Abstract
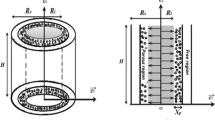
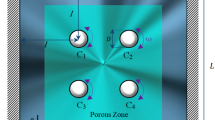
Convective heat transfer in a porous cavity conjugated with an active rotating cylinder is investigated in this paper. Copper–water nanofluid fills the porous cavity. The rotating active cylinder is positioned in such a way conveying heat from the cavity and discharges it outside. The vertical walls of the cavity are thermally insulated while the bottom wall is moving to the right and kept at a constant high temperature. The governing equations are facilitated with the ability to study the tilt of the cylinder-cavity assembly. The effects of Richardson number, Darcy number, inclination angle, conductivity ratio, rotational speed, and nanofluid volume fraction are studied at a constant Rayleigh number of 105. Galerkin finite element method of weak formulation is used to solve the dimensionless governing equation with appropriate boundary conditions. Darcy–Brinkman–Forchheimer model is adopted to govern the flow inside porous medium. Results show that the rotation of the cylinder can enlarge the average Nusselt number more than 223%, while ten times increase of thermal conductivity ratio amplifies Nusselt number by 136%. It is also found that the Richardson number plays an adverse role on the average Nusselt number. Physical explanations and thorough validations are given in the paper.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C p :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure (J kg−1 K−1)
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration (m s−2)
- h :
-
Heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- L :
-
Length & height of the cavity (m)
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- P :
-
Dimensionless pressure
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number (νf/αf)
- q :
-
Heat transfer rate (W m−2)
- R :
-
Radius of the solid cylinder
- Ra:
-
Rayleigh number \((g\beta _{{{\text{bf}}}} L^{3} (T_{{\text{h}}} - T_{\infty } )/\nu _{{{\text{bf}}}} \alpha _{{{\text{bf}}}} )\)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- U :
-
Dimensionless velocity component in x-direction
- u :
-
Velocity component in x-direction (m s−1)
- V :
-
Dimensionless velocity component in y-direction
- v :
-
Velocity component in y-direction (m s−1)
- X, Y :
-
Dimensionless coordinate
- x, y :
-
Cartesian coordinates (m)
- x 0, y 0 :
-
Cartesian coordinate of the rotating cylinder
- X 0,Y 0 :
-
Dimensionless coordinate of the rotating cylinder
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity (m2 s−1)
- β :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient (K−1)
- θ :
-
Dimensionless temperature (T − T∞/Th − T∞)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg s m−1)
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity (μ /ρ)(Pa s−1)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- ϕ :
-
Nanoparticle volume fraction (%)
- ψ :
-
Dimensional stream function (m2 s−1)
- Ψ :
-
Dimensionless stream function
- ω :
-
Angular velocity (rad s−1)
- Ω :
-
Dimensionless angular velocity
- ave:
-
Average
- bf:
-
Base fluid (pure)
- c:
-
Cold
- h:
-
Hot
- loc:
-
Local
- na:
-
Nanofluid
- so:
-
Conductive solid cylinder
- sp:
-
Solid particle
- Cond.:
-
Conduction
- Conv.:
-
Convection
References
Lai FC, Kulacki FA, Prasad V. Mixed convection in saturated porous media. Convective heat and mass transfer in porous media. Dordrecht: Springer; 1991. p. 225–287.
Papanicolaou E, Yogesh J. Mixed convection from simulated electronic components at varying relative positions in a cavity. J Heat Transf. 1994;116:960–70.
Wooding RA. Rayleigh instability of a thermal boundary layer in flow through a porous medium. J Fluid Mech. 1960;9(2):183–92.
Ghaffarpasand O, Dariush F. Numerical analysis of MHD mixed convection flow in a parallelogramic porous enclosure filled with nanofluid and in the presence of magnetic field induction. Scientia Iranica Trans F. 2018;25(3):1789–807.
Rajarathinam M, Nithyadevi N, Chamkha AJ. Heat transfer enhancement of mixed convection in an inclined porous cavity using Cu–water nanofluid. Adv Powder Technol. 2018;29(3):590–605.
Khanafer K, Vafai K. Double-diffusive mixed convection in a lid-driven enclosure filled with a fluid-saturated porous medium. Numer Heat Transf A. 2002;42(5):465–86.
Muthukumar S, Sureshkumar S, Chamkha AJ, Muthtamilselvan M, Perm E. Combined MHD convection and thermal radiation of nanofluid in a lid-driven porous enclosure with irregular thermal source on vertical sidewalls. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138(1):583–96.
Muthtamilselvan M, Kandaswamy P, Lee J. Hydromagnetic mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity filled with a fluid-saturated porous medium. Int J Appl Math Mech. 2009;5(7):28–44.
