Abstract
In this study, we present the formation of mikania micrantha (MM)/chitosan (CS) electrospun nanocomposites using polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) back layer. The therapeutic compounds of MM were extracted through a methanol extraction process. Results show that the nanocomposites exhibit antibacterial activity against gram-positive (S. aureus) and gram-negative (E. coli) bacteria, with a zone of inhibition of around 20–25 mm. MM-2/CS was found to be more effective than MM-1/CS due to the increased amount of MM extraction. The nanofibers exhibited smooth fiber formation with a mean diameter of around 173–185 nm as observed by SEM. Moreover, the incorporation of PVA with MM-chitosan nanocomposites improved their thermal and moisture management properties. Cytotoxicity test showed that only around 5% of the exposed cells survived in the Vero cell line. The FTIR spectra demonstrated the presence of functional groups of PVA, chitosan, and MM in the nanofibers. Based on our findings, we suggest that nanofibers prepared from bioactive agents of MM may have the potential for biomedical applications, such as wound dressing materials.
Graphical Abstract

Highlights
-
Biobased antibacterial nanofibers for potential biomedical applications.
-
Plant extract (Mikania micrantha) was employed in biopolymers for electrospinning.
-
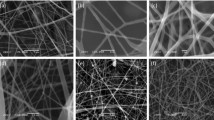
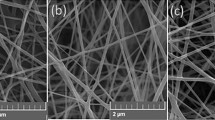
Smooth fiber formation was observed by SEM analysis.
-
Prepared nanocomposites demonstrated good mechanical, absorbance, and antibacterial properties.
-
PVA back layer improved the overall properties of nano mat.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandrasekar S, Vijayakumar S, Rajendran R (2014) Application of chitosan and herbal nanocomposites to develop antibacterial medical textile. Biomed Aging Pathol 4(1):59–64
Li Y, Li J, Li Y, Wang X-X, Cao A-C (2013) Antimicrobial Constituents of the Leaves of Mikania micrantha HB K. Plos one 8(10):e76725
Zohmachhuana A, Tlaisun M, Mathipi V, Khawlhring L, Priya JS (2022) Suppression of the RAGE gene expression in RAW 264.7 murine leukemia cell line by ethyl acetate extract of Mikania micrantha (L.) Kunth. J Appl Biol Biotechnol 10(5):107–114
Islam MA, Begum HA, Shahid MA, Ali A (2020) Antibacterial electrospun nanofibers from poly (vinyl alcohol) and Mikania micrantha with augmented moisture properties: formation and evaluation. J Text Inst 112(10):1–9
Islam MA, Begum HA, Shahid MA, Ali A (2021) Antibacterial electrospun nanofibers from poly (vinyl alcohol) and Mikania micrantha with augmented moisture properties: formation and evaluation. J Text Inst 112(10):1602–1610
Matawali A, Chin LP, Eng HS, Gansau JA (2016) Antibacterial and phytochemical investigations of Mikania micrantha HBK (Asteraceae) from Sabah, Malaysia. Trans Sci Technol 3(1-2):244–250
Zhuang S, Hao C, Feng J, Zhang X (2010) Active antifungal components of Mikania micrantha HBK. J Zhejiang Univ (Agriculture Life Sci) 36(3):293–298
Facey PC, Pascoe KO, Porter RB, Jones AD (1999) Investigation of Plants used in Jamaican Folk Medicine for Anti‐bacterial Activity. J Pharm Pharmacol 51(12):1455–1460
Sheam M, Haque Z, Nain Z (2020) Towards the antimicrobial, therapeutic and invasive properties of Mikania micrantha Knuth: a brief overview. J Adv Biotechnol Exp Ther 3(2):92–101
Bakir M, Facey PC, Hassan I, Mulder WH, Porter RB (2004) Mikanolide from Jamaican Mikania micrantha. Acta Crystallogr Sect C: Cryst Struct Commun 60(11):o798–o800
No JTK, Baru P (2018) Isolation of antibacterial compound from the leaves of mikania micrantha kunth. Available from https://www.jpsr.pharmainfo.in/Documents/Volumes/ispst2018/jpsr112018con16.pdf
