Abstract
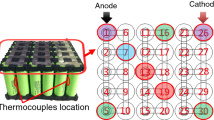
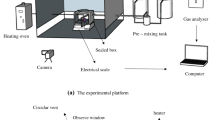
The lithium-ion battery (LIB) pack for an electric vehicle immersed in seawater is easy to induce short circuit and other thermal runaway (TR) safety accidents. In order to better understand the TR characteristics of LIB pack after immersion, and to effectively prevent safety accidents, a series of experiments on LIBs immersed in seawater have been conducted. In this study, LIB packs under 100% charging state were immersed in 3.5 mass% NaCl solution (used as seawater) for different immersion times (0–12 h). The maximum temperature, surface electric fire temperature, total mass loss, heat release rate (HRR) and total heat release (THR) were measured to evaluate the fire hazard of LIBs. The experimental results showed that the ignition temperature decreased with the increase of immersion times. However, the maximum temperature increased with increase in immersion times. The total mass loss firstly decreased and then stabilized with the increase of immersion times. The loss of electrolyte and combustible materials was the largest when immersion times reaches 3 h. Both HRR peak value and THR reached the maximum value when immersion times reaches 3 h. The spread rate of thermal runaway remains a stable value when the immersion time is larger than 3 h.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B:
-
Battery
- \(F_{{{\text{rb}}}}\) :
-
Rebounding force, g
- LIBS :
-
Lithium-ion batteries
- HRR:
-
Heat release rate, kW
- THR:
-
Total heat release, kJ
- SOC:
-
Stage of charge
- \(t_{{{\text{im}}}}\) :
-
Immersing time, s
- \(T_{\max }\) :
-
The maximum temperature, °C
- \(T_{{{\text{ig}}}}\) :
-
The injection temperature, °C
- TR:
-
Thermal runaway
- TML:
-
Total mass loss, g
- \(T_{{{\text{ave}}}}\) :
-
The average time of triggering TR
References
Chen M, Ouyang DX, Liu J, Wang J. Investigation on thermal and fire propagation behaviors of multiple lithium-ion batteries within the package. Appl Therm Eng. 2019;157:113750.
Wu C, Zhu C, Ge Y, Zhao Y. A review on fault mechanism and diagnosis approach for Li-Ion batteries. J Nanomater. 2015;2015:1–9.
Xu C, Liu J, He Y, Yuen R, Wang J. Preliminary study on the mechanism of lithium ion battery pack under water immersion. ECS Trans. 2017;77(11):209–16.
Zhang L, Zhao C, Liu Y, Xu J, Sun J, Wang Q. Electrochemical performance and thermal stability of lithium ion batteries after immersion. Corros Sci. 2021;184:109384.
Blanco S. Report, Fisker loses over 300 Karmas in sandy floods at port Newark; 2012.
Chen M, Zhou D, Chen X, Zhang W, Liu J, Yuen R, Wang J. Investigation on the thermal hazards of 18650 lithium ion batteries by fire calorimeter. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;122(2):755–63.
Chen M, Liu J, He Y, Yuen R, Wang J. Study of the fire hazards of lithium-ion batteries at different pressures. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;125:1061–74.
Finegan DP, Tjaden B, Michiel M, Heenan T, Jervis R, Michiel MD, Rack A, Hinds G, Dan JL, Brett D, Shearing PR. Tracking internal temperature and structural dynamics during nail penetration of lithium-ion cells. J Electrochem Soc. 2017;164(13):3285–91
Gao T, Wang Z, Chen S, Guo L. Hazardous characteristics of charge and discharge of lithium-ion batteries under adiabatic environment and hot environment. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;141:419–31.
Leising RA, Palazzo MJ, Takeuchi ES, Takeuchi KJ. Abuse testing of lithium-ion batteries: characterization of the overcharge reaction of LiCoO2/graphite cells. J Electrochem Soc. 2001;148(8):838–44.
Larsson F, Bertilsson S, Furlani M, Albinsson I, Mellander B-E. Gas explosions and thermal runaways during external heating abuse of commercial lithium-ion graphite-LiCoO2 cells at different levels of ageing. J Power Sour. 2018;373:220–31.
Mao B, Chen H, Cui Z, Wu T, Wang Q. Failure mechanism of the lithium ion battery during nail penetration. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;122:1103–15.
Zhu X, Wang H, Wang X, Gao Y, Allu S, Cakmak E, Wang Z. Internal short circuit and failure mechanisms of lithium-ion pouch cells under mechanical indentation abuse conditions: an experimental study. J Power Sources. 2020;455
Bugryniec PJ, Davidson JN, Cumming DJ, Brown SF. Pursuing safer batteries: thermal abuse of LiFePO4 cells. J Power Sources. 2019;414:557–68.
Yuan C, Wang Q, Wang Y, Zhao Y. Inhibition effect of different interstitial materials on thermal runaway propagation in the cylindrical lithium-ion battery module. Appl Therm Eng. 2019;153:39–50.
