Abstract
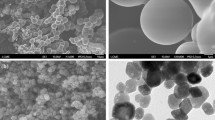
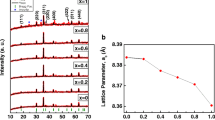
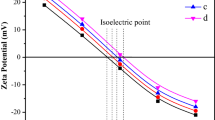
The CuxFe3-xO4 nanoparticles with a cubic structure and varying ratios of copper (Cu) and iron (Fe) (x = 0.75, 1, 1.25) were synthesized using the one-step solution combustion synthesis (SCS) method. CuxFe3-xO4 nanoparticles were synthesized via solution combustion synthesis, utilizing copper nitrate and iron nitrate as the oxidizing agents, and glycine as the fuel. The synthesis was carried out under different conditions, including the presence and absence of air, to investigate their effects on the final product. X-ray diffraction (XRD), the Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry analysis (DSC), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), high-resolution (HR) TEM and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) measurements were used to confirm the formation and structure of the as-prepared nanopowders. The use of the open system during the synthesis process leads to a higher occurrence of secondary phase formation in the structure of the material. The findings obtained from various analysis confirms that the closed system used in the study yields efficient results.
Graphical Abstract

CuxFe3-xO4 nanoparticles were synthesized via solution combustion synthesis in a closed system.
Highlights
-
CuxFe3-xO4 nanoparticles were synthesized using the solution combustion synthesis.
-
Effect of open and closed systems were investigated on nanoparticle properties.
-
Structural, magnetic, and thermal properties were studied in detail.
-
The advantages of a closed system were demonstrated.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lazarova T, Georgieva M, Tzankov D, Voykova D, Aleksandrov L, Cherkezova-Zheleva Z, Kovacheva D (2017) Influence of the type of fuel used for the solution combustion synthesis on the structure, morphology and magnetic properties of nanosized NiFe2O4. J Alloy Compd 700:272–283
Houshiar M, Zebhi F, Razi ZJ, Alidoust A, Askari Z (2014) Synthesis of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles using combustion, coprecipitation, and precipitation methods: A comparison study of size, structural, and magnetic properties. J Magn Magn Mater 371:43–48
Vinosha PA, Mely LA, Jeronsia JE, Krishnan S, Das SJ (2017) Synthesis and properties of spinel ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles by facile co-precipitation route. Optik 134:99–108
Selvan RK, Augustin CO, Berchmans LJ, Saraswathi R (2003) Combustion synthesis of CuFe2O4. Mater Res Bull 38:41–54
Aslibeiki B, Kameli P, Ehsani MH, Salamati H, Muscas G, Agostinelli E, Foglietti V, Casciardi S, Peddis D (2016) Solvothermal synthesis of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles: the role of polymer coating on morphology and magnetic properties. J Magn Magn Mater 399:236–244
Liu YC, Fu YP (2010) Magnetic and catalytic properties of copper ferrite nanopowders prepared by a microwave-induced combustion process. Ceram Int 36(5):1597–1601
Gingasu D, Mindru I, Patron L, Cizmas C-B (2008) Tetragonal copper ferrite obtained by self-propagating combustion. J Alloy Compd 460(1-2):627–631
Estrella M, Barrio L, Zhou G, Wang X, Wang Q, Wen W, Hanson JC, Frenkel AI, Rodriguez JA (2009) In situ characterization of CuFe2O4 and Cu/Fe3O4 water-gas shift catalysts. J Phys Chem C 113:14411–14417
Manova E, Tsoncheva T, Paneva D, Popova M, Velinov N, Kunev B, Tenchev K, Mitov I (2011) Nanosized copper ferrite materials: mechanochemical synthesis and characterization. J Solid State Chem 184(5):1153–1158
Zhuravlev VA, Minin RV, Itin VI, Lilenko IY (2017) Structural parameters and magnetic properties of copper ferrite nanopowders obtained by the sol-gel combustion. J Alloy Compd 692:705–712
Sun Z, Liu L, Jia DZ, Pan W (2007) Simple synthesis of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles as gas-sensing materials. Sens Actuators B 125(1):144–148