Bondarenko DS, Sheremet MA, Oztop HF. Mixed convection heat transfer of a nanofluid in a lid-driven enclosure with two adherent porous blocks. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135(2):1095–105.
Oztop HF, Varol A. Combined convection in inclined porous lid-driven enclosures with sinusoidal thermal boundary condition on one wall. Prog Comput Fluid Dyn Int J. 2009;9(2):127–31.
Sheikholeslami M. Influence of magnetic field on Al2O3-H2O nanofluid forced convection heat transfer in a porous lid driven cavity with hot sphere obstacle by means of LBM. J Mol Liq. 2018;26:472–88.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA, Abbsi FM. Nanofluid flow and forced convection heat transfer due to Lorentz forces in a porous lid driven cubic enclosure with hot obstacle. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2018;338:491–505.
Hatami M, Zhou J, Gang J, Song D, Jing D. Optimization of a lid-driven T-shaped porous cavity to improve the nanofluids mixed convection heat transfer. J Mol Liq. 2017;231:620–31.
Hussein AK, Hamzah HK, Ali FH, Kolsi L. Mixed convection in a trapezoidal enclosure filled with two layers of nanofluid and porous media with a rotating circular cylinder and a sinusoidal bottom wall. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08963-6.
Billah MM, Rahman MM, Sharif UM, Rahim NA, Saidur R, Hassanuzzaman M. Numerical analysis of fluid flow due to mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity having a heated circular hollow cylinder. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2011;38(8):1093–103.
Billah MM, Rahman MM, Saidur R, Hassanuzzaman M. Simulation of MHD mixed convection heat transfer enhancement in a double lid-driven obstructed enclosure. Int J Mech Mater Eng. 2011;6(1):18–30.
Rabbi KM, Saha S, Mojumder S, Rahman MM, Saidur R, Ibrahim TA. Numerical investigation of pure mixed convection in a ferrofluid-filled lid-driven cavity for different heater configurations. Alexandria Eng J. 2016;55(1):127–39.
Mohammad RH, Mohammad HE, Mohammad HH, Mohammad A, Seyed SM. Mixed convection heat transfer in a double lid-driven inclined square enclosure subjected to Cu–water nanofluid with particle diameter of 90 nm. Heat Transf Res. 2014;45:75–95.
Alsabery AI, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ, Hashim I. Effects of two-phase nanofluid model on MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity in the presence of conductive inner block and corner heater. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135(1):729–50.
Perumal DA, Anoop KD. Simulation of incompressible flows in two-sided lid-driven square cavities: part I-FDM. CFD Lett. 2010;2(1):13–24.
Perumal DA, Anoop KD. Simulation of incompressible flows in two-sided lid-driven square cavities. Part II-LBM. CFD Lett. 2010;2(1):25–38.
Mahmoodi M. Mixed convection inside nanofluid filled rectangular enclosures with moving bottom wall. Therm Sci. 2011;15(3):889–903.
Nasrin R. Mixed magnetoconvection in a lid-driven cavity with a sinusoidal wavy wall and a central heat conducting body. J Naval Architect Mar Eng. 2011;8(1):13–24.
Alam MS, Alim MA, Mollah MS. Mixed magneto convection in a lid driven square enclosure with a sinusoidal vertical wall and Joule heating. Procedia Eng. 2017;194:463–70.
Rahmati AR, Roknabadi AR, Abbaszadeh M. Numerical simulation of mixed convection heat transfer of nanofluid in a double lid-driven cavity using lattice Boltzmann method. Alexandria Eng J. 2016;55(4):3101–14.
Albensoeder S, Kuhlmann HC, Rath HJ. Multiplicity of steady two-dimensional flows in two-sided lid-driven cavities. Theoret Comput Fluid Dyn. 2001;14(4):223–41.
Mahapatra SK, Nanda P, Sarkar A. Interaction of mixed convection in two-sided lid driven differentially heated square enclosure with radiation in presence of participating medium. Heat Mass Transf. 2006;42(8):739–57.
Oztop HF, Ihsan D. Mixed convection in two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2004;47(8–9):1761–9.
Oztop HF, Zhao Z, Yu B. Fluid flow due to combined convection in lid-driven enclosure having a circular body. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2009;30(5):886–901.
Wahba ES, EMIRATES UA. Bifurcation phenomena for two-sided non-facing lid driven cavity flow. In: WSEAS International Conference on Engineering Mechanics Structures, Engineering Geology (EMESEG'08), Heraklion, Crete Island, Greece 2008 Jul 22 (pp. 111–116).
Wahba EM. Multiplicity of states for two-sided and four-sided lid driven cavity flows. Comput Fluids. 2007;38(2):247–53.
Al-Amiri A, Kanafar K, Bull J, Pop I. Effect of sinusoidal wavy bottom surface on mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2007;50(9–10):1771–800.
