Abstract
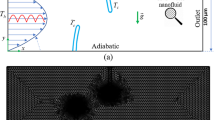
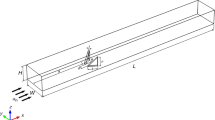
In the current study, turbulent flow and heat transfer in a three-dimensional channel is simulated numerically. The main purpose of this study is investigating the effect of using dimpled fin and CuO nanoparticles on the heat transfer enhancement and the improvement in cooling performance in a channel under the heat flux (100 kW m−2). Pure water flow is simulated at Reynolds numbers of 5000, 10,000, 15,000 and 20,000 with nanoparticles volume fractions 2 and 4%, and the effect of dimpled fins is investigated. To ensure the accuracy of the numerical solving procedure, the obtained results are compared with other experimental results and acceptable coincidence is observed. The results show that dimpled fins cause the improvement in heat transfer and using nanoparticles inside a dimpled fin causes better cooling performance than using pure water flow in a smooth channel. According to the obtained results at lower Reynolds numbers, the dimpled fin has more efficient performance in heat transfer enhancement than higher Reynolds numbers. Hence, using dimpled fin at lower Reynolds numbers flow is recommended.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Area (m2)
- C f :
-
Skin fraction coefficient
- C p :
-
Specific heat (kJ kg−1 K−1)
- D h :
-
Hydraulic diameter (m)
- d :
-
Molecular diameter of particles (m)
- C f :
-
Friction coefficient
- h :
-
Channel height (m)
- h :
-
Convection heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity coefficient (W m−1 K−1)
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- P :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- PP:
-
Pumping power (W)
- q″:
-
Heat flux (W m−2)
- u :
-
Velocity parameter along x (m s−1)
- v :
-
Velocity parameter along y (m s−1)
- w :
-
Velocity parameter along z (m s−1)
- PEC:
-
Performance evaluation criteria
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- μ :
-
Viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- φ :
-
Nanoparticles volume fraction
References
Vicente PG, García, Viedma A. Experimental study of mixed convection and pressure drop in helically dimpled tubes for laminar and transition flow. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2002;45:5091–105.
Vicente PG, García A, Viedma A. Heat transfer and pressure drop for low Reynolds turbulent flow in helically dimpled tubes. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2002;45:543–53.
Shen S, Xu JL, Zhou JJ, Chen Y. Flow and heat transfer in microchannels with rough wall surface. Energy Convers Manag. 2006;47:1311–25.
Elyyan MA, Tafti DK. A novel split-dimple interrupted fin configuration for heat transfer augmentation. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2009;52:1561–72.
Liou T-M, Hwang J-J, Chen S-H. Simulation and measurement of enhanced turbulent heat transfer in a channel with periodic ribs on one principal wall. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 1993;36:507–17.
Isaev SA, Kornev NV, Leontiev AI, Hassel E. Influence of the Reynolds number and the spherical dimple depth on turbulent heat transfer and hydraulic loss in a narrow channel. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2010;53:178–97.
Hwang SD, Kwon HG, Cho HH. Local heat transfer and thermal performance on periodically dimple-protrusion patterned walls for compact heat exchangers. Energy. 2010;35:5357–64.
Promvonge P, Thianpong C. Thermal performance assessment of turbulent channel flows over different shaped ribs. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2008;35:1327–34.
Xie G, Sundén B. Numerical predictions of augmented heat transfer of an internal blade tip-wall by hemispherical dimples. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2010;53:5639–50.
Kim H-M, Moon M-A, Kim K-Y. Multi-objective optimization of a cooling channel with staggered elliptic dimples. Energy. 2011;36:3419–28.
Xie G, Liu J, Ligrani PM, Zhang W. Numerical analysis of flow structure and heat transfer characteristics in square channels with different internal-protruded dimple geometrics. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2013;67:81–97.
Rao Y, Wan C, Xu Y, Zang S. Spatially-resolved heat transfer characteristics in channels with pin fin and pin fin-dimple arrays. Int J Therm Sci. 2011;50:2277–89.
Akbari OA, Toghraie D, Karimipour A. Numerical simulation of heat transfer and turbulent flow of water nanofluids copper oxide in rectangular microchannel with semi-attached rib. Adv Mech Eng. 2016;8:1687814016641016.
