Abstract
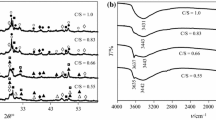
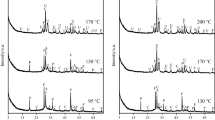
In this work, an unconventional method for calcium silicate hydrate synthesis combining utilization of silica gel waste and immobilization of F− ions in formed products, during hydrothermal treatment, was presented. The hydrothermal synthesis of calcium silicate hydrates was performed for 4, 8, 16, 24, 48 and 72 h at 200 °C when the molar ratio of the primary CaO/SiO2 mixtures was 0.83. It was estimated that F− ions were bound into a calcium fluoride during hydrothermal synthesis, because the concentration of these ions in the synthesis solution was not higher than 10 ppm. It was determined that the mechanism of hydrothermal reactions and the sequence of the compounds formed in CaO–silica gel waste–H2O mixtures are quite different from that in pure mixtures because part of the CaO reacts with F− and Al3+ ions and forms calcium fluoride and hydrogarnet, respectively. The obtained results were confirmed by the thermodynamic calculations and instrumental analysis data.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melo CR, Angioletto E, Riella HG, Peterson M, Rocha MR, Melo AR, Silva L, Strugale S. Production of metakaolin from industrial cellulose waste. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;109:1341–5.
Wajima T, Rakovan JF. Removal of fluoride ions using calcined paper sludge. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113:1027–35.
Teixeira S, Monteiro E, Silva V, Rouboa A. Prospective application of municipal solid wastes for energy production in Portugal. Energy Policy. 2014;71:159–68.
Angin D. Utilization of activated carbon produced from fruit juice industry solid waste for the adsorption of Yellow 18 from aqueous solutions. Bioresour Technol. 2014;168:259–66.
Lua Z, Caib M. Disposal methods of solid wastes from mines in transition from open-pit to underground mining. Procedia Environ Sci. 2012;16:715–21.
Park JY, Chertow MR. Establishing and testing the “reuse potential” indicator for managing wastes as resources. J Environ Manag. 2014;137:45–53.
Yu R, Shui Z. Efficient reuse of the recycled construction waste cementitious materials. J Clean Prod. 2014;78:202–7.
Kro D, Poskrobko S. Waste and fuels from waste. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;109:619–28.
Zimmermann MVG, Zattera AJ. Recycling and reuse of waste from electricity distribution networks as reinforcement agents in polymeric composites. Waste Manag. 2013;33:1667–74.
Sharma G, Pathania D, Naushad M, Kothiyal NC. Fabrication, characterization and antimicrobial activity of polyaniline Th(IV) tungstomolybdophosphate nanocomposite material: efficient removal of toxic metal ions from water. Chem Eng J. 2014;251:413–21.
Kanagaraj P, Nagendran A, Rana D, Matsuura T, Neelakandan S. Separation of macromolecular proteins and rejection of toxic heavy metal ions by PEI/cSMM blend UF membranes. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;72:223–9.
Li X, Du Y, Wu G, Li Z, Li H, Sui H. Solvent extraction for heavy crude oil removal from contaminated soils. Chemosphere. 2012;88:245–9.
Lambert A, Drogui P, Daghrir R, Zaviska F, Benzaazoua M. Removal of copper in leachate from mining residues using electrochemical technology. J Environ Manag. 2014;133:78–85.
Khan NA, Hasan Z, Jhung SH. Adsorptive removal of hazardous materials using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): a review. J Hazard Mater. 2013;244–245:444–56.
Awual MR, Hasan MM. Novel conjugate adsorbent for visual detection and removal of toxic lead(II) ions from water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014;196:261–9.
Singha AS, Guleria A. Application of vinyl monomers functionalized cellulosic biopolymer for removal of dissolved toxic metal ions from polluted water samples. J Environ Chem Eng. 2014;2:1456–66.
Awual MR, Hasan MM, Ihara T, Yaita T. Mesoporous silica based novel conjugate adsorbent for efficient selenium(IV) detection and removal from water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014;197:331–8.
Sharma A, Lee BK. Cd(II) removal and recovery enhancement by using acrylamide–titanium nanocomposite as an adsorbent. Appl Surf Sci. 2014;313:624–32.
