Abstract
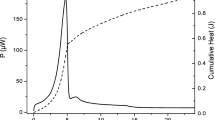
The inhibitory effects of three berberine alkaloids (BAs) from Coptis chinensis Franch on Bifidobacterium adolescentis growth were investigated by microcalorimetry. The growth rate constant (k) and maximum heat-output power (Pmax) decreased and peak time of maximum heat-output power (tp) prolonged with the increase of BAs concentration. Half inhibitory ratios (IC50) BAs were respectively 790.3 (berberine), 339.6 (coptisine) and 229.8 μL−1 (palmatine), which indicated the sequence of their antimicrobial activity: berberine<coptisine<palmatine. Combined with previous findings, the sequence which could show the bioactivity of Bacillus shigae and Escherichia coli was: berberine>coptisine>palmatine. The structure-function relationship of BAs indicated that the functional group methylenedioxy or methoxyl at C2 and C3 might be the major group inducing the activities of BAs on E. coli and B. adolescentis. Meanwhile, the substituent groups at C2, C3, C9 and C10 almost had equal effect on B. shigae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
China Pharmacopoeia Committee, Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (1st Div., 2005 ed.), Beijing 2005, p. 213.
D. M. Ding, Pharmacodynamic Action and Clinic of Chinese Medicinal Materials, Beijing 1999, p. 154.
H. X. Guo, Foundation and Application of Probiotics, Beijing 2002, p. 3.
R. Roškar, M. Vivoda and V. Kmetec, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 92 (2008) 791.
X. S. Shen, Y. Liu, C. P. Zhou and R. M. Zhao, Acta Chim. Sinica, 58 (2000) 1463.
L. N. Yang, F. Xu, L. X. Sun, Z. B. Zhao and C. G. Song, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 93 (2008) 417.
L. Ruan, Y. Wang, L. Wai and Y. Hoi-Fu, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 89 (2007) 953.
Y. W. Wu, W. Y. Gao, X. H. Xiao and Y. Liu, Thermochim. Acta, 429 (2005) 167.
X. Li, C. Wang, J. Li and Z. Wang, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 89 (2007) 899.
X. J. Chen, W. S. Feng, W. Miao, Y. H. Yu, Y. F. Shen, C. Y. Wan and J. H. Peng, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 94 (2008) 779.
Y. Liu, C. N. Yan, T. Z. Wang and R. M Zhao, Thermochim. Acta, 333 (1999) 103.
A. M. Tan, Y. Q. Huang and S. S. Qu, J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods, 37 (1998) 91.
R. N. Alnoncourt, B. Graf, X. Xia and M. Muhler, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 91 (2008) 173.
M. L. Antonelli and R. F. Tornelli, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 91 (2008) 113.
L. N. Yang, F. Xu, L. X. Sun and Z. B. Zhao, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 93 (2008) 583.
D. Yan, C. Jin, X. H. Xiao and X. P. Dong, Sci. China Ser. B-Chem., 50 (2007) 638.
D. Yan, C. Jin, X. H. Xiao and X. P. Dong, J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods, 70 (2008) 845.
X. Li, Y. Liu, J. Wu, H. G Liang and S. S. Qu, Thermochim. Acta, 387 (2002) 57.
X. Y. Su, PhD Thesis, Dalian Institute Chem. Phys., Chin. Acad. Sci., China (2006) Dalian.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, D., Han, Y.M., Wei, L. et al. Effect of berberine alkaloids on Bifidobacterium adolescentis growth by microcalorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim 95, 495–499 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9273-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9273-y