Abstract
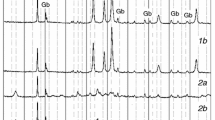
Effect of mechanical grinding of hydromagnesite on the reaction pathway and kinetic behaviors of the thermal decomposition process was investigated by means of thermoanalytical techniques, together with crystallographic and morphological measurements. A crystalline hydromagnesite, the as-received sample, was decomposed in two distinguished mass loss steps of overlapped dehydration-dehydroxylation and dehydroxylation-decarbonation via an amorphous intermediate of carbonate compound. Thermal decomposition of an amorphous hydromagnesite, obtained by mechanical grinding of the as-received sample, was characterized by three well-separated decomposition processes of dehydration, dehydroxylation and decarbonation. The kinetic behaviors of the respective decomposition steps were estimated separately using a mathematical deconvolution of the partially overlapped reaction steps. From the formal kinetic analyses of the respective reaction processes, it was revealed that the dehydration and dehydroxylation processes indicate the decelerate rate behaviors controlled by diffusion, while the rate behavior of nucleation limited type is predominant for the decarbonation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Sawada, K. Uematsu, N. Mizutani and M. Kato, J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem., 40 (1978) 979.
Y. Sawada, K. Uematsu, N. Mizutani and M. Kato, Thermochim. Acta, 27 (1978) 45.
Y. Sawada, J. Yamaguchi, O. Sakurai, K. Uematsu, N. Mizutani and M. Kato, Thermochim. Acta, 32 (1979) 277.
Y. Sawada, J. Yamaguchi, O. Sakurai, K. Uematsu, N. Mizutani and M. Kato, Thermochim. Acta, 33 (1979) 127.
Y. Sawada, J. Yamaguchi, O. Sakurai, K. Uematsu, N. Mizutani and M. Kato, Thermochim. Acta, 34 (1979) 233.
C. Padeste, H. R. Oswald and A. Reller, Mater. Res. Bull., 26 (1991) 1263.
G. Helou and S. A. Tariq, Thermochim. Acta, 228 (1993) 123.
V. R. Choudhary, S. G. Pataskar, V. G. Gunjikar and G. B. Zope, Thermochim. Acta, 232 (1994) 95.
T. R. Rao and V. S. Chohan, Chem. Eng. Technol., 18 (1995) 359.
N. Khan, D. Dollimore, K. Alexander and F. W. Wilburn, Thermochim. Acta, 367/368 (2001) 321.
Y. Sawada, Mater. Integr., 12 (1999) 65, in Japanese.
S. A. Morozov, A. A. Malkov and A. A. Matygin, Russ. J. Gen. Chem., 73 (2003) 41.
S. A. Morozov, A. A. Malkov and A. A. Matygin, Russ. J. Gen. Chem., 76 (2003) 7.
Q. Li, Y. Ding, G. Yu, C. Li, F. Li and Y. Qian, Solid State Commun., 125 (2003) 117.
J. Y. Kim, H. S. Jung and K. S. Hong, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 88 (2005) 784.
M. Senna, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 90 (2007) 107.
O. T. Sorensen and J. Rouquerol, Eds, Sample Controlled Thermal Analysis. Kluwer, Dordrecht 2003.
N. Koga, J. M. Criado and H. Tanaka, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 60 (2000) 943.
JCPDS 25-0513.
A. Botha and C. A. Strydom, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 71 (2003) 987.
J. Lanas and J. I. Alvarez, Thermochim. Acta, 421 (2004) 123.
Y. Waseda and A. Muramatsu, Eds, Morphology Control of Materials and Nanoparticles, Springer, 2004.
JCPDS 08-0479.
JCPDS 31-0804.
JCPDS 45-0946.
H. L. Friedman, J. Polym. Sci. C, 6 (1964) 183.
T. Ozawa, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 38 (1965) 1881.
T. Ozawa, J. Thermal Anal., 2 (1970) 301.
T. Ozawa, Thermochim. Acta, 100 (1986) 109.
T. Ozawa, J. Thermal Anal., 31 (1986) 547.
N. Koga, Thermochim. Acta, 258 (1995) 145.
F. J. Gotor, J. M. Criado, J. Malek and N. Koga, J. Phys. Chem. A, 104 (2000) 10777.
J.M. Criado, L. A. Perez-Maqueda, F. J. Gotor, J. Malek and N. Koga, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 72 (2003) 901.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koga, N., Yamane, Y. Effect of mechanical grinding on the reaction pathway and kinetics of the thermal decomposition of hydromagnesite. J Therm Anal Calorim 93, 963–971 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-007-8616-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-007-8616-4