Abstract
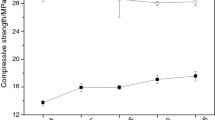
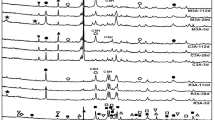
Thermogravimetric (TG) analysis was applied to the characterisation of the pozzolanic reaction in mortars containing the supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) pitchstone fines (PF) and fly ash (FA) as partial replacements for Portland cement (PC). TG analysis was used to determine the proportion of calcium hydroxide (CH) present from the hydration of the PC based on the dehydroxylation of the CH present in the blended PC-SCM mortars. The consumption of CH indicated that both SCMs underwent the pozzolanic reaction and that PF was found to compare favourably in its pozzolanic reactivity of FA, the industry and globally accepted standard artificial pozzolan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Roszczynialski, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 70 (2002) 387.
J. I. Bhatty and K. J. Reid, Thermochim. Acta, 91 (1985) 95.
A. Moropoulou, A. Bakolas and E. Aggelakopoulou, Thermochim. Acta, 420 (2004) 135.
B. Uzal, L. Turanli and P. K. Mehta, ACI Mater. J., 104 (2007) 535.
S. K. Das and Yudhbir, Cem. Concr. Res., 36 (2006) 1827.
R. J. Detwiler and P. K. Mehta, ACIMater. J., 86 (1989) 609.
C. Duran Atis and C. Bilim, Building Environ., 42 (2007) 3060.
A. L. A. Fraay, J. M. Bijen and Y. M. de Haan, Cem. Concr. Res., 19 (1989) 235.
M. O’Farrell, B. B. Sabir and S. Wild, Cem. Concr. Compos., 28 (2006) 790.
L. H. Yu, H. Ou and L. L. Lee, Cem. Concr. Res., 33 (2003) 73.
A. Ray, R. Sriravindrarajah, J. P. Guerbois, P. S. Thomas, S. Border, H. Ray, J. Haggman and P. Joyce, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 88 (2007) 279.
ASTM C 311-05, Standard test methods for sampling and testing fly ash or natural pozzolans for use in Portland-cement concrete. 2005, ASTM Int.
ASTM C 618-05, Standard specification for coal fly ash and raw or calcined natural pozzolan for use in concrete, 2005, ASTM Int.
ASTM C 1240-05, Standard specification for silica fume used in cementitious mixtures. 2005, ASTM Int.
ASTM C 305-99, Standard practice for mechanical mixing of hydraulic cement pastes and mortars of plastic consistency. 1999, ASTM International.
K. Hover and T. Stokes, Concr. Int., 17 (1995) 52.
ASTM C 109/C 109M-05, Standard test method for compressive strength of hydraulic cement mortars (using 2-in. or [50-mm] cube specimens). 2005, ASTM Int.
ASTM C 511-05, Standard specification for mixing rooms, moist cabinets, moist rooms and water storage tanks used in the testing of hydraulic cements and concretes, 2005, ASTM Int.
K. Vessalas, A. S. Ray, P. S. Thomas, R. S. Ravindrarajah., P. Joyce, J. Haggman, P. A. Joyce and T. M. K. Vo, Cem. Concr. Res., in preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vessalas, K., Thomas, P.S., Ray, A.S. et al. Pozzolanic reactivity of the supplementary cementitious material pitchstone fines by thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim 97, 71–76 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9708-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9708-5