Abstract
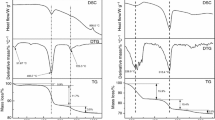
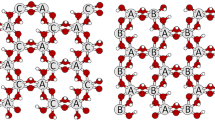
Kaolinite/quaternary ammonium salt complexes were prepared by intercalation and displacement of kaolinite–N-methylformamide (Kaol–NMF) with methanol (Me) and quaternary ammonium salt. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and thermogravimetry and differential scanning calorimetry (TG–DSC) analysis. The d-values of the kaolinite/quaternary ammonium salts complexes increase with the alkyl chain length of the quaternary ammonium salts. Based on the results and the available evidence pointing toward the interlayer structure of kaolinite intercalation complexes, the most possible structural model for the kaolinite/quaternary ammonium salt intercalation complexes was proposed. For the kaolinite–dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride, kaolinite–trimethyl tetradecyl ammonium chloride and kaolinite–hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride, the intercalation molecules are oriented perpendicular to the kaolinite surface in a single layer. However, for kaolinite–stearyl trimethyl ammonium chloride, the cationic head of intercalated stearyl trimethyl ammonium chloride molecules may be partially hydrated and arrayed aslant in the interlayer space of kaolinite with an inclination angle of 35°. Thermal analysis results revealed that the thermal decomposition of kaolinite/quaternary ammonium salt complexes occurs in two main steps. The function of the most probable mechanism, activation energy E and pre-exponential factor were obtained by mutual authentication using KAS and Ozawa methods, Satava integral method and Achar–Brindley–Sharp–Wendworth methods. The average activation energy E of four kaolinite/quaternary ammonium salt intercalation complexes is 108.147, 153.478, 125.723 and 88.008 kJ mol−1, respectively. The optimized mechanism function for de-intercalation process of quaternary ammonium salt is f(α) = 1 − α and G(α) = −ln(1 − α).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li YF, Sun DW, Pan XB, Zhang B. Kaolinite intercalation precursors. Clay Clay Miner. 2009;57(6):779–86.
Cheng H, Liu Q, Liu J, Sun B, Kang Y, Frost RL. TG-MS-FTIR (evolved gas analysis) of kaolinite-urea intercalation complex. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;116(1):195–203.
Cheng H, Liu Q, Yang J, Zhang Q, Frost RL. Thermal behavior and decomposition of kaolinite-potassium acetate intercalation composite. Thermochim Acta. 2010;503–504:16–20.
Makó É, Kristóf J, Horváth E, Vágvölgyi V. Kaolinite–urea complexes obtained by mechanochemical and aqueous suspension techniques—a comparative study. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;330(2):367–73.
Costanzo P, Giesse R. Ordered halloysite; dimethylsulfoxide intercalate. Clay Clay Miner. 1986;34(1):105–7.
Theng B. Intercalation method using formamide for differentiating halloysite from kaolinite. Clay Clay Miner. 1984;32(4):241–8.
Cruz MDR, Franco F. Thermal behavior of the kaolinite-hydrazine intercalation complex. Clay Clay Miner. 2000;48(1):63–7.
Frost RL, Kristof J, Horvath E, Kloprogge JT. Rehydration and phase changes of potassium acetate-intercalated halloysite at 298 k. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2000;226(2):318–27.
Kuroda Y, Ito K, Itabashi K, Kuroda K. One-step exfoliation of kaolinites and their transformation into nanoscrolls. Langmuir. 2011;27(5):2028–35.
Matusik J, Gaweł A, Bahranowski K. Grafting of methanol in dickite and intercalation of hexylamine. Appl Clay Sci. 2012;56(1):63–7.
Cheng H, Hou X, Liu Q, Li X, Frost RL. New insights into the molecular structure of kaolinite–methanol intercalation complexes. Appl Clay Sci. 2015;109–110:55–63.
Komori Y, Sugahara Y, Kuroda K. Intercalation of alkylamines and water into kaolinite with methanol kaolinite as an intermediate. Appl Clay Sci. 1999;15(1–2):241–52.
