Abstract
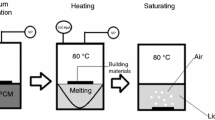
The polyethylene glycol/wood-flour (PEG/WF) composites were synthesized as novel form-stable phase change materials (PCMs) using PEG as phase change material and WF as supporting material. The composite products were investigated by Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the leakage test, X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimeter (DSC), accelerated thermal cycling testing and thermogravimetry analysis (TG), respectively. The results revealed that the maximum latent heats and encapsulation ratio of the synthesized PEG/WF composite form-stable PCMs can reach 90.9 J g−1 and 52.8%, respectively. SEM images demonstrated that the porous tubular-like channel spaces of WF are completely blocked by PEG. The thermal cycling test showed that the synthesized PEG/WF composite form-stable PCMs have superior thermal reliability after 200 melting and freezing cycles without leakage. Additionally, TG results revealed that the prepared PEG/WF composite form-stable PCMs have good thermal stability with the decomposition temperature higher than 200 °C. Thus, the novel PEG/WF composite form-stable PCMs are a promising candidate using in wallboard and building materials due to its excellent thermal properties and thermal reliability.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang F, Su D, Tang Y, Fang G. Synthesis and thermal properties of fatty acid eutectics and diatomite composites as shape-stabilized phase change materials with enhanced thermal conductivity. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2015;141:218–24.
Liu Z, Wu B, Fu X, Yan P, Yuan Y, Zhou C, Lei J. Two components based polyethylene glycol/thermosetting solid-solid phase change material composites as novel form stable phase change materials for flexible thermal energy storage application. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2017;170:197–204.
Alva G, Lin Y, Liu L, Fang G. Synthesis, characterization and applications of microencapsulated phase change materials in thermal energy storage. Energy Build. 2017;144:276–94.
Wei H, Xie X, Li X, Lin X. Preparation and characterization of capric-myristic-stearic acid eutectic mixture/modified expanded vermiculite composite as a form-stable phase change material. Appl Energy. 2016;178:616–23.
Fu X, Xiao Y, Hu K, Wang J, Lei J, Zhou C. Thermosetting solid-solid phase change materials composed of poly(ethylene glycol)-based two components: Flexible application for thermal energy storage. Chem Eng J. 2016;291:138–48.
Huang X, Alva G, Liu L, Fang G. Microstructure and thermal properties of cetyl alcohol/high density polyethylene composite phase change materials with carbon fiber as shape-stabilized thermal storage materials. Appl Energy. 2017;200:19–27.
Liu Z, Fu X, Liang J, Wu B, Wang J, Lei J. Solvent-free synthesis and properties of novel solid–solid phase change materials with biodegradable castor oil for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2016;147:177–84.
Kong W, Yang Y, Zhou C, Lei J. Novel thermosetting phase change materials with polycarbonatediol based curing agent as supporting skeleton for thermal energy storage. Energy Build. 2017;146:12–8.
Zhang L, Yang W, Jiang Z, He F, Zhang K, Fan J, Wu J. Graphene oxide-modified microencapsulated phase change materials with high encapsulation capacity and enhanced leakage-prevention performance. Appl Energy. 2017;197:354–63.
Yu Q, Tchuenbou-Magaia F, Al-Duri B, Zhang Z, Ding Y, Li Y. Thermo-mechanical analysis of microcapsules containing phase change materials for cold storage. Appl Energy. 2018;211:1190–202.
Wang T, Wang S, Luo R, Zhu C, Akiyama T, Zhang Z. Microencapsulation of phase change materials with binary cores and calcium carbonate shell for thermal energy storage. Appl Energy. 2016;171:113–9.
Luo J, Zhao L, Yang Y, Song G, Liu Y, Chen L, Tang G. Emulsifying ability and cross-linking of silk fibroin microcapsules containing phase change materials. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2016;147:144–9.
Tang F, Liu L, Alva G, Jia Y, Fang G. Synthesis and properties of microencapsulated octadecane with silica shell as shape–stabilized thermal energy storage materials. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2017;160:1–6.
Döğüşcü DK, Kızıl Ç, Biçer A, Sarı A, Alkan C. Microencapsulated n-alkane eutectics in polystyrene for solar thermal applications. Sol Energy. 2018;160:32–42.
Xiong W, Chen Y, Hao M, Zhang L, Mei T, Wang J, Li J, Wang X. Facile synthesis of PEG based shape-stabilized phase change materials and their photo-thermal energy conversion. Appl Therm Eng. 2015;91:630–7.
Liu Z, Chen Z, Yu F. Microencapsulated phase change material modified by graphene oxide with different degrees of oxidation for solar energy storage. Solar Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2018;174:453–9.
