Abstract
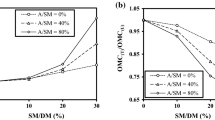
In this work, nanocomposites of ABS/PC blends reinforced with organically modified montmorillonite (OMMT) were prepared by melt blending in a twin screw extruder, and an assessment of the thermal degradation mechanisms was performed by thermogravimetric analysis. The incorporation of PC improves the thermal resistance of ABS/PC blends, with respect to pure ABS. The addition of OMMT alters the degradation mechanism and modifies the properties of blends with higher PC content, where an increase of the degradation temperature corresponding to PC becomes obvious, in comparison with the respective unreinforced blends. The gross calorific value was calculated using an oxygen bomb calorimeter, and in most of the examined nanocomposites, an inverse trend was observed between this property and the residue calculated after thermogravimetric analysis in inert atmosphere. Based on the above results, the thermal degradation behavior of ABS/PC nanocomposites was interpreted by the heat barrier effect, caused via the formation of a carbonaceous silicate char, which insulates the underlying material creating a protective barrier to heat and mass transfer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levchik SV, Weil ED. A review of recent progress in phosphorus-based flame retardants. J Fire Sci. 2006;5:345–64.
Perrer B, Pawlowski KH, Schartel B. Fire retardancy mechanisms of arylphosphates in polycarbonate (PC) and PC/acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;97:949–58.
Feyz E, Jahani Y, Esfandeh M. Effect of a nanoclay/triphenyl phosphate hybrid System on the fire retardancy of polycarbonate/acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene blend. J Appl Polym Sci. 2011;120:3435–42.
Qin H, Zhang S, Zhao C, Hu G, Yang M. Flame retardant mechanism of polymer/clay nanocomposites based on polypropylene. Polymer. 2005;46:8386–95.
Gilman JW. Flammability and thermal stability studies of polymer layered-silicate (clay) nanocomposites. Appl Clay Sci. 1999;15:31–49.
Gilman JW, Jackson CL, Morgan AB, Harris R Jr, Manias E, Giannelis EP, Wuthenow M, Hilton D, Philips SH. Flammability properties of polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites. Polypropylene and polystyrene nanocomposites. Chem Mater. 2000;12:1866–73.
Leszczyńska A, Njuguna J, Pielichowski K, Banerjee JR. Polymer/montmorillonite nanocomposites with improved thermal properties Part I. Factors influencing thermal stability and mechanisms of thermal stability improvement. Thermochim Acta. 2007;453:75–96.
Zanetti M, Kashiwagi T, Falqui L, Camino G. Cone calorimeter combustion and gasification studies of polymer layered silicate nanocomposites. Chem Mater. 2002;14:881–7.
Lomakin SM, Dubnikova IL, Shchegolikhin AN, Zaikov GE, Kozlowski R, Kim G-M, Michler GH. Thermal degradation and combustion behavior of the polyethylene/clay nanocomposite prepared by melt intercalation. J Thermal Anal Calorim. 2008;94:719–26.
Ma H, Tong L, Xu Z, Fang Z. Clay network in ABS-graft-MAH nanocomposites: rheology and flammability. Polym Degrad Stab. 2007;92:1439–45.
Barbosa R, Alves TS, Araújo EM, Mélo TJA, Camino G, Fina A, Ito EN. Flammability and morphology of HDPE/clay nanocomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:627–34.
Kannan M, Bhagawan SS, Thomas S, Joseph K. Thermogravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetric studies on nanoclay-filled TPU/PP blends. J Thermal Anal Calorim. 2013;112:1231–44.
Zhu J, Uhl FM, Morgan AB, Wilkie CA. Studies on the mechanism by which the formation of nanocomposites enhances thermal stability. Chem Mater. 2001;13:4649–54.
Galvan D, Carneiro F, Mazzucco M, Bartoli JR, Akira d’Avila M, Morales AR, Fernandes EG. Effect of organoclay mixture on the rheological properties of ABS-clay nanocomposites. Macromol Symp J. 2012;319:167–72.
Walters RN, Hackett SM, Lyon RE. Heats of combustion of high temperature polymers. Fire Mater. 2000;24:245–52.
Van Krevelen DW, TeNijenhuis K. Properties of polymers, 4th revised ed. New York: Elsevier; 2009.
Walters RN. Molar group contributions to the heat of combustion. Fire Mater. 2002;26:131–45.
Meraz L, Dominguez A, Kornhauser I, Rojas F. A thermochemical concept-based equation to estimate waste combustion enthalpy from elemental composition. Fuel. 2003;82:1499–507.
Lee KM, Han CD. Effect of hydrogen bonding on the rheology of polycarbonate/organoclay nanocomposites. Polymer. 2009;44:4573–88.
Ambre A, Jagtap R, Dewagan B. ABS nanocomposites containing modified clay. J Reinf Plast Compos. 2009;28:343–52.
Lim SK, Hong EP, Song YH, Park BJ, Choi HJ, Chin IJ. Preparation and interaction characteristics of exfoliated ABS/organoclay nanocomposite. Polym Eng Sci. 2010;50:506–12.
Hong JH, Sung YT, Song KH, Kim WN, Kang BI, Kim SL, Lee CH. Morphology and dynamic mechanical properties of poly(acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene)/polycarbonate/clay nanocomposites prepared by melt mixing. Compos Interfaces. 2007;14:519–32.
Zong R, Hu Y, Liu N, Wang S, Liao G. Evaluation of the thermal degradation of PC/ABS/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Polym Adv Technol. 2005;16:725–31.
Wang S, Hu Y, Wang Z, Yong T, Chen Z, Fan W. Synthesis and characterization of polycarbonate/ABS/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stab. 2003;80:157–61.
Nigam I, Nigam D, Marthur GN. Effect of rubber content of ABS on properties of PC/ABS blends. I. Rheological, mechanical, and thermal properties. Polym-Plast Technol Eng. 2005;44:815–32.
Balart R, Sánchez L, López J, Jiménez A. Kinetic analysis of thermal degradation of recycled polycarbonate/acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene mixtures from waste electric and electronic equipment. Polym Degrad Stab. 2006;91:527–34.
Feyz E, Jahani Y, Esfandeh M. Comparison of the effect of an organoclay, triphenylphosphate, and a mixture of both on the degradation and combustion behaviour of PC/ABS blends. Macromol Symp. 2010;298:130–7.
Bayer, Macrolon and Vivak Environmental Aspects. Technical information, June 2004.
Othman N, Basri NEA, Yunus MNM, Sidek LM. Determination of physical and chemical characteristics of electronic plastic waste (Ep-waste) resin using proximate and ultimate analysis method. ICCBT. 2008;D16:169–80.
Ozkaraca AC, Kaynak C. Contribution of nanoclays to the performance of traditional flame retardants in ABS. Polym Compos. 2012;33:420–9.
Zong R, Hu Y, Wang S, Song L. Thermogravimetric evaluation of PC/ABS/montmorillonite nanocomposite. Polym Degrad Stab. 2004;83:423–8.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the Bodossaki Foundation for its financial support. Special thanks go to Prof. D. Karonis and Dr A. Deligiannidis, Lab. of Lubricants and Fuels, School of Chemical Eng. NTUA, for carrying out the Gross Calorific value measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Triantou, M.I., Chatzigiannakis, E.M. & Tarantili, P.A. Evaluation of thermal degradation mechanisms and their effect on the gross calorific value of ABS/PC/organoclay nanocomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim 119, 337–347 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4152-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4152-1