Li K, Liang H, Qu F, Shao S, Yu H, Han Z, Du X, Li G. Control of natural organic matter fouling of ultrafiltration membrane by adsorption pretreatment: comparison of mesoporous adsorbent resin and powdered activated carbon. J Membr Sci. 2014;471:94–102.
Rad LR, Momeni A, Ghazani BF, Irani M, Mahmoudi M, Noghreh B. Removal of Ni2+ and Cd2+ ions from aqueous solutions using electrospun PVA/zeolite nanofibrous adsorbent. Chem Eng J. 2014;256:119–27.
Gusmão KAG, Gurgel LVA, Melo TMS, Carvalho CF, Gil LF. Adsorption studies of etherdiamine onto modified sugarcane bagasses in aqueous solution. J Environ Manag. 2014;133:332–42.
Bankauskaite A, Baltakys K, Eisinas A, Zadaviciute S. Study on adsorption of heavy metal ions in wastewater by synthetic layered inorganic adsorbents. Desalin Water Treat (in press), available online 26 Aug 2014; doi: 10.1080/19443994.2014.951074.
Mostafa NY, Kishar EA, Abo-El-Enein SA. FTIR study and cation exchange capacity of Fe3+- and Mg2+-substituted calcium silicate hydrates. J Alloys Compd. 2009;473:538–42.
Vespa M, Dähn R, Wieland E. Competition behaviour of metal uptake in cementitious systems: an XRD and EXAFS investigation of Nd- and Zn-loaded 11 Å tobermorite. Phys Chem Earth. 2014;70–71:32–8.
Baltakys K, Eisinas A, Dizhbite T, Jasina L, Siauciunas R, Kitrys S. The influence of hydrothermal synthesis conditions on gyrolite texture and specific surface area. Mater Struct. 2011;44:1687–701.
Baltakys K, Siauciunas R. Gyrolite formation in CaO–SiO2·nH2O–γ–Al2O3–Na2O–H2O system under hydrothermal conditions. Pol J Chem. 2007;81:103–14.
Baltakys K, Eisinas A, Barauskas I, Prichockienė E, Zaleckas E. Removal of Zn(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution using gyrolite. J Sci Ind Res. 2012;71:566–72.
Bankauskaitė A, Baltakys K. The sorption of copper ions by gyrolite in alkaline solution. Mater Sci Pol. 2009;27(3):899–908.
Napia C, Sinsiri T, Jaturapitakkul C, Chindaprasirt P. Leaching of heavy metals from solidified waste using Portland cement and zeolite as a binder. Waste Manag. 2012;32:1459–67.
Eisinas A, Baltakys K, Siauciunas R. The effect of gyrolite additive on the hydration properties of Portland cement. Cem Concr Res. 2012;42:27–38.
Eisinas A, Baltakys K, Siauciunas R. Utilization of gyrolite with impure Cd2+ ions in cement stone. Adv Cem Res. 2013;25:69–79.
Antonovič V, Aleknevičius M, Kerienė J, Pundienė I, Stonys R. Investigating the hydration of deflocculated calcium aluminate cement-based binder with catalyst waste. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;109:537–44.
Richardson IG. The calcium silicate hydrates. Cem Concr Res. 2008;38:137–58.
Baltakys K, Eisinas A, Siauciunas R. The effect of gyrolite substituted with cadmium ions on the hydration kinetics of OPC at early stages. Adv Cem Res (in press), available online 22 March 2014; doi: 10.1680/adcr.13.00048.
Aлeкин OA. Xимичecкий aнaлиз вoд cyши– (пpи cтaциoнapнoм иxизyчeнии). Гидpoмeтeopoлoгичecкoe изд-вo; 1954.
Iljina A, Baltakys K, Baltakys M, Siauciunas R. Neutralization and removal of compounds containing fluoride ions from waste silica gel. Roman J Mater. 2014;44(3):265–71.
Baltakys K. Influence of gypsum additive on the formation of calcium silicate hydrates in mixtures with C/S = 0.83 or 1.0. Mater Sci Pol. 2009;27(41):1091–101.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by a Grant (No. MIP—025/2014) from the Research Council of Lithuania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baltakys, K., Iljina, A. & Bankauskaite, A. Thermal properties and application of silica gel waste contaminated with F− ions for C-S-H synthesis. J Therm Anal Calorim 121, 145–154 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4663-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4663-4