Ghosh A, Das BK, Roy A, Mandal B, Chandra G (2008) Antibacterial activity of some medicinal plant extracts. J Nat Med 62(2):259–262
Ali A, Islam SM, Mohebbullah M, Uddin MN, Hossain MT, Saha SK, Jamal MSI (2020) Antibacterial electrospun nanomat from nigella/PVA system embedded with silver. J Text Inst 112(4):1–7
Li R, Cheng Z, Yu X, Wang S, Han Z, Kang L (2019) Preparation of antibacterial PCL/PVP-AgNP Janus nanofibers by uniaxial electrospinning. Mater Lett 254:206–209
Yang S, Liu Y, Jiang Z, Gu J, Zhang D (2018) Thermal and mechanical performance of electrospun chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers with graphene oxide. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 1(4):722–730
Dziemidowicz K, Sang Q, Wu J, Zhang Z, Zhou F, Lagaron JM, Mo X, Parker GJ, Yu D-G, Zhu L-M, Williams GR (2021) Electrospinning for healthcare: recent advancements. J Mater Che 9:939–951
Hu H, Ye B, Lv Y, Zhang Q (2019) Preparing antibacterial and in-situ formable double crosslinking chitosan/hyaluronan composite hydrogels. Mater Lett 254:17–20
Uddin MN, Jamal MSI, Ali MY, Darda MA, Mahedi SI (2023) Tissue engineering and the potential use of chitin. Emergent Mater 1–13
Huang Z-M, Zhang Y-Z, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2003) A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 63(15):2223–2253
Fong H (2001) Electrospinning and the formation of nanofibers. J Fiber Sci Technol 64(1):36–44
Ziyadi H, Baghali M, Bagherianfar M, Mehrali F, Faridi-Majidi R (2021) An investigation of factors affecting the electrospinning of poly (vinyl alcohol)/kefiran composite nanofibers. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4(3):768–779
Rieger KA, Birch NP, Schiffman JD (2013) Designing electrospun nanofiber mats to promote wound healing–a review. J Mater Chem B 1(36):4531–4541
Zhang Y, Lim CT, Ramakrishna S, Huang Z-M (2005) Recent development of polymer nanofibers for biomedical and biotechnological applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 16(10):933–946
Yokoyama Y, Hattori S, Yoshikawa C, Yasuda Y, Koyama H, Takato T, Kobayashi H (2009) Novel wet electrospinning system for fabrication of spongiform nanofiber 3-dimensional fabric. Mater Lett 63(9-10):754–756
Ali A, Mohebbullah M, Shahid MA, Alam S, Uddin MN, Miah MS, Jamal MSI, Khan MS (2020) PVA-Nigella sativa nanofibrous mat: antibacterial efficacy and wound healing potentiality. J Text Inst 112(10):1–11
Chen Y, Qian Q, Liu X, Xiao L, Chen Q (2010) LaOCl nanofibers derived from electrospun PVA/Lanthanum chloride composite fibers. Mater Lett 64(1):6–8
Stone SA, Gosavi P, Athauda TJ, Ozer RR (2013) In situ citric acid crosslinking of alginate/polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers. Mater Lett 112:32–35
Shao C, Kim H-Y, Gong J, Ding B, Lee D-R, Park S-J (2003) Fiber mats of poly (vinyl alcohol)/silica composite via electrospinning. Mater Lett 57(9-10):1579–1584
Koski A, Yim K, Shivkumar S (2004) Effect of molecular weight on fibrous PVA produced by electrospinning. Mater Lett 58(3-4):493–497
Krumova M, Lopez D, Benavente R, Mijangos C, Perena J (2000) Effect of crosslinking on the mechanical and thermal properties of poly (vinyl alcohol). Polymer 41(26):9265–9272
Shahid MA, Ali A, Uddin MN, Miah S, Islam SM, Mohebbullah M, and Jamal MSI (2020) Antibacterial wound dressing electrospun nanofibrous material from polyvinyl alcohol, honey and Curcumin longa extract. J Industrial Text
Liu C, Lin Y, Dong Y, Wu Y, Bao Y, Yan H, Ma J (2020) Fabrication and investigation on Ag nanowires/TiO2 nanosheets/graphene hybrid nanocomposite and its water treatment performance. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 3(3):402–414
