Abstract
Pristine- and copper-doped ZnO thin films with various concentrations were deposited on tin-doped indium oxide–coated glass substrates using the sol–gel method followed by the spin-coating technique. All the deposited samples were further processed with annealing at 450 °C with the aim of decreasing defects in the sample. Structural properties revealed that films are polycrystalline in nature and morphological study represented an increase in particle size with increasing Cu-doping concentration. The absorption data show band gap narrowing and electrical analysis shows an increase in conductivity and carrier concentration with optimized Cu-doping concentration. This study shows that sol–gel–derived Cu-doped ZnO thin films show low band gap, low electrical resistivity, and high transmittance and can be used for optoelectronic devices. Furthermore, films were tested for photoelectrochemical performance in 0.5 M Na2SO4 electrolyte solution. An optimum amount of Cu dopant with ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) has shown enhanced photocurrent density which six times enhanced and increased photoconversion efficiency compared to those of the bare ZnO NPs.
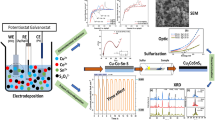
Graphical abstract

Structural, surface morphological and photoelectrochemical study of Cu-doped ZnO samples. The formation of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles with various concentrations of Cu dopants. The enhanced photocurrent density in the optimized sample is more than six times compared to those of the bare ZnO nanoparticles
Highlights
-
Low cost hydrothermal method was used to prepare Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles based thin films.
-
Cu doping exhibit change in band gap compared to undoped ZnO nanoparticles based thin films.
-
The increase of conductivity is caused by extra electron carrier with Cu doping.
-
Electrochemical measurements confirm applicability in photoelectrochemical cells.
-
Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles enhanced the photocurrent density and photo-conversion efficiency which is more than 06 times compared to those of the bare ZnO nanoparticles.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park WI, Kim DH, Jung SW, Yi GC (2002) Appl Phys Lett 80:4232–4234
Dwivedi C, Dutta V (2012) Nanotechnology 3:015011
Liu KW, Salley GM, Gamelin DR (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:14486–14495
Majidi H, Baxter JB (2011) Electrochim Acta 56:2703–2711
Chattopadhyay S, Chen LC, Chen KH (2011) NPG Asia Mater 3:74–81
Yu A, Qianb J, Pan H, Cui Y, Xu M, Tu L, Chai Q, Zhou X, Sens (2011) Actuators B 158:9–16
Gratzel M (2001) Nature 414:338–344
Sharma A, Chakraborty M, Thangavel R (2018) J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:14710–14722
Rokade A, Rondiyam S, Sharma V, Prasad M, Pathan H, Jadkar S (2017) J Solid State Electrochem 21:2639–2648
Zhang W, Yan D, Appavoo K, Cen J, Wu Q (2017) Chem Mater 29:4036–4043
Liu M, Nam CY, Black CT, Kamcey K (2013) J Phys Chem C 117:13396–13402
Look DC (2001) J Mater Sci Eng B 80:383–387
Jiang C, Moniz SJA, Khraisheh M (2014) Chem Eur J 20:12954–12961
Gupta M, Sharma V, Shrivastava J, Solanki A, Singh AP, Satsangi VR, Dass S, Shrivastav R (2009) Bull Mater Sci 32:23–30
Sharma V, Kumar P, Shrivastava J, Solanki A, Satsangi VR, Dass S, Shrivastav R (2011) J Mater Sci 46:3792–3801
Tyona MD, Osuji RU, Asogwa PU, Jambure SB, Ezema FI (2017) J Solid State Electrochem 21(9):2629–2638
Chakraborty M, Ghosh A, Thangavel R (2015) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 74:756–764
Joshi BC, Chaudhri AK (2022) ACS Omega 7(25):21877–21881
Horzum S, Torun E, Serin T, Peeters F (2016) Philos Mag 96:1743–1756
Joshi K, Rawat M, Gautam SK, Singh RG, Ramola RC, Singh F (2016) J Alloy Compd 680:252–258
Krishna VSG, Mahesha MG (2022) J Alloy Compd 899:163357
Thankalekshmi RDR, Samwad D, Rastogi AC (2013) Adv Mater Lett 4:9–14
Sajjad M, Ullah I, Khan MI, Khan J, Khan MY, Qureshi MT (2018) Results Phys 9:1301–1309
Bakhtiargonbadi F, Esfahani H, Moakhar RS, Dabir F (2020) Mater Chem Phys 252:123270
Aboud AA, Shaban MD, Revaprasadu N (2019) RSC Adv 9:7729–7736
Singhal S, Kaur J, Sharma TNR (2012) Phys B Condens Matter 407(8):1223–1226
Jothilakshmi R, Ramakrishnan V, Thangavel R, Kumar J, Sarua A, Kuball M (2009) J Raman Spectrosc 40(5):556–561
Udayabhaskar R, Karthikeyan B (2014) J Appl Phys 116(9):094310
Ryoken H, Sakaguchi I, Ohashi N, Sekiguchi T, Hishita S, Haneda H (2005) J Mater Res 20:2866–2872
Iandolo B, Zhang H, Wickman B, Zoric I, Conibeer G, Hellman A (2015) RSC Adv 5:61021–61030
Liu Y, Gu Y, Yan X, Kang Z, Lu S, Sun Y, Zhang Y (2015) Nano Res 8(9):2891–2900
Acknowledgements
MC and RT would like to acknowledge Dr S. K. Sharma, Indian School of Mines, Dhanbad, for his support in getting photoluminescence measurements. MC and RT acknowledge the financial support from the Indian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines), Dhanbad, India. MC would like to acknowledge the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India, for providing Indo-US Science and Technology Forum (IUSSTF) Bhaskara Advanced Solar Energy (BASE) fellowship-2016 and National Postdoctoral Fellowship with the project no. PDF/2017/001629.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, M., Thangavel, R. & Roy, D. Enhancement in photoelectrochemical performance of ZnO nanoparticle–based photoelectrodes with incorporation of Cu dopant source. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 107, 467–473 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06118-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06118-6