Gardolinski JE, Carrera LCM, Cantao MP, Wypych F. Layered polymer-kaolinite nanocomposites. J Mater Sci. 2000;35(12):3113–9.
Gardolinski JE, Ramos LP, de Souza GP, Wypych F. Intercalation of benzamide into kaolinite. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2000;221(2):284–90.
Cheng H, Liu Q, Zhang J, Yang J, Frost RL. Delamination of kaolinite-potassium acetate intercalates by ball-milling. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010;348(2):355–9.
Franco F, Pérez-Maqueda LA, Pérez-Rodríguez JL. The effect of ultrasound on the particle size and structural disorder of a well-ordered kaolinite. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2004;274(1):107–17.
Gardolinski JEFC, Lagaly G. Grafted organic derivatives of kaolinite: I. Synthesis, chemical and rheological characterization. Clay Miner. 2005;40:537–46.
Gardolinski J, Lagaly G. Grafted organic derivatives of kaolinite: Ii. Intercalation of primary n-alkylamines and delamination. Clay Miner. 2005;40(4):547–56.
Benazzouz BK, Zaoui A. Thermal behaviour and superheating temperature of kaolinite from molecular dynamics. Appl Clay Sci. 2012;58:44–51.
Šatava V. Mechanism and kinetics from non-isothermal tg traces. Thermochim Acta. 1971;2(5):423–8.
Elder JP. The ‘e–ln(a)–f(α)’ triplet in non-isothermal reaction kinetics analysis. Thermochim Acta. 1998;318(1–2):229–38.
Sharp JH, Wentworth SA. Kinetic analysis of thermogravimetric data. Anal Chem. 1969;41(14):2060–2.
Komori Y, Sugahara Y. A kaolinite-NMF-methanol intercalation compound as a versatile intermediate for further intercalation reaction of kaolinite. J Mater Res. 1998;13(4):930–4.
Uwins PJR, Mackinnon IDR, Thompson JG, Yago AJE. Kaolinite-nmf intercalates. Clay Clay Miner. 1993;41(6):707–17.
Caglar B. Structural characterization of kaolinite-nicotinamide intercalation composite. J Mol Struct. 2012;1020:48–55.
Matusik J, Scholtzova E, Tunega D. Influence of synthesis condition on the formation of a kaolintie-methanol complex and simulation its vibrational spectra. Clay Clay Miner. 2012;60(3):227–39.
Lapides I, Yariv S. Thermo-x-ray-diffraction analysis of dimethylsulfoxide-kaolinite intercalation complexes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;97(1):19–25.
Tonle IK, Letaief S, Ngameni E, Detellier C. Nanohybrid materials from the grafting of imidazolium cations on the interlayer surfaces of kaolinite. Application as electrode modifier. J Mater Chem. 2009;19(33):5996–6003.
Caglar B, Çırak Ç, Tabak A, Afsin B, Eren E. Covalent grafting of pyridine-2-methanol into kaolinite layers. J Mol Struct. 2013;1032:12–22.
Hirsemann D, Köster TKJ, Wack J, van Wüllen L, Breu J, Senker J. Covalent grafting to μ-hydroxy-capped surfaces? A kaolinite case study. Chem Mater. 2011;23(13):3152–8.
Yui T, Uppili SR, Shimada T, Tryk DA, Yoshida H, Inoue H. Microscopic structure and microscopic environment of a polyfluorinated surfactant/clay hybrid compound: Photochemical studies of rose bengal. Langmuir. 2002;18(11):4232–9.
He H, Frost RL, Bostrom T, Yuan P, Duong L, Yang D, et al. Changes in the morphology of organoclays with HDTMA+ surfactant loading. Appl Clay Sci. 2006;31(3–4):262–71.
Ledoux RL, White JL. Infrared study of the OH group in expanded kaolinite. Science. 1964;143(3603):244–6.
Frost RL, Kristof J, Kloprogge JT, Horvath E. Rehydration of potassium acetate-intercalated kaolinite at 298 k. Langmuir. 2000;16(12):5402–8.