Mangiapia G, Ricciardi R, Auriemma F, De Rosa C, Lo Celso F, Triolo R, Heenan RK, Radulescu A, Tedeschi AM, D'Errico G (2007) Mesoscopic and microscopic investigation on poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels in the presence of sodium decylsulfate. J Phys Chem B 111(9):2166–2173
Qi M, Gu Y, Sakata N, Kim D, Shirouzu Y, Yamamoto C, Hiura A, Sumi S, Inoue K (2004) PVA hydrogel sheet macroencapsulation for the bioartificial pancreas. Biomaterials 25(27):5885–5892
Qi L, Xu Z, Jiang X, Hu C, Zou X (2004) Preparation and antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr Res 339(16):2693–2700
Chandy T, Sharma CP (1990) Chitosan-as a biomaterial. Biomater, Artif cells Artif organs 18(1):1–24
Bhattarai N, Edmondson D, Veiseh O, Matsen FA, Zhang M (2005) Electrospun chitosan-based nanofibers and their cellular compatibility. Biomaterials 26(31):6176–6184
Xu J, Zhang J, Gao W, Liang H, Wang H, Li J (2009) Preparation of chitosan/PLA blend micro/nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater Lett 63(8):658–660
Liu Y, Park M, Shin HK, Pant B, Park S-J, Kim H-Y (2014) Preparation and characterization of chitosan-based nanofibers by ecofriendly electrospinning. Mater Lett 132:23–26
Kim JH, Lee H, Jatoi AW, Im SS, Lee JS, Kim I-S (2016) Juniperus chinensis extracts loaded PVA nanofiber: Enhanced antibacterial activity. Mater Lett 181:367–370
Shekarforoush E, Ajalloueian F, Zeng G, Mendes AC, Chronakis IS (2018) Electrospun xanthan gum-chitosan nanofibers as delivery carrier of hydrophobic bioactives. Mater Lett 228:322–326
Ali A, Shahid MA, Hossain MD, Islam MN (2019) Antibacterial bi-layered polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-chitosan blend nanofibrous mat loaded with Azadirachta indica (neem) extract. Int J Biol Macromol 138:13–20
Saifuddin N, Dinara S (2011) Pretreatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) using magnetic chitosan. E-J Chem 8(S1):S67–S78
Satpathy A, Pal A, Sengupta S, Das A, Hasan MM, Ratha I, Barui A, Bodhak S (2019) Bioactive nano-hydroxyapatite doped electrospun PVA-chitosan composite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering applications. J Indian Inst Sci 99:289–302
Fathollahipour S, Abouei Mehrizi A, Ghaee A, Koosha M (2015) Electrospinning of PVA/chitosan nanocomposite nanofibers containing gelatin nanoparticles as a dual drug delivery system. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 103(12):3852–3862
Koosha M, Mirzadeh H, Shokrgozar MA, Farokhi M (2015) Nanoclay-reinforced electrospun chitosan/PVA nanocomposite nanofibers for biomedical applications. RSC Adv 5(14):10479–10487
Liu C, Chan KW, Shen J, Wong HM, Yeung KWK, Tjong SC (2015) Melt-compounded polylactic acid composite hybrids with hydroxyapatite nanorods and silver nanoparticles: Biodegradation, antibacterial ability, bioactivity and cytotoxicity. RSC Adv 5(88):72288–72299
Shahid MA, Khan MS (2022) Preparation and characterization of electrospun nanofiber membrane from polyvinyl alcohol loaded with Glycyrrhiza glabra extract. Polym Polym Compos 30:09673911221109422
Rufatto LC, Gower A, Schwambach J, Moura S (2012) Genus Mikania: chemical composition and phytotherapeutical activity. Rev Brasileira de Farmacogn 22:1384–1403
Khatun R, Nasrin L, Roy S, Tantry M, Abdur Rahman M (2017) Comparative antimicrobial evaluation of available Mikania species in Bangladesh. Int J Plant Res 7:36–38
Sumantri IB, Wahyuni HS, Mustanti LF (2020) Total phenolic, total flavonoid and phytochemical screening by FTIR spectroscopic of standardized extract of Mikania micrantha leaf. Pharmacognosy J 12(6):1395–1401
Demétrio AM, Rodrigues AC, de Athayde AE, Biavatti MW, Oliveira FMC, Garcia FL, Lusa MG (2023) Structural, histochemical, and phytochemical characterization of Mikania cordifolia (L. f.) Willd.(Asteraceae) in a coastal dune environment. Flora. 152318