Pal SK, Bhattacharyya S, Pop I. Effect of solid-to-fluid conductivity ratio on mixed convection and entropy generation of a nanofluid in a lid-driven enclosure with a thick wavy wall. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;127:885–900.
Luo WJ, Yang RJ. Multiple fluid flow and heat transfer solutions in a two-sided lid-driven cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2007;50(11–12):2394–405.
Noor DZ, Kanna PR, Ming JC. Flow and heat transfer in a driven square cavity with double-sided oscillating lids in anti-phase. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2009;52(13–14):3009–233.
Karim A, Billah MM, Newton MT, Rahman MM. Influence of the periodicity of sinusoidal boundary condition on the unsteady mixed convection within a square enclosure using an Ag–water nanofluid. Energies. 2017;10(12):2167.
Al-Salem K, Oztop HF, Pop I, Varol T. Effects of moving lid direction on MHD mixed convection in a linearly heated cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55(4):1103–12.
Ogut EB. Magnetohydrodynamic mixed convection in a lid-driven rectangular enclosure partially heated at the bottom and cooled at the top. Therm Sci. 2017;21(2):863–74.
Ismael MA. Numerical solution of mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with arc-shaped moving wall. Eng Comput. 2017;34(3):869–91.
Fu WS, Cheng CS, Shieh WJ. Enhancement of natural convection heat transfer of an enclosure by a rotating circular cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 1994;37(13):1885–977.
Nguyen HD, Seungho P, Douglass RW. Unsteady mixed convection about a rotating circular cylinder with small fluctuations in the free-stream velocity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 1996;39(3):511–25.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Numerical study of MHD mixed convection in a nanofluid filled lid driven square enclosure with a rotating cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;78:741–54.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. MHD mixed convection of nanofluid filled partially heated triangular enclosure with a rotating adiabatic cylinder. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2014;45(5):2150–62.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Effect of a rotating cylinder in forced convection of ferrofluid over a backward facing step. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;71:142–8.
Costa VAF, Raimundo AM. Steady mixed convection in a differentially heated square enclosure with an active rotating circular cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2010;53(5–6):1208–19.
Ali FH. Study of mixed convection in a square enclosure with a rotating circular cylinder at different vertical location. Iraqi J Mech Mater Eng. 2011;11(2):242–61.
Fasiel M, Duraid FM, Farooq HA. Numerical Investigation of mixed convection by non-concentric positions of rotating circular cylinder in square enclosure. Al-Qadisiya J Eng Sci. 2018;11(1):55–79.
Liao CC, Lin CA. Mixed convection of a heated rotating cylinder in a square enclosure. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;72:9–22.
Qi C, Liang L, Rao Z. Study on the flow and heat transfer of liquid metal based nanofluid with different nanoparticle radiuses using two-phase lattice Boltzmann method. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;94:316–26.
Qi C, Yang L, Wang G. Numerical study on convective heat transfer enhancement in horizontal rectangle enclosures filled with Ag-Ga nanofluid. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2017;12(1):326.
Qi C, Wang G, Yang L, Wan Y, Rao Z. Two-phase lattice Boltzmann simulation of the effects of base fluid and nanoparticle size on natural convection heat transfer of nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;105:664–72.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, Estellé P, Ahmadi G, Kleinstreuer C, Marshall JS, Siavashi M, Taylor RA, Niazmand H, Wongwises S, Hayat T, Kolanjiyil A, Kasaeian A, Pop I. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows-part I: fundamentals and theory. Phys Rep. 2019;790:1–48.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, Estellé P, Ahmadi G, Kleinstreuer C, Marshall JS, Taylor RA, Abu-Nada E, Rashidi S, Niazmand H, Wongwises S, Hayat H, Kasaeian A, Pop I. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows—part II: applications. Phys Rep. 2019;791:1–59.
Brinkman HC. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J Chem Phys. 1952;20(4):571–571.
Garnett JM. Colours in metal glasses and in metallic films. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser A. 1904;203:385–420.
Ergun S. Fluid flow through packed columns. Chem Eng Prog. 1952;48:89–94.
Bergman TL, Incropera FP. Introduction to Heat Transfer. 6th ed. New York, NY: Wiley; 2011.
Reddy JN. An introduction to the finite element method. New York: McGraw. Hill; 1993.
Dogonchi AS, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ, Ganji DD. Numerical analysis of natural convection of Cu–water nanofluid filling triangular cavity with semicircular bottom wall. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135(6):3485–97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jabbar, M.Y., Hamzah, H.K., Ali, F.H. et al. Thermal analysis of nanofluid saturated in inclined porous cavity cooled by rotating active cylinder subjected to convective condition. J Therm Anal Calorim 144, 1299–1323 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09668-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09668-x