Abstract
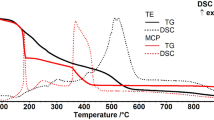
The cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles were synthesized by the sol–gel auto-combustion method in the presence of various amounts (0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1 g) of egg white protein (albumin). The preparation steps were completed by a heat treatment at 800 °C. The phase formation and morphology of the resulting nanoparticles were investigated by the simultaneous differential thermal analysis-thermogravimetric (DTA-TG), X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), and Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Further studies were performed on the critical impact of the heat treatment on crystalline phase formation. The phase identification by XRD demonstrated the formation of the cubic spinel structure of the cobalt ferrite phase. XRD data were also refined by the Rietveld method for a more accurate calculation of structural parameters. The addition of albumin reduced the average crystallite size from ~70 to ~27 nm. Magnetic properties were measured by a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), and the curves show the ferromagnetic behavior of the nanoparticles with an increase in the coercivity (from ~290 to ~470 Oe) and saturation magnetization (from ~41 to ~51 emu.g−1) as a result of albumin addition. The cation redistribution due to the presence of albumin is the reason for the variation of coercivity and magnetization through its effect on magnetic anisotropy and inversion degree, respectively.
Graphical Abstract

The cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles were synthesized by the solgel auto-combustion method in the presence of various amounts of egg white protein (albumin) and then the effect of presence of this agent on the structural and magnetic properties of these nanoparticles was investigated.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Routray KL, Saha S, Behera D (2018) