Abstract
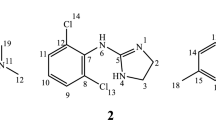
Aripiprazole (ARP), an innovative atypical antipsychotic drug, exhibits very low aqueous solubility, affecting its dissolution and absorption and high lipophilicity. Its complexation with cyclodextrins (CDs) was designed to improve drug solubility and consequently its bioavailability. The inclusion complexes of aripiprazole with two β-cyclodextrin derivative, namely random methyl-β-cyclodextrin (RAMEB) and heptakis(2,3,6-tri-O-methyl)-β-cyclodextrin, were obtained and investigated both in solution and in solid state. The kneading method was used to prepare the inclusion complexes, and they were characterized with different analytical techniques, including thermal analysis, powder X-ray diffractometry, universal attenuated total reflectance Fourier-transform IR spectroscopy and UV spectroscopy. The stoichiometry of both APR/CDs inclusion complexes was found as 1:2 by employing continuous variation method. Benesi–Hildebrand equation was used for the apparent constant stability determination. Structural studies of the inclusion complexes were carried out using molecular modeling techniques in order to explain the complexation mechanism. The results of the studies demonstrate that the physicochemical properties of the kneaded products are different from ARP, testifying the inclusion complexes formation between aripiprazole and CDs when the kneading method is used. The solubility of the drug substance was improved upon complexation with CDs; higher increase in ARP solubility was noticed in the presence of RAMEB.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Sciascio G, Riva MA. Aripiprazole: from pharmacological profile to clinical use. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:2635–47.
Casey AB, Canal CE. Classics in chemical neuroscience: aripiprazole. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017;8(6):1135–46.
Abdelbary AA, Elshafeey AH, El-Nabarawi M, Elassasy A, Li X, Jasti B. Comparative in vivo evaluation of aripiprazole coprecipitate, nanoparticles and marketed tablets in healthy human volunteers and in vitro-in vivo correlation. Curr Trends Biotechnol Pharm. 2011;5(4):1397–409.
Silki, Sinha VR. Enhancement of in vivo efficacy and oral bioavailability of aripiprazole with solid lipid nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018;19(3):1264–73.
Brittain HG. Aripiprazole: polymorphs and solvatomorphs. In: Brittain HG, editor. Profile of drug substances, excipients and related metodology, vol. 37. Amsterdam: Esevier; 2012. p. 1–29.
Saifee M, Inamdar N, Dhamecha D, Rathi A. Drug polymorphism: a review. Int J Health Res. 2009;2(4):291–306.
Censi R, Di Martino P. Polymorph impact on the bioavailability and stability of poorly soluble drugs. Molecules. 2015;20:18759–76.
Loftsson T, Jarho P, Masson M, Jarvinen T. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2005;2:335–51.
D’Aria F, Serri C, Niccoli M, Mayol L, Quagliariello V, Iaffaioli RV, Biondi M, Giancola C. Host–guest inclusion complex of quercetin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;130:451–6.
Usacheva T, Kabirov D, Beregova D, Gamov G, Sharnin V, Biondi M, Mayol L, D’Aria F, Giancola C. Thermodynamics of complex formation between hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and quercetin in water–ethanol solvents at T = 298.15 K. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138(1):417–24.
Pires FQ, Pinho LA, Freire DO, Silva ICR, Sa-Barreto LL, Cardozo-Filho L, Gratieri T, Gelfuzo GM, Cunha-Filho M. Thermal analysis used to guide the production of thymol and Lippia origanoides essential oil inclusion complexes with cyclodextrin. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137(2):543–53.
Júnior FJLR, da Silva KMA, Brandão DO, Junior JVC, dos Santos JAB, de Andrade FHD, de Araujo Batista RS, Lins TB, de Sousa DP, Dantas Medeiros AC, Conceiçã MM, Macȇdo RO, de Souza FS. Investigation of the thermal behavior of inclusion complexes with antifungal activity. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;133(1):641–8.
Garcia A, Leonardi D, Salazar MO, Lamas MC. Modified β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex to improve the physicochemical properties of albendazole: complete in vitro evaluation and characterization. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88234. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088234.
Sbârcea L, Ledeţi A, Udrescu L, Văruţ RM, Barvinschi P, Vlase G, Ledeţi I. Betulonic acid-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138:2787–97.
Sbârcea L, Udrescu L, Ledeţi I, Szabadai Z, Fuliaş A, Sbârcea C. β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes of lisinopril and zofenopril. Physicochemical characterization and compatibility study of lisnopril-β-cyclodextrin with lactose. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123:2377–90.
Sbârcea L, Udrescu L, Drăgan L, Trandafirescu C, Szabadai Z, Bojiţă M. Fosinopril–cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: phase solubility and physicochemical analysis. Pharmazie. 2011;66:584–9.
Cȋrcioban D, Ledeţi A, Vlase G, Coricovac D, Moaca A, Farcaş C, Vlase T, Ledeţi I, Dehelean C. Guest–host interactions and complex formation for artemisinin with cyclodextrins: instrumental analysis and evaluation of biological activity. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;134:1375–84.
Brusnikina M, Silyukov O, Chislov M, Volkova T, Proshin A, Mazur A, Tolstoy P, Terekhova I. Effect of cyclodextrin complexation on solubility of novel anti-Alzheimer 1,2,4-thiadiazole derivative. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;130:443–50.
Sbârcea L, Udrescu L, Drăgan L, Trandafirescu C, Sasca V, Barvinschi P, Bojiţă M. Characterization of fosinopril natrium-hydroxypropil-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Rev Chim Buchar. 2011;62(3):349–51.
