Abstract
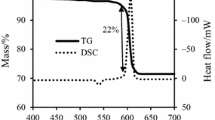
Presented herein is a study on the ignition reaction kinetics and mechanism of B4C/KNO3 and B4C/KClO4 pyrotechnic smoke compositions using the non-isothermal thermogravimetry and differential scanning calorimetry techniques. The pyrotechnics in oxygen balance of − 10%, − 20% and − 30% were prepared for the experiments. The results of measurements showed that the pyrotechnics in oxygen balance of − 20% had the highest enthalpy. The activation energy (Ea) of ignition reactions was calculated by using Ozawa–Flynn–Wall (OFW) and Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose (KAS) methods. The Ea values of B4C/KNO3 and B4C/KClO4 were 139.5 and 214.6 kJ mol−1 calculated by OFW method, and 129.3 and 210.7 kJ mol−1 by KAS method. The differential and integral reaction mechanism functions of B4C/KNO3 and B4C/KClO4 were determined, respectively, by z(α) master plots method, f1(α) = 2(1 − α)[− ln(1 − α)]1/2, g1(α) = [− ln(1 − α)]1/2, and f2(α) = 3(1 − α)[− ln(1 − α)]2/3, g2(α) = [− ln(1 − α)]1/3. The pre-exponential factors, lnA = 11.6 and 22.3 min−1, were obtained by the intercept of KAS method for ignition reaction of B4C/KNO3 and B4C/KClO4 pyrotechnics. Based on the results, the burning rates, thermal sensitivities and application methods of B4C/KNO3 and B4C/KClO4 were predicted.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eaton JC, Lopinto RJ, Palmer WG. Health effects of hexachloroethane (HC) smoke; accession number ADA277838; Defense Technical Information Center (DTIC): Fort Belvoir, VA, 1994; pp 1–60.
Shaw AP, Poret JC, Gilbert RA, et al. Development and performance of boron carbide-based smoke compositions. Propellants Explos Pyrotech. 2013;38(5):622–8.
Shaw AP, Diviacchi G, Black EL, et al. Versatile boron carbide-based visual obscurant compositions for smoke munitions. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2015;3(6):150423154904007.
Thévenot F. Boron carbide—a comprehensive review. J Eur Ceram Soc. 1990;6(4):205–25.
Reddy RG, Wang T, Mantha D. Thermodynamic properties of potassium nitrate–magnesium nitrate compound [2KNO3·Mg(NO3)2]. Thermochim Acta. 2012;531:6–11.
Benenson W, Harris JW, Stocker H et al. Handbook of physics; 2002. ISBN 978-0387952697.
Pan GP, Yang S. Pyrotechnic technology. Nanjing: Initiators and Pyrotechnics Technology Committee; 1995.
Wendlandt WW. Thermal analysis. 3rd ed. Hoboken: Wiley; 1986.
Vyazovkin S, Burnham AK, Criado JM, et al. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim Acta. 2011;520(1–2):1–19.
Pouretedal HR, Loh Mousavi S. Study of the ratio of fuel to oxidant on the kinetic of ignition reaction of Mg/Ba(NO3)2 and Mg/Sr(NO3)2 pyrotechnics by non-isothermal TG/DSC technique. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:1307–15.
Vyazovkin S. Alternative description of process kinetics. Thermochim Acta. 1992;211(1):181–7.
Flynn JH. The ‘temperature integral’—its use and abuse. Thermochim Acta. 1997;300(1–2):83–92.
Miyata K. Combustion of boron-pyrotechnics. In: Joint propulsion conference and exhibit. 2013.
El-Awad AM. Catalytic effect of some chromites on the thermal decomposition of KClO4 mechanistic and non-isothermal kinetic studies. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2000;61(1):197–208.
Liu PJ, Liu LL, He GQ. Effect of solid oxidizers on the thermal oxidation and combustion performance of amorphous boron. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124(3):1587–93.
Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1965;38:1881.
Flynn JH, Wall LA. General treatment of the thermogravimetry of polymers. J Res Natl Bureau Stand Part A. 1966;70:487.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;29(11):1702–6.
Akahira T, Sunose T. Method of determining activation deterioration constant of electrical insulating materials. Res Rep (Chiba Inst Technol) Sci Technol. 1971;16:22–31.
Malek J. The applicability of Johnson–Mehl–Avrami model in the thermal analysis of the crystallization kinetics of glasses. Thermochim Acta. 1995;267:61–73.
Brown ME. Introduction to thermal analysis. 2nd ed. Dodrecht: Kluwer; 2001.
Pouretedal HR, Ebadpour R. Application of Non-isothermal thermogravimetric method to interpret the decomposition kinetics of NaNO3, KNO3, and KClO4. Int J Thermophys. 2014;35(5):942–51.
Acknowledgements
The support for this work was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 51676100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Zhu, C., Xie, X. et al. A study on kinetics of ignition reaction of B4C/KNO3 and B4C/KClO4 pyrotechnic smoke compositions. J Therm Anal Calorim 140, 2317–2324 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09015-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09015-9