceptualization, investigation, methodology, data curation, validation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, writing—original draft and writing—review and editing. MS, WC and BL contributed to data curation, investigation and software. CD, HZ and JJ contributed to resources. SQ and ZH contributed to supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there are no financial or non-financial interests that are directly or indirectly related to the work submitted for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Zhang, H., Sun, M. et al. Evaluating the bioenergy potential of kitchen wastes fermentation residues through pyrolysis kinetics, thermodynamics and Py-GC/MS analysis technique. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 995–1010 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11711-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11711-y