Xing Z, Ju Z, Yang J, Xu H, Qian Y (2013) One-step solid state reaction to selectively fabricate cubic and tetragonal CuFe2O4 anode material for high power lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 102:51–57
Rani BJ, Saravanakumar B, Ravi G, Ganesh V, Ravichandran S, Yuvakkumar R (2017) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29(3):1975–1984
Li XH, Xu CL, Han XH, Qiao L, Wang T, Li FS (2010) Synthesis and magnetic properties of nearly monodisperse CoFe2O4 nanoparticles through a simple hydrothermal condition. Nanoscale Res Lett 5(6):1039–1044
Huang Z, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Yin G (2007) Stable biomimetic superhydrophobicity and magnetization film with Cu-Ferrite nanorods. J Phys Chem C 111:6821–6825
Zhu M, Meng D, Wang C, Diao G (2013) Facile fabrication of hierarchically porous CuFe2O4 nanospheres with enhanced capacitance property. Appl Mater Interfaces 5(13):6030–6037
Karthigayan N, Manimuthu P, Priya M, Sagadevan S (2017) Synthesis and characterization of NiFe2O4, CoFe2O4 and CuFe2O4 Thin films for anode material in li-ion batteries. Nanomater Nanotechnol 7:1–5
Malana MA, Qureshi RB, Ashiq MN, Zafar ZI (2013) Synthesis, electrical and dielectric characterization of cerium doped nano copper ferrites. Mater Res Bull 48(11):4775–4779
Kombaiah K, Vijaya JJ, Kennedy LJ, Bououdina M, Al-Najar B (2018) Conventional and microwave combustion synthesis of optomagnetic CuFe2O4 nanoparticles for hyperthermia studies. J Phys Chem Solids 115:162–171
Kombaiah K, Vijaya JJ, Kennedy LJ, Bououdina M, Ramalingam RJ, Al-Lohedan HA (2017) Comparative investigation on the structural, morphological, optical, and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram Int 43(10):7682–7689
Pourgolmohammad B, Masoudpanah SM, Aboutalebi MR (2017) Effect of starting solution acidity on the characteristics of CoFe2O4 powders prepared by solution combustion synthesis. J Magn Magn Mater 424:352–358
Alves AK, Bergmann CP, Berutti FA (2013) Novel synthesis and characterization of nanostructured materials. Springer Science+Business Media, Berlin
Raja G, Saranya R, Saravanan K (2018) Microwave combustion method: effect of starch, urea and glycine as processing fuels in the Co3O4 nanostructures. Optik 153:73–80
Umadevi M, Christy AJ (2013) Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of CuO nanoflowers. Spectrochim Acta A 109:133–137
Sudheesh VD, Thomas N, Roona N, Baghya PK, Sebastian V (2017) Synthesis, characterization and influence of fuel to oxidizer ratio on the properties of spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M = Co and Ni) prepared by solution combustion method. Ceram Int 43(17):15002–15009
Cui K, Sun M, Gong T, Xu J, Hou L, Yuan C (2022) Construction of single-crystal nanoparticles assembled CuFe2O4 spinel microspheres towards high infrared emissivity. J Alloys Compd 929:167365
Ianoş R, Tăculescu A, Păcurariu C, Lazău I, Joy P (2012) Solution combustion synthesis and characterization of magnetite, Fe3O4, nanopowders. J Am Ceram Soc 95(7):2236–2240
Cahyana AH, Liandi AR, Yulizar Y, Romdoni Y, Wendari TP (2021) Green synthesis of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles mediated by Morus alba L. leaf extract: crystal structure, grain morphology, particle size, magnetic and catalytic properties in Mannich reaction. Ceram Int 47(15):21373–21380
Dippong T, Deac IG, Cadar O, Levei EA, Petean I (2020) Impact of Cu2+ substitution by Co2+ on the structural and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4 synthesized by sol-gel route. Mater Charac 163:110248
İçin K, Öztürk S, Çakıl DD, Sünbül SE (2021) Mechanochemical synthesis of SrFe12O19 from recycled mill scale: Effect of synthesis time on phase formation and magnetic properties. J Alloys Compd 873:159787
Fathi H, Masoudpanah SM, Alamolhoda S, Parnianfar H (2017) Effect of fuel type on the microstructure and magnetic properties of solution combusted fe3o4 powders. Ceram Int 43(10):7448–7453
