Abstract
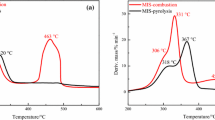
The co-combustion of biomass and biochar was investigated by thermogravimetric analysis. Several thermal parameters and mean reactivity index (R M) for different blends were used to evaluate co-combustion features. As the biomass content increased from 30 to 90 mass%, volatile releasing temperature (T v), burnout temperature (T b), and the temperature at the maximal peak (T max) generally reduced, while average mass loss rates (R a) and R M increased, the maximum mass loss rate (R max) initially decreased and then increased. Results showed that biochar additions enhanced biomass fuel reactivity over weighted average in main combustion region. Besides, blends with 10–30 mass% of biochar behaved better than those with higher biochar ratio. Synergy exists between the two components and better combustibility is feasible by co-firing biochar with biomass.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ndiema CKW, Manga PN, Ruttoh CR. Influence of die pressure on relaxation characteristics of briquetted biomass. Energy Convers Manag. 2002;43:2157–61.
Horio M, Suri A, Asahara J, Sagawa S, Aida C. Development of biomass charcoal combustion heater for household utilization. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2009;48:361–72.
Rubiera F, Arenillas A, Arias B, Pis JJ. Modification of combustion behaviour and NO emissions by coal blending. Fuel Process Technol. 2002;77:111–7.
Cumming JW, McLaughlin J. The thermogravimetric behaviour of coal. Thermochim Acta. 1982;57:253–72.
Luo SY, Xiao B, Hu ZQ, Liu SM, Guan YW. Experimental study on oxygen-enriched combustion of biomass micro fuel. Energy. 2009;34:1880–4.
Munir S, Daood SS, Nimmo W, Cunliffe AM, Gibbs BM. Thermal analysis and devolatilization kinetics of cotton stalk, sugar cane, bagasse and shea meal under nitrogen and air atmospheres. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100:1413–8.
Yu LJ, Wang S, Jiang XM, Wang N, Zhang CQ. Thermal analysis studies on combustion characteristics of seaweed. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;93:611–7.
Wang XB, Si JP, Tan HZ, Niu YQ, Xu C, Xu TM. Kinetics investigation on the combustion of waste capsicum stalks in Western China using thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011. doi:10.1007/s10973-011-1556-z.
Otero M, Gomez X, Garcıa AI, Moran A. Non-isothermal thermogravimetric analysis of the combustion of two different carbonaceous materials coal and sewage sludge. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;93:619–26.
Sasmal S, Goud VV, Mohanty K. Determination of salutary parameters to facilitate bio-energy production from three uncommon biomasses using thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011. doi:10.1007/s10973-011-1891-0.
Sun XY, Yin SM, Wang HY, Li CS, Zhang SJ. Effect of the addition of cornstalk to coal powder/coal tar combustion. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;109:817–23.
Dumanli AG, Tas S, Yurum Y. Co-firing of biomass with coals Part 1. Thermogravimetric kinetic analysis of combustion of fir (Abies bornmulleriana) wood. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;103:925–33.
Gil MV, Riaza J, Alvarez L, Pevida C, Pis JJ, Rubiera F. A study of oxy-coal combustion with steam addition and biomass blending by thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;109:49–55.
Gil MV, Casal D, Pevida C, Pis JJ, Rubiera F. Thermal behaviour and kinetics of coal/biomass blends during co-combustion. Bioresour Technol. 2010;101:5601–8.
Li XG, Lv Y, Ma BG, Jian SW, Tan HB. Thermogravimetric investigation on co-combustion characteristics of tobacco residue and high-ash anthracite coal. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102:9783–7.
Varol M, Atimtay AT, Bay B, Olgun H. Investigation of co-combustion characteristics of low quality lignite coals and biomass with thermogravimetric analysis. Thermochim Acta. 2010;510:195–201.
Backreedy RI, Jones JM, Pourkashanian M, Williams A. Burn-out of pulverised coal and biomass chars. Fuel. 2003;82:2097–105.
Kastanaki E, Vamvuka D. A comparative reactivity and kinetic study on the combustion of coal–biomass char blends. Fuel. 2006;85:1186–93.
Sahu SG, Sarkar P, Chakraborty N, Adak AK. Thermogravimetric assessment of combustion characteristics of blends of a coal with different biomass chars. Fuel Process Technol. 2010;91:369–78.
Tillman DA. Biomass cofiring: the technology, the experience, the combustion consequences. Biomass Bioenergy. 2000;19:365–84.
Haykiri-Acma H, Yaman S. Effect of co-combustion on the burnout of lignite/biomass blends: a Turkish case study. Waste Manag. 2008;28:2077–84.
Ghetti P, Ricca L, Angelini L. Thermal analysis of biomass and corresponding pyrolysis products. Fuel. 1996;75:565–73.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20876066) and Hubei Province Scientific and Technological Project (No. 2007AA204B01). The authors are grateful to the Analytical and Testing Center of Huazhong University of Science and Technology for carrying out the ultimate analysis and the thermogravimetric analysis of the samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, Q., Qi, F., Cheng, G. et al. Thermogravimetric analysis of co-combustion of biomass and biochar. J Therm Anal Calorim 112, 1475–1479 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2744-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2744-1