Cheng H, Liu Q, Yang J, Zhang J, Frost RL, Du X. Infrared spectroscopic study of halloysite-potassium acetate intercalation complex. J Mol Struct. 2011;990(1–3):21–5.
Venkataraman NV, Vasudevan S. Conformation of methylene chains in an intercalated surfactant bilayer. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105(9):1805–12.
MacPhail RA, Strauss HL, Snyder RG, Elliger CA. Carbon-hydrogen stretching modes and the structure of n-alkyl chains. 2. Long, all-trans chains. J Phys Chem. 1984;88(3):334–41.
Cheng H, Liu Q, Yang J, Ma S, Frost RL. The thermal behavior of kaolinite intercalation complexes-a review. Thermochim Acta. 2012;545:1–13.
Matusik J, Kłapyta Z, Olejniczak Z. NMR and IR study of kaolinite intercalation compounds with benzylalkylammonium chlorides. Appl Clay Sci. 2013;83–84:426–32.
Wang W, Li L, Xi S. A Fourier transform infrared study of the coagel to micelle transition of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1993;155(2):369–73.
Brown KG, Bicknell-Brown E, Ladjadj M. Raman-active bands sensitive to motion and conformation at the chain termini and backbones of alkanes and lipids. J Phys Chem. 1987;91(12):3436–42.
Kristof J, Frost RL, Felinger A, Mink J. FTIR spectroscopic study of intercalated kaolinite. J Mol Struct. 1997;410–411:119–22.
Frost RL, Kristof J, Tran TH. Kinetics of deintercalation of potassium acetate from kaolinite; a Raman spectroscopic study. Clay Miner. 1998;33(4):605–17.
Vaia RA, Teukolsky RK, Giannelis EP. Interlayer structure and molecular environment of alkylammonium layered silicates. Chem Mater. 1994;6(7):1017–22.
Lagaly G. Characterization of clays by organic compounds. Clay Miner. 1981;16(1):1–21.
Beneke K, Lagaly G. The brittle mica-like KNiAsO4 and its organic derivatives. Clay Miner. 1982;17(2):175–83.
Kwolek T, Hodorowicz M, Stadnicka K, Czapkiewicz J. Adsorption isotherms of homologous alkyldimethylbenzylammonium bromides on sodium montmorillonite. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2003;264(1):14–9.
Brindley GW, Moll WF. Complexes of natural and synthetic ca-montmorillonites with fatty acids. Am Mineral. 1965;50:1355–70.
Yuan P, Tan D, Annabi-Bergaya F, Yan W, Liu D, Liu Z. From platy kaolinite to aluminosilicate nanoroll via one-step delamination of kaolinite: effect of the temperature of intercalation. Appl Clay Sci. 2013;83–84:68–76.
Zhou Q, Shen W, Zhu J, Zhu R, He H, Zhou J, et al. Structure and dynamic properties of water saturated CTMA-montmorillonite: molecular dynamics simulations. Appl Clay Sci. 2014;97–98:62–71.
Cheng H, Li K, Liu Q, Zhang S, Li X, Frost RL. Insight into the thermal decomposition of kaolinite intercalated with potassium acetate: An evolved gas analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;117(3):1231–9.
Sahnoune F, Saheb N, Khamel B, Takkouk Z. Thermal analysis of dehydroxylation of Algerian kaolinite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107(3):1067–72.
Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1965;38(11):1881–6.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;29(11):1702–6.
Wen X, He H, Zhu J, Jun Y, Ye C, Deng F. Arrangement, conformation, and mobility of surfactant molecules intercalated in montmorillonite prepared at different pillaring reagent concentrations as studied by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2006;299(2):754–60.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Beijing Nova Program (xx2015B081), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (8164062) and Beijing talent plan (2014000020124G164), and the Open Research Project of State Key Laboratory for Coal Resources and Safe Mining, China University of Mining & Technology (SKLCRSM14KFB02)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, H., Xu, P., Wang, D. et al. Thermal decomposition behavior and de-intercalation kinetics of kaolinite/quaternary ammonium salt complexes. J Therm Anal Calorim 126, 421–433 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5572-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5572-x