Ikeda H, Fukushige Y, Matsubara T, Inenaga M, Kawahara M, Yukawa M, Fujisawa M, Yukawa E, Aki H. Improving water solubility of nateglinide by complexation of β-cyclodextrin. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123:1847–50.
Sbârcea L, Ledeţi I, Drăgan L, Kurunczi L, Fuliaş A, Udrescu L. Fosinopril sodium–Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex: thermal decomposition kinetics and compatibility studies. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;120:981–90.
Stella VJ, He Q. Cyclodextrins. Toxicol Pathol. 2008;36:30–42.
Laza-Knoerr AL, Gref R, Couvreur P. Cyclodextrin for drug delivery. J Drug Target. 2010;18:645–56.
Brusnikina M, Silyukov O, Chislov M, Volkova T, Proshin A, Terekhova I. New water-soluble dosage forms of 1,2,4-thiadiazole derivative on the basis of inclusion complexes with cyclodextrins. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127:1815–24.
Szente L, Szejtli. Highly soluble cyclodextrin derivatives: chemistry, properties, and trends in development. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1999;36:17–28.
Mihajlovic T, Kachrimanis K, Graovac A, Djuric Z, Ibric S. Improvement of aripiprazole solubility by complexation with 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin using spray drying technique. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012;3(2):623–31.
Badr-Eldin SM, Ahmed TA, Ismail HR. Aripiprazole-cyclodextrin binary systems for dissolution enhancement: effect of preparation technique, cyclodextrin type and molar ratio. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2013;16:1223–31.
Brewster ME, Loftsson T. Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:645–66.
Garcia A, Leonardi D, Vasconi MD, Hinrichsen LI, Lamas MC. Characterization of albendazole-randomly methylated-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex and in vivo evaluation of its antihelmitic activity in a murine model of trichinellosis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(11):e113296. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113296.
Chislov M, Silyukov O, Kumeev R, Proshin A, Perlovich G, Terekhova I. Complex formation of cyclodextrins with some pharmacologically active 1,2,4-thiadiazole derivatives. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127:1797–805.
Benesi HA, Hildebrand JH. A spectrophotometric investigation of the interaction of iodine with aromatic hydrocarbons. J Am Chem Soc. 1949;71(8):2703–7.
Srinivasan K, Stalin T, Sivakumar K. Spectral and electrochemical study of host–guest inclusion complex between 2,4-dinitrophenol and -cyclodextrin. Spectrochimica Acta Part A. 2012;94:89–100.
Salústio J, Feio G, Figueirinhas JL, Pinto JF, Cabral Marques HM. The influence of the preparation methods on the inclusion of model drugs in a ß-cyclodextrin cavity. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;71:377–86.
Protein Data Bank. http://www.pdb.org/pdb/home/home.do. Accessed 15 Sept 2019.
DeLano, W. L. PyMOL. DeLano Scientific, San Carlos, CA, 700, 2002.
Job P. Formation and stability of inorganic complexes in solution. Ann Chim. 1928;9:113–203.
Chalumot G, Yao C, Pino V, Anderson JL. Determiming the stoichiometry and binding constants of inclusion complexes formed between aromatic compounds and β-cyclodextrin by solid-phase microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2009;1216:5242–8.
Fousteris E, Tarantili PA, Karavas E, Bikiaris D. Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone)–poloxamer-188 solid dispersions prepared by hot melt extrusion. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113(3):1037–47.
Łaszcz M, Witkowska A. Studies of phase transitions in the aripiprazole solid dosage form. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016;117:298–303.
Doile MM, Fortunato KA, Schműcker IC, Schucko SK, Silva MAS, Rodrigues PO. Physicochemical properties and dissolution studies of dexamethasone acetate-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes produced by different methods. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2008;9:314–32.
Lavorgna M, Iacovino R, Russo C, Di Donato C, Piscitelli C, Isidori M. A new approach for improving the antibacterial and tumor cytotoxic activities of pipemidic acid by including it in trimethyl-β-CYCLODEXTRIN. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(2):416.
Braun DE, Gelbrich T, Kahlenberg V, Tessadri R, Wieser J, Griesser UJ. Conformational polymorphism in aripiprazole: preparation, stability and structure of five modifications. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98:2010–26.
Lin-Vien D, Colthup NB, Fateley WG, Grasselli JG. The handbook of infrared and raman characteristic frequencies of organic molecules. New York: Academic Press; 1991.
Febry A, Lestari LEDM, Indrayanto G. Aripiprazole. Profile of drug substances, excipients and related methodology. 2013;38:35–85.
Mennini N, Maestrelli F, Cirri M, Mura P. Analysis of physicochemical properties of ternary systems of oxaprozin with randomly methylated-ß-cyclodextrin and l-arginine aimed to improve the drug solubility. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016;129:350–8.
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comp Chem. 1998;19:1639–62.
Baka E, Comer JEA, Takács-Novák K. Study of equilibrium solubility measurement by saturation shake-flask method using hydrochlorothiazide as model compound. J Pharm Biomed. 2008;46:335–41.
Detrich Á, Dömötör KJ, Katona MT, Markovits I, Láng JV. Polymorphic forms of bisoprolol fumarate. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135(6):3043–55.
Udrescu L, Sbârcea L, Fuliaş A, Ledeţi I, Vlase G, Barvinschi P, Kurunczi L. Physicochemical analysis and molecular modeling of the fosinopril β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. J Spectrosc Spetrosc-Int J. 2014;2014:748468.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tănase, IM., Sbârcea, L., Ledeți, A. et al. Physicochemical characterization and molecular modeling study of host–guest systems of aripiprazole and functionalized cyclodextrins. J Therm Anal Calorim 141, 1027–1039 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09549-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09549-3