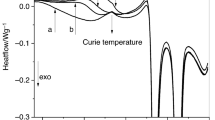
Abstract
The frequency dependences of the complex-specific heat of the sodium borate glasses, xNa2O·(100 − x)B2O3, where x denotes molar concentration of Na2O, have been investigated by temperature-modulated DSC. The temperature dependences of α-relaxation time have been analyzed in Angell plot, and the fragility index has been determined. The composition dependence of the fragility index has been discussed on the basis of the variations of the structural units of the borate network. The origin of the fragility of the borate system relates to the distribution of the coordination number of boron atom.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laughlin WT, Unlman DR. Viscous flow in simple organic liquids. J Phys Chem. 1972;76:2317–25.
Angell CA. Relaxation in liquids, polymers and plastic crystals—strong/fragile patterns and problems. J Non-Cryst Solids. 1991;131–133:13–31.
Bray PJ, O’Keefe JG. Nuclear magnetic resonance investigations of the structure of alkali borate glasses. Phys Chem Glasses. 1963;4:37–46.
Zhong J, Bray PJ. Change in boron coordination in alkali borate glasses, and mixed alkali effects, as elucidated by NMR. J Non-Cryst Solids. 1989;111:67–76.
Chryssikos GD, Kamitsos EI. Borate structures by vibrational spectroscopy. In: Wright AC, Feller AC, Hannon AC, editors. Borate glasses, crystals & melts. Sheffielf: The Society of Glass Technology; 1997. p. 128–39.
Hassan AK, Torell LM, Börjesson L, Doweidar H. Structural changes of B2O3 through the liquid-glass transition range: a Raman-scattering study. Phys Rev B. 1992;45:12797–805.
Fukumi K, Ogawa K, Hayakawa J. Intensities of Raman bands in borate glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids. 1992;151:217–21.
Fukawa Y, Matsuda Y, Ike Y, Kodama M, Kojima S. Glass transitions and elastic properties of lithium borate glasses over a wide composition range studied by micro-brillouin scattering. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2008;47:3833–5.
Ike Y, Matsuda Y, Kojima S, Kodama M. Brillouin scattering study of liquid glass transition in lithium borate glass. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2006;45:4474–8.
Kodama M. Ultrasonic velocity in sodium-borate glasses. J Mater Sci. 1991;26:4048–53.
Kodama M, Matsushita T, Kojima S. Velocity of sound and elastic properties of Li2O–B2O3 glasses. Jpn J Appl Phys. 1995;34:2570.
Matsuda Y, Fukawa Y, Ike Y, Kodama M, Kojima S. Dynamic specific heat, glass transition, and non-Debye nature of thermal relaxation in lithium borate glasses. J Phys Soc Jpn. 2008;77:084602-1–8.
Matsuda Y, Fukawa Y, Matsui C, Ike Y, Kodama M, Kojima S. Calorimetric study of the glass transition dynamics in lithium borate glasses over a wide composition range by modulated DSC. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2007;256:127–31.
Matsuda Y, Matsui C, Ike Y, Kodama M, Kojima S. Non-Debye nature in thermal relaxation and thermal properties of lithium borate glasses studied by Modulated DSC. J Therm Anal Cal. 2006;85:725–30.
Weyer S, Hensel A, Schick C. Phase angle correction for TMDSC in the glass-transition region. Thermochim Acta. 1997;304–305:267–75.
Matsuda Y, Fukawa Y, Kawashima M, Kojima S. Fragility variation of lithium borate glasses studied by temperature-modulated DSC. AIP Conf Proc. 2008;982:207. doi:10.1063/1.2897785.
Chryssikos GD, Kamitsos EI, Yiannopoulos YD. Towards a structural interpretation of fragility and decoupling trends in borate systems. J Non-Cryst Solids. 1996;196:244–8.
Vilgis TA. Random energies, random coordination numbers, the Vogel-Fulcher law, and nonexponential relaxation. J Phys: Condens Matter. 1990;2:3667–71.
Vilgis TA. Strong and fragile glasses—a powerful classification and its consequences. Phys Rev B. 1993;47:2882–5.
Matsuda Y, Fukawa Y, Kawashima M, Mamiya S, Kojima S. Dynamic glass transition and fragility of lithium borate binary glass. Solid State Ionics. 2008;179:2424–7.
Majerus O, Cormier L, Calas G, Beuneu B. Temperature-induced boron coordination change in alkali borate glasses and melts. Phys Rev B. 2003;67:024210-1–7.
Yano T, Kunimine N, Shibata S, Yamane M. Structural investigation of sodium borate glasses and melts by Raman spectroscopy. II. Conversion between BO4 and BO2O− units at high temperature. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2003;321:147–56.
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (Y.M.) is thankful for the JSPS Research Fellowship 19-574.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukawa, Y., Matsuda, Y., Kawashima, M. et al. Determination of complex-specific heat and fragility of sodium borate glasses by temperature-modulated DSC. J Therm Anal Calorim 99, 39–44 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0522-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0522-5