Abstract
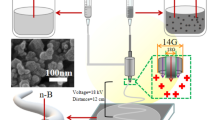
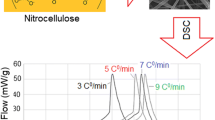
Nanometal fuels have a great potential in energetic field for their high reactivity and their low ignition temperature. However, their high surface energy makes them aggregate. In this work, the electrospinning was employed to fabricate the nanoboron/nitrocellulose nanofibers expecting to enhance the reactivity of nanoboron. The results of SEM and TEM show that nanoboron is well dispersed in the nitrocellulose fiber matrix. TG–DSC confirms that the nanoboron in the fibers reacted more drastically than pure nanoboron and nanoboron/nitrocellulose powders resulted from the thermal analysis. Combustion propagation velocity shows that the presence of nanoboron in nitrocellulose fibers causes the faster and more intensive burning than the mechanical mixture of nanoboron and nitrocellulose.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang BY, Huang C, Yan S. Enhanced reactivity of boron, through adding nano-aluminum and wet ball milling. Appl Surf Sci. 2013;286:91–8.
Conner RW, Dlott DD. Comparing boron and aluminum nanoparticle combustion in teflon using ultrafast emission spectroscopy. J Phys Chem C. 2012;116:2751–60.
Acharya S, Karmakar S, Dooley KM. Ignition and combustion of boron nanoparticles in ethanol spray flame. J Propuls Power. 2012;28(4):707–18.
Brian VD, Jesus PLP, Scott LA. Air-stable, unoxidized, hydrocarbon-dispersible boron nanoparticles. J Mater Res. 2009;24:3462–4.
Liang D, Liu J, Li H, Zhou Y, Zhou J. Improving effect of boron carbide on the combustion and thermal oxidation characteristics of amorphous boron. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;128:1771–82.
Li YC, Cheng Y, Hui YL, Yan S. The effect of ambient temperature and boron content on the burning rate of the B/Pb3O4 delay compositions. J Energ Mater. 2010;28(2):77–84.
Li X, Huang C, Yang H, Li Y, Cheng Y. Thermal reaction properties of aluminum/copper (II) oxide/poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124:899–907.
Bognitzki M, Becker M, Graeser M, Massa W, et al. Preparation of sub-micrometer copper fibers via electrospinning. Adv Mater. 2006;18:2384–6.
Kong L, Ziegler GR. Fabrication of pure starch fibers by electrospinning. Food Hydrocoll. 2014;36:20–5.
Liu D, Zhang X, Zhu L, Wua J, Lü X. Alternating ring-opening copolymerization of styrene oxide and maleic anhydride using asymmetrical bis-Schiff-base metal (III) catalysts. Catal Sci Technol. 2015;5:562–71.
Pourmortazavi SM, Sadri M, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M, et al. Thermal decomposition kinetics of electrospun azidodeoxy cellulose nitrate and polyurethane nanofibers. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:281–90.
Wu S-H, Qin X-H. Effects of the stabilization temperature on the structure and properties of polyacrylonitrile-based stabilized electrospun nanofiber microyarns. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;116:303–8.
Volova T, Goncharov D, Sukovatyi A, Shabanov A, Nikolaeva E, Shishatskaya E. Electrospinning of polyhydroxyalkanoate fibrous scaffolds: effects on electrospinning parameters on structure and properties. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2014;25:370–93.
Staley CS, Raymond KE, Thiruvengadathan R, Apperson SJ, Gangopadhyay K, Swaszek SM, Taylor RJ, Gangopadhyay S. Fast-Impulse nanothermite solid-propellant miniaturized thrusters. J Propuls Power. 2013;29:1400–9.
Korampally M, Apperson SJ, Staley CS, Castorena JA, Thiruvengadathan R, Gangopadhyay K, Mohan RR, Ghosh A, Polo-Parada L, Gangopadhyay S. Transient pressure mediated intranuclear delivery of FITC-Dextran into chicken cardiomyocytes by MEMS-based nanothermite reaction actuator. Sens Actuators, B. 2012;1292:171–2.
Wang Haiyang, Jian Guoqiang, Yan Shi, DeLisio Jeffery B, Huang Chuan, Zachariah Michael R. Electrospray formation of gelled nano-aluminum microspheres with superior reactivity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:6797–801.
Tabacof A, de Araújo Calado VM. Thermogravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetry for investigating the stability of yellow smoke powders. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;128:387–98.
Trache D, Khimeche K, Mezroua A, Benziane M. Physicochemical properties of microcrystalline nitrocellulose from Alfa grass fibres and its thermal stability. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124:1485–96.
Xie L, Shao ZQ, Wang W, Wang FJ. Preparation of AlNPs/NC composite nanofibers by electrospinning. Integr Ferroelectr Int J. 2011;127:184–92.
Yan S, Jian GQ, Zachariah MR. Electrospun nanofiber-based thermite textiles and their reactive properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4:6432–5.
Li R, Xu HM, Hu HL, Yang GC, Wang J, Shen JP. Microstructured Al/Fe2O3/nitrocellulose energetic fibers realized by electrospinning. J Energ Mater. 2014;32:50–9.
Huwei L, Ruonong F. Studies on thermal decomposition of nitrocellulose by pyrolysis-gas chromatography. J Anal Pyrolysis. 1988;14:163–7.
Sovizi MR, Hajimirsadeghia SS, Naderizadehb B. Effect of particle size on thermal decomposition of nitrocellulose. J Hazard Mater. 2009;168:1134–9.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Laboratory Fund (9140C370304140C37173).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Yang, H., Hong, Y. et al. Electrospun nanofiber-based nanoboron/nitrocellulose composite and their reactive properties. J Therm Anal Calorim 130, 1063–1068 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6607-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6607-7