Moosvi SK, Majid K, Ara T (2016) Studying the electrical, thermal, and photocatalytic activity of nanocomposite of polypyrrole with the photoadduct of K3[Fe(CN)6] and Diethylenetriamine. Mater Res 19(5):983–990
Horch M, Lauterbach L, Saggu M, Hildebrandt P, Lendzian F, Bittl R, Lenz O, Zebger I (2010) Probing the active site of an O2−tolerant NAD+−reducing [NiFe]-hydrogenase from Ralstonia eutropha H16 by in situ EPR and FTIR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(43):8026–8029
Rathod SM, Chavan AR, Jadhav SS, Batoo KM, Hadi M, Raslan EH (2021) Ag+ ion substituted CuFe2O4 nanoparticles: analysis of structural and magnetic behavior. Chem Phys Lett 765:138308
Mazrouei A, Saidi A (2018) Microstructure and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nano powder prepared by solution combustion synthesis. Mater Chem Phys 209:152–158
Wang X, Qin M, Fang F, Jia B, Wu H, Qu X, Volinsky AA (2017) Effect of glycine on one-step solution combustion synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 719:288–295
Shanmugavani A, Selvan RK (2016) Improved electrochemical performances of CuCo2O4/CuO nanocomposites for asymmetric supercapacitors. Electrochim Acta 188:852–862
Li NH, Lo SL, Hu CY, Hsieh CH, Chen CL (2011) Stabilization and phase transformation of CuFe2O4 sintered from simulated copper-laden sludge. J Hazard Mater 190(1-3):597–603
Rodríguez MA, Aguilar CL, Aghayan MA (2012) Solution combustion synthesis and sintering behavior of CaAl2O4. Ceram Int 38(1):395–399
Toniolo J, Takimi AS, Andrade MJ, Bonadiman R, Bergmann CP (2007) Synthesis by the solution combustion process and magnetic properties of iron oxide (Fe3O4 and α-Fe2O3) particles. J Mater Sci 42(13):4785–4791
Aali H, Mollazadeh S, Khaki JV (2018) Single-phase magnetite with high saturation magnetization synthesized via modified solution combustion synthesis procedure. Ceram Int 44(16):20267–20274
Ranjith Kumar E, Jayaprakash R, Chandrasekaran J (2013) Effect of fuel ratio and the impact of annealing temperature on particle size, magnetic and dielectric properties of manganese substituted CuFe2O4 nanoparticles. Superlattices Microstruct 64:343–353
Laokul P, Amornkitbamrung V, Seraphin S, Maensiri S (2011) Characterization and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline CuFe2O4, NiFe2O4, ZnFe2O4 powders prepared by the aloe vera extract solution. Curr Appl Phys 11(1):101–108
Nedkov I, Vandenberghe RE, Marinova T, Thailhades P, Merodiiska T, Avramova I (2006) Magnetic structure and collective Jahn–Teller distortions in nanostructured particles of CuFe2O4. Appl Surf Sci 253(5):2589–2596
Raja G, Gopinath S, Raj RA, Shukla AK, Alhoshan MS, Sivakumar K (2016) Comparative investigation of CuFe2O4 nano and microstructures for structural, morphological, optical and magnetic properties. Phys E Low Dimens 83:69–73
Ponhan W, Maensiri S (2009) Fabrication and magnetic properties of electrospun copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanofibers. Solid State Sci 11(2):479–484
Kurian J, Jacob MM (2017) A facile approach to the elucidation of magnetic parameters of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal route. J Magn Magn Mater 428:204–212
Paramasivan P, Venkatesh P (2016) Controllable synthesis of CuFe2O4 nanostructures through simple hydrothermal method in the presence of thioglycolic acid. Phys E Low Dimens 84:258–262
Vergis BR, Hari Krishna R, Kottam N, Nagabhushana BM, Sharath R, Darukaprasad B (2017) Removal of malachite green from aqueous solution by magnetic CuFe2O4 nano-adsorbent synthesized by one pot solution combustion method. J Nanostructure Chem 8(1):1–12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bilgin, S., Alver, Ü. A comparative study of structural, magnetic, and thermal properties of CuxFe3-xO4 nanoparticles prepared in open and closed systems using solution combustion synthesis. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 107, 810–820 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06170-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06170-2