Abstract
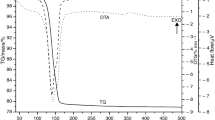
A method was proposed to use XRD-data for thermal analyses of crystalline solids. Therefore, the XRD-pattern was recorded for natural and preheated sepiolite samples at the different temperatures in the interval of 25–800 °C for 4 h. The temperature-dependent intensity (I) of the most characteristic 001 reflection was used as a crystallite variable. The assumed parameters \(k = - (\partial I/\partial T)_{\text{p}} / I\) and \(K = \left( {1 - x} \right)/ x\) were calculated for each heating temperature, where I0 is the intensity for the natural sample and \(x = I/I_{0}\) is the relative crystallite of the heated ones, since the k and K supply Arrhenius equation and van’t Hoff equation behave as reaction rate constant and equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction, respectively. Arrhenius plot showed that the degradation has three kinetic steps. Two of these are due to the stepwise (1, 2) dehydration and third (3) originated from dehydroxylation of sepiolite crystal. Three activation energies were obtained such as \(E_{1}^{\# } = 8.6\) kJ mol−1, \(E_{2}^{\# } = 28.5\) kJ mol−1, and \(E_{3}^{\# } = 124.8\) kJ mol−1 from the slope of three intersected straight lines which are plotted according to the Arrhenius equation. Otherwise, van’t Hoff plot indicated that the degradation has two thermodynamic steps which are due to the dehydration (1, 2) and dehydroxylation (3). The basic thermodynamic relationship, \(\Delta G^{0} = \Delta H^{0} - T\Delta S^{0} ,\) for these steps are \(\Delta G_{1,2}^{0} = 46{,}933 - 65.7T\) and \(\Delta G_{3}^{0} = 143{,}491 - 177.1T\), respectively. Finally, the spontaneous tendency for the thermal degradation was discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu L, Chen H, Shiko E, Fan X, Zhou Y, Zhang G, Lou X, Hu XE. Low-cost DETA impregnation of acid-activated sepiolite for CO2 capture. Chem Eng J. 2018;353:940–8.
Tian G, Wang W, Kang Y, Wang A. Study on thermal activated sepiolite for enhancing decoloration of crude palm oil. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;117:1211–9.
Akkari M, Arando P, Belver C, Bedia J, Amara AB, Ruiz-Hitzky E. ZnO/sepiolite heterostructured materials for solar photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceutical in wastewater. Appl Clay Sci. 2018;156:104–9.
Zhou F, Yan C, Sun Q, Komarneni S. TiO2/sepiolite nanocomposites doped with rare earth ions: preparation, characterization and visible light photocatalytic activity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019;274:25–32.
Gonzalez del Campto MM, Darder M, Aranda P, Akkari M, Huttel Y, Mayoral A, Bettini J, Ruiz-Hitzky E. Functional hybrid nanopaper by assembling nanaofibers of cellulose and sepiolite. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28:1703048(1-13).
Hou K, Wang G, Zhu Y, Ezzatahmadi N, Fu L, Tang A, Yang H, Xi Y. Sepilote/Fe3O4 composite for effective degradation of diuron. Appl Clay Sci. 2019;181:105243(1-9).
Galan E. Properties and applications of palygorskites-sepiolite clays. Clay Miner. 1996;31:443–53.
Murray HH. Applied clay mineralogy today and tomorrow. Clay Miner. 1999;34:39–49.
Brunauer K, Preisinger A. Structur und entstehung des sepioliths. Tschermaks Min Petr Mitt. 1959;6:120–40.
Wang F, Liang J, Tang Q, Chen C, Chen Y. Channel microstructure and thermal insulation mechanism of sepiolite mineral nanofibers. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014;14:3937–42.
Prost R. Infrared study of the interactions between the different kinds of water molecules present in sepiolite. Spectrochim Acta. 1975;31A:1497–9.
Ahlrichs JL, Serna C, Serratosa JM. Structural hydroxyls in sepiolites. Clay Clay Miner. 1989;23:119–24.
Perraki Th, Orfanoudaki A. Study of raw and thermally treated sepioite from the Mantoudi area, Euboea, Greece: X-ray diffraction, TG/DTG/DTA and FTIR investigations. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;9:589–93.
Serna C, Ahlrichs JL, Serratosa JM. Folding in sepiolite crystals. Clay Clay Miner. 1975;23:452–7.
Yener N, Önal M, Üstünışık G, Sarıkaya Y. Thermal behavior of a mineral mixture of sepiolite and dolomite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;88:813–7.
Frost RL, Ding Z. Controlled rate thermal analysis and differential scanning calorimetry of sepiolites and palygorskites. Thermochim Acta. 2003;397:119–28.
Kök MV. Thermal characterization of sepiolite samples. Energy Sources Part A. 2013;35:173–83.
Dandy AJ, Nadiye-Tabbiruka MS. The effect of heating in vacuum on the microporosity of sepiolite. Clay Clay Miner. 1975;23:428–30.
Grillet Y, Cases JM, Francois M, Rouquerol J, Poirier JE. Modification on the porous structure and surface area on sepiolite under vacuum thermal treatment. Clay Clay Miner. 1988;36:233–42.
Malek Z, Balek V, Garfinkel-Shweky D, Yariv S. The study of the dehydration and dehydroxylation of smectites by emanation thermal analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 1997;48:83–92.
Göktaş AA, Mısırlı Z, Baykara T. Sintering behavior of sepiolite. Ceram Int. 1997;23:305–11.
Yebra-Rodriquez A, Martin-Ramos JD, Del Rey F, Viseras C, Lopez-Gainda A. Effect of acid treatment on the structure of sepiolite. Clay Miner. 2003;38:353–60.
Ogorodova LP, Kiseleva IA, Vigasina MF, Kabalov YK, Grishchenko RO, Mel’chakova LV. Natural sepiolite: enthalpies of dehydration, dehydroxylation, and formation derived from thermochemical studies. Am Mineral. 2014;99:2369–73.
Kıyohiro T, Otsuka R. Dehydration mechanism of bound water in sepiolite. Thermochim Acta. 1989;147:127–38.
Yılmaz M, Kalpaklı Y, Pişkin S. Thermal behavior and dehydroxylation kinetics of naturally occurring sepiolite and bentonite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;114:1191–9.
Balcı S. Effect of heating and pre-treatment on pore size distribution of sepiolite. Clay Miner. 1971;34:647–55.
Otsuka R, Moriko T, Sakamoto T. Mineralogische Eigenschaften vom Meerschaum von Eskişehir, Turkei. Mem Sch Sci Eng Waseda Univ. 1973;37:43–52.
Ece ÖI, Çoban F. Geology, occurrence, and genesis of Eskişehir sepiolites, Turkey. Clay Clay Miner. 1994;42:81–92.
Önal M, Yılmaz H, Sarıkaya Y. Some physicochemical properties of the white sepiolite known as pipestone from Eskişehir, Turkey. Clay Clay Miner. 2008;56:511–9.
Moore DM, Reynolds RC Jr. X-ray diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1997.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Ankara University Research Fund (Project No. 12B4240016) for financial support to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarıkaya, Y., Önal, M. & Pekdemir, A.D. Kinetic and thermodynamic approaches on thermal degradation of sepiolite crystal using XRD-analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim 140, 2667–2672 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09053-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09053-3