Arani AAA, Akbari OA, Safaei MR, Marzban A, Alrashed AAAA, Ahmadi GR, et al. Heat transfer improvement of water/single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) nanofluid in a novel design of a truncated double-layered microchannel heat sink. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;113:780–95.
Alipour H, Karimipour A, Safaei MR, Semiromi DT, Akbari OA. Influence of T-semi attached rib on turbulent flow and heat transfer parameters of a silver-water nanofluid with different volume fractions in a three-dimensional trapezoidal microchannel. Phys E Low-Dimens Syst Nanostruct. 2017;88:60–76.
Manca O, Nardini S, Ricci D. A numerical study of nanofluid forced convection in ribbed channels. Appl Therm Eng. 2012;37:280–92.
Mohammadi M, Abadeh A, Nemati-Farouji R, Passandideh-Fard M. An optimization of heat transfer of nanofluid flow in a helically coiled pipe using Taguchi method. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08167-y.
Zadeh AD, Toghraie D. Experimental investigation for developing a new model for the dynamic viscosity of silver/ethylene glycol nanofluid at different temperatures and solid volume fractions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131(2):1449–61.
Kandlikar SG. Chapter 3—Single-phase liquid flow in minichannels and microchannels. In: Kandlikar SG, Garimella S, Li D, Colin S, King MRBT-HT and FF in M and M, editors. Heat transfer and fluid flow in minichannels and microchannels. Oxford: Elsevier Science Ltd; 2006. p. 87–136. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780080445274500050.
Arabpour A, Karimipour A, Toghraie D, Akbari OA. Investigation into the effects of slip boundary condition on nanofluid flow in a double-layer microchannel. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131(3):2975–91.
Hosseinnezhad R, Akbari OA, Afrouzi HH, Biglarian M, Koveiti A, Toghraie D. Numerical study of turbulent nanofluid heat transfer in a tubular heat exchanger with twin twisted-tape inserts. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132(1):741–59.
Arabpour A, Karimipour A, Toghraie D. The study of heat transfer and laminar flow of kerosene/multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) nanofluid in the microchannel heat sink with slip boundary condition. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131(2):1553–66.
Parsaiemehr M, Pourfattah F, Akbari OA, Toghraie D, Sheikhzadeh G. Turbulent flow and heat transfer of Water/Al2O3 nanofluid inside a rectangular ribbed channel. Phys E Low-Dimens Syst Nanostruct. 2018;96:73–84.
Rashidi S, Eskandarian M, Mahian O, Poncet S. Combination of nanofluid and inserts for heat transfer enhancement. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135:437–60.
Rashidi S, Karimi N, Mahian O, Abolfazli Esfahani J. A concise review on the role of nanoparticles upon the productivity of solar desalination systems. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135:1145–59.
Alkasmoul FS, Al-Asadi MT, Myers TG, Thompson HM, Wilson MCT. A practical evaluation of the performance of Al2O3-water, TiO2-water and CuO-water nanofluids for convective cooling. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;126:639–51.
Wilcox DC. Turbulence modeling for CFD. 3rd ed. La Canada: DCW Industries Inc; 2006.
Xuan Y, Roetzel W. Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2000;43:3701–7.
Pak BC, Cho YI. Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles. Exp Heat Transf. 1998;11:151–70.
Pourfattah F, Yousefi S, Akbari OA, Adhampour M, Toghraie D, Hekmatifar M. Numerical simulation of the effect of using nanofluid in phase change process of cooling fluid. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-12-2018-0806.
Pourfattah F, Motamedian M, Sheikhzadeh G, Toghraie D, Ali Akbari O. The numerical investigation of angle of attack of inclined rectangular rib on the turbulent heat transfer of Water-Al2O3 nanofluid in a tube. Int J Mech Sci. 2017;131–132:1106–16.
Toghraie D, Abdollah MMD, Pourfattah F, Akbari OA, Ruhani B. Numerical investigation of flow and heat transfer characteristics in smooth, sinusoidal and zigzag-shaped microchannel with and without nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131(2):1757–66.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourfattah, F., Akbari, O.A., Jafrian, V. et al. Numerical simulation of turbulent flow and forced heat transfer of water/CuO nanofluid inside a horizontal dimpled fin. J Therm Anal Calorim 139, 3711–3724 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08752-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08752-1