Abstract
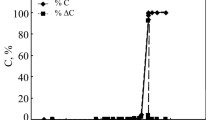
Ten multiwall carbon nanotubes purchased from two companies with diameters ranging from 7 to 100 nm with tapped bulk densities from 57 to 250 kg m−3 and with similar lengths and powder sizes were analyzed by thermogravimetric analysis in dynamic and isothermal mode to investigate the importance of the diameter size and tapped bulk density on the degradation behavior of carbon nanotubes. In the case where mass/heat transfer effects were eliminated, results showed that the oxidation temperature depends on diameter only at sufficiently small diameters. The number of surface defects as measured from the ID/IG ratio obtained from Raman spectroscopy was not correlated with degradation stability. The tapped bulk density, on the other hand, dominated the pattern of degradation at high enough heating rates where mass/heat transfer effects become appreciable. As found in previous work which examined nanotubes with roughly constant diameter, tapped bulk density linearly correlated with the ending oxidation temperature at sufficiently high heating rates.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iijima S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature. 1991;354(6348):56–8.
Mehra NK, Mishra V, Jain NK. A review of ligand tethered surface engineered carbon nanotubes. Biomaterials. 2014;35(4):1267–83.
Chen SJ, Zou B, Collins F, Zhao XL, Majumber M, Duan WH. Predicting the influence of ultrasonication energy on the reinforcing efficiency of carbon nanotubes. Carbon. 2014;77:1–10.
Eatemadi A, Daraee H, Karimkhanloo H, Kouhi M, Zarghami N, Akbarzadeh A, et al. Carbon nanotubes: properties, synthesis, purification, and medical applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014;9(1):1–13.
Mansfield E, Kar A, Hooker SA. Applications of TGA in quality control of SWCNTs. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010;396(3):1071–7.
Kim D-Y, Yun YS, Kwon S-M, Jin H-J. Preparation of aspect ratio-controlled carbon nanotubes. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst. 2009;510(1):79/[1213]-86/[20].
Xu F, Sun LX, Zhang J, Qi YN, Yang LN, Ru HY, et al. Thermal stability of carbon nanotubes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;102(2):785–91.
Singh DK, Iyer PK, Giri PK. Diameter dependence of oxidative stability in multiwalled carbon nanotubes: role of defects and effect of vacuum annealing. J Appl Phys. 2010;108(8):084313.
Kim DY, Yang C-M, Park YS, Kim KK, Jeong SY, Han JH, et al. Characterization of thin multi-walled carbon nanotubes synthesized by catalytic chemical vapor deposition. Chem Phys Lett. 2005;413(1–3):135–41.
Zhang H, Chen Y, Zeng G, Huang H, Xie Z, Jie X. The thermal properties of controllable diameter carbon nanotubes synthesized by using AB5 alloy of micrometer magnitude as catalyst. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2007;464(1–2):17–22.
Zhou W, Ooi YH, Russo R, Papanek P, Luzzi DE, Fischer JE, et al. Structural characterization and diameter-dependent oxidative stability of single wall carbon nanotubes synthesized by the catalytic decomposition of CO. Chem Phys Lett. 2001;350(1–2):6–14.
Ma J, Yu F, Yuan Z, Chen J. Diameter-dependent thermal-oxidative stability of single-walled carbon nanotubes synthesized by a floating catalytic chemical vapor deposition method. Appl Surf Sci. 2011;257(24):10471–6.
Kowalska E, Kowalczyk P, Radomska J, Czerwosz E, Wronka H, Bystrzejewski M. Influenceof high vacuum annealing treatment on some properties of carbon nanotubes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;86(1):115–9.
Lin W, Moon K-S, Zhang S, Ding Y, Shang J, Chen M, et al. Microwave makes carbon nanotubes less defective. ACS Nano. 2010;4(3):1716–22.
Huang W, Wang Y, Luo G, Wei F. 99.9% purity multi-walled carbon nanotubes by vacuum high-temperature annealing. Carbon. 2003;41(13):2585–90.
Hsieh Y-C, Chou Y-CL, Lin C-P, Hsieh T-F, Shu C-M. Thermal analysis of multi-walled carbon nanotubes by Kissinger’s corrected kinetic equation. Aerosol Air Qual Res. 2010;10(3):212–8.
Liu P, Wang T. Ultrasonic-assisted chemical oxidative cutting of multiwalled carbon nanotubes with ammonium persulfate in neutral media. Appl Phys A. 2009;97(4):771–5.
Li H, Zhao N, He C, Shi C, Du X, Li J. Thermogravimetric analysis and TEM characterization of the oxidation and defect sites of carbon nanotubes synthesized by CVD of methane. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2008;473(1–2):355–9.
McKee GSB, Vecchio KS. Thermogravimetric analysis of synthesis variation effects on CVD generated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110(3):1179–86.
Zapata HJA, Crossley S, Grady BP. Influence of tapped density on the degradation profile of multiwall carbon nanotubes. Thermochim Acta. 2017;654:140–5.
Zhou W, Ooi YH, Russo R, Papanek P, Luzzi DE, Fischer JE, et al. Structural characterization and diameter-dependent oxidative stability of single wall carbon nanotubes synthesized by the catalytic decomposition of CO. Chem Phys Lett. 2001;350(1):6–14.
Warner JH, Schäffel F, Zhong G, Rümmeli MH, Büchner B, Robertson J, et al. Investigating the diameter-dependent stability of single-walled carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano. 2009;3(6):1557–63.
Flynn JH, Wall LA. A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. J Polym Sci, Part C: Polym Lett. 1966;4(5):323–8.
Sharma HN, Pahalagedara L, Joshi A, Suib SL, Mhadeshwar AB. Experimental study of carbon black and diesel engine soot oxidation kinetics using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Fuels. 2012;26(9):5613–25.
Zacharia RE, Simon SL. Dynamic and isothermal thermogravimetric analysis of a polycyanurate thermosetting system. Polym Eng Sci. 1998;38(4):566–72.
Acknowledgements
Funding to support this project was provided by the University of Oklahoma and Texas Tech University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zapata H, J.A., Simon, S.L. & Grady, B.P. Influence of diameter on the degradation profile of multiwall carbon nanotubes. J Therm Anal Calorim 138, 1351–1362 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08137-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08137-4