Borkataky M, Bhusan B, Saikia L (2013) Antimicrobial activity and phytochemical screening of some common weeds of asteraceae family. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 23(1):116–120
Dev VG, Venugopal J, Sudha S, Deepika G, Ramakrishna S (2009) Dyeing and antimicrobial characteristics of chitosan treated wool fabrics with henna dye. Carbohydr Polym 75(4):646–650
Mc P-A, Ocotero VM, Balcazar RI, Jiménez FG (2010) Phytochemical and pharmacological studies on Mikania micrantha HBK (Asteraceae). Phyton 79:77
Uddin MN, Mohebbullah M, Islam SM, Uddin MA, Jobaer M (2022) Nigella/honey/garlic/olive oil co-loaded PVA electrospun nanofibers for potential biomedical applications. Prog Biomater 11:431–446
Uddin MN, Jobaer M, Mahedi SI, Ali A (2022) Protein–based electrospun nanofibers: electrospinning conditions, biomedical applications, prospects, and challenges. J Text Inst 1–26
Marutescu L, Popa M, Saviuc C, Lazar V, Chifiriuc MC (2017) Botanical pesticides with virucidal, bactericidal, and fungicidal activity. New Pesticides Soil Sensors 311–335
Asif M (2012) Antimicrobial potential of Azadirachta indica against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 1(4):78–83
Ali A, Islam SM, Mohebbullah M, Uddin MN, Hossain MT, Saha SK, Jamal MSI (2021) Antibacterial electrospun nanomat from nigella/PVA system embedded with silver. J Text Inst 112(4):561–567
Abidi N, Hequet E, Cabrales L, Gannaway J, Wilkins T, Wells LW (2008) Evaluating cell wall structure and composition of developing cotton fibers using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis. J Appl Polym Sci 107(1):476–486
Lee HW, Karim MR, Park JH, Bae DG, Oh W, Cheong IW, Yeum JH (2009) Electrospinning and characterisation of poly (vinyl alcohol) blend submicron fibres in aqueous solutions. Polym Polym Compos 17(1):47–54
Naeimi A, Payandeh M, Ghara AR, Ghadi FE (2020) In vivo evaluation of the wound healing properties of bio-nanofiber chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol incorporating honey and Nepeta dschuparensis. Carbohydr Polym 240:116315
Pakravan M, Heuzey M-C, Ajji A (2011) A fundamental study of chitosan/PEO electrospinning. Polymer 52(21):4813–4824
Sharma R, Singh N, Gupta A, Tiwari S, Tiwari SK, Dhakate SR (2014) Electrospun chitosan–polyvinyl alcohol composite nanofibers loaded with cerium for efficient removal of arsenic from contaminated water. J Mater Chem A 2(39):16669–16677
Cotesta S, Stahl M (2006) The environment of amide groups in protein–ligand complexes: H-bonds and beyond. J Mol Modeling 12:436–444
Mayilswamy N, Jaya Prakash N, Kandasubramanian B (2022) Design and fabrication of biodegradable electrospun nanofibers loaded with biocidal agents. International J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 72(6):433–459
Acknowledgements
Immense gratitude goes to the Department of Textile Engineering, DUET, for providing lab facilities.
Author contributions
CRediT authorship contribution statement. MdNU: Concept generation, experimental, drafted manuscript. MdM: Experimental and proofread. SMI: Experimental, proofread. MdJ: Raw material collection and proofread. SIM: Proofreading and correction. AA: Supervised the work, edited, and proofread.
Funding
The research team did not receive grants or funds from any public, private, or commercial organizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Uddin, M.N., Mohebbullah, M., Islam, S.M. et al. Preparation and characterization of mikania micrantha (MM)/chitosan (CS) nanocomposites with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) back layer. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 108, 84–97 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06182-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06182-y