Zhang X, Yin Z, Meng D, Huang Z, Wen R, Huang Y, Min X, Liu Y, Fang M, Wu X. Shape-stabilized composite phase change materials with high thermal conductivity based on stearic acid and modified expanded vermiculite. Renew Energy. 2017;112:113–23.
Wen R, Zhang X, Huang Z, Fang M, Liu Y, Wu X, Min X, Gao W, Huang S. Preparation and thermal properties of fatty acid/diatomite form-stable composite phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2018;178:273–9.
Luo Z, Zhang H, Gao X, Xu T, Fang Y, Zhang Z. Fabrication and characterization of form-stable capric-palmitic-stearic acid ternary eutectic mixture/nano-SiO2 composite phase change material. Energy Build. 2017;147:41–6.
Fu X, Liu Z, Xiao Y, Wang J, Lei J. Preparation and properties of lauric acid/diatomite composites as novel form-stable phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Energy Build. 2015;104:244–9.
Li L, Wang G, Guo C. Influence of intumescent flame retardant on thermal and flame retardancy of eutectic mixed paraffin/polypropylene form-stable phase change materials. Appl Energy. 2016;162:428–34.
Wang W, Yang X, Fang Y, Ding J. Preparation and performance of form-stable polyethylene glycol/silicon dioxide composites as solid–liquid phase change materials. Appl Energy. 2009;86(2):170–4.
Karaman S, Karaipekli A, Sarı A, Biçer A. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)/diatomite composite as a novel form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2011;95(7):1647–53.
Zhang S, Tao Q, Wang Z, Zhang Z. Controlled heat release of new thermal storage materials: the case of polyethylene glycol intercalated into graphene oxide paper. J Mater Chem. 2012;22:20166–9.
Wang C, Feng L, Yang H, Xin G, Li W, Zheng J, Tian W, Li X. Graphene oxide stabilized polyethylene glycol for heat storage. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2012;14:13233–8.
Fang Y, Kang H, Wang W, Hong L, Gao X. Study on polyethylene glycol/epoxy resin composite as a form-stable phase change material. Energy Convers Manage. 2010;51:2757–61.
Yang J, Tang L, Bao R, Bai L, Liu Z, Xie B, Yang M, Yang W. Hybrid network structure of boron nitride and graphene oxide in shape-stabilized composite phase change materials with enhanced thermal conductivity and light-to-electric energy conversion capability. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2018;174:56–64.
Sun K, Kou Y, Zheng H, Liu X, Tan Z, Shi Q. Using silicagel industrial wastes to synthesize polyethylene glycol/silica-hydroxyl form-stable phase change materials for thermal energy storage applications. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2018;178:139–45.
Yang Y, Pang Y, Liu Y, Guo H. Preparation and thermal properties of polyethylene glycol/expanded graphite as novel form-stable phase change material for indoor energy saving. Mater Lett. 2018;216:220–3.
Zhu H, Zhu S, Jia Z, Parvinian S, Li Y, Vaaland O, Hu L, Li T. Anomalous scaling law of strength and toughness of cellulose nanopaper. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(29):8971–6.
Ma L, Guo C, Ou R, Sun L, Wang Q, Li L. Preparation and Characterization of Modified Porous Wood Flour/Lauric-Myristic Acid Eutectic Mixture as a Form-Stable Phase Change Material. Energy Fuel. 2018;32:5453–61.
Marcovich N, Reboredo M, Aranguren M. Dependence of the mechanical properties of woodflour-polymer composites on the moisture content. J Appl Polym Sci. 2015;68:2069–76.
Song J, Chen C, Zhu S, Zhu M, Dai J, Ray U, et al. Processing bulk natural wood into a high-performance structural material. Nature. 2018;554:224–8.
Tang B, Wang Y, Qiu M, Zhang S. A full-band sunlight-driven carbon nanotube/PEG/SiO 2 composites for solar energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2014;123(123):7–12.
Sarı A, Bicer A, Al-Ahmed A, Al-Sulaiman FA, Zahir MH, Mohamed SA. Silica fume/capric acid-palmitic acid composite phase change material doped with CNTs for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2018;179:261–353.
Salunkhe PB, Shembekar PS. A review on effect of phase change material encapsulation on the thermal performance of a system. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2012;16:5603–16.
Guan WM, Li JH, Qian TT, Wang X, Deng Y. Preparation of paraffin/expanded vermiculite with enhanced thermal conductivity by implanting network carbon in vermiculite layers. Chem Eng J. 2015;277:56–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Lei, Y., Liu, Q. et al. Facile preparation of polyethylene glycol/wood-flour composites as form-stable phase change materials for thermal energy storage. J Therm Anal Calorim 139, 137–146 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08394-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08394-3