Ping P, Wang Q, Huang P, Li K, Sun J, Kong D, Chen C. Study of the fire behavior of high-energy lithium-ion batteries with full-scale burning test. J Power Sour. 2015;285:80–9.
Wang T, Tseng KJ, Zhao J, Wei Z. Thermal investigation of lithium-ion battery module with different cell arrangement structures and forced air-cooling strategies. Appl Energy. 2014;134:229–38.
Feng X, Sun J, Ouyang M, Wang F, He X, Lu L, Peng H. Characterization of penetration induced thermal runaway propagation process within a large format lithium ion battery module. J Power Sour. 2015;275:261–73.
Saw LH, Ye Y, Tay AAO, Chong WT, Kuan SH, Yew MC. Computational fluid dynamic and thermal analysis of lithium-ion battery pack with air cooling. Appl Energy. 2016;177:783–92.
Yan J, Li K, Chen H, Wang Q, Sun J. Experimental study on the application of phase change material in the dynamic cycling of battery pack system. Energy Convers Manag. 2016;128:12–9.
Cheng X, Li T, Ruan X, Wang Z. Thermal runaway characteristics of a large format lithium-ion battery module. Energies. 2019;12(16):3099.
Liu Y, Duan Q, Xu J, Chen H, Lu W, Wang Q. Experimental study on the efficiency of dodecafluoro-2-methylpentan-3-one on suppressing lithium-ion battery fires. RSC Adv. 2018;8(73):42223–32.
Worwood D, Marco J, Kellner Q, Hosseinzadeh E, McGlen R, Mullen D, Lynn K, Greenwood D. Experimental analysis of a novel cooling material for large format automotive lithium-ion cells. Energies 2019;12(7):1251
Zhong G, Li H, Wang C, Xu K, Wang Q. Experimental analysis of thermal runaway propagation risk within 18650 lithium-ion battery modules. J Electrochem Soc. 2018;165(9):1925–34.
Ouyang D, Liu J, Chen M, Weng J, Wang J. An experimental study on the thermal failure propagation in lithium-ion battery pack. J Electrochem Soc. 2018;165(10):2184–93.
Min H, Wang B, Sun W, Zhang Z, Yu Y, Zhang Y. Research on the combined control strategy of low temperature charging and heating of lithium-ion power battery based on adaptive fuzzy control. Energies. 2020;13(7):1584.
Chen M, Liu J, Ouyang D, Wang J. Experimental investigation on the effect of ambient pressure on thermal runaway and fire behaviors of lithium-ion batteries. Int J Energy Res. 2019;43(9):4898–911.
Tao C, Ye Q, Wang C, Qian Y, Wang C, Zhou T, Tang Z. An experimental investigation on the burning behaviors of lithium ion batteries after different immersion times. J Clean Prod. 2020;242:118539
Ouyang D, He Y, Chen M, Liu J, Wang J. Experimental study on the thermal behaviors of lithium-ion batteries under discharge and overcharge conditions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;132(1):65–75.
Tao C, Li G, Zhao J, Chen G, Wang Z, Qian Y, Cheng X, Liu X. The investigation of thermal runaway propagation of lithium-ion batteries under different vertical distances. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;142(4):1523–32.
Safizadeh F, Sorour N, Ghali E, Houlachi G. Corrosion behavior of Fe-Mo and Fe-Mo-P cathodic coatings in the simulated electrolyte for sodium chlorate production. Electrochim Acta. 2018;269:340–9.
Wang H, Yang Y, Liang Y, Robinson JT, Li Y, Jackson A, Cui L, Dai H. Graphene-wrapped sulfur particles as a rechargeable lithium-sulfur battery cathode material with high capacity and cycling stability. Nano Lett. 2011;11(7):2644–7.
Chen M, He Y, De Zhou C, Richard Y, Wang J. Experimental study on the combustion characteristics of primary lithium batteries fire. Fire Technol. 2014;52(2):365–85.
Chen M, Dongxu O, Cao S, Liu J, Wang Z, Wang J. Effects of heat treatment and SOC on fire behaviors of lithium-ion batteries pack. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;136(6):2429–37.
Zhang J, Yang J, Liu Z, Zheng B. Interaction mechanisms between lithium polysulfides/sulfide and small organic molecules. ACS Omega. 2021;6(7):4995–5000.
Babrauskas V, Peacock RD. Heat release rate: the single most important variable in fire hazard. Fire Saf J. 1992;18:255–72.
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1933131), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. PA2020GDKC0017, PA2021KCPY0033 and JZ2021HGTA0151).
Funding
The National Natural Science Foundation of, U1933131, Changfa Tao, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, PA2020GDKC0017, Changfa Tao, Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, PA2021KCPY0033, Changfa Tao, JZ2021HGTA0151, Yu Zhang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, C., Chen, Z., Ye, Q. et al. The study of thermal runaway characteristics of multiple lithium batteries under different immersion times. J Therm Anal Calorim 147, 11457–11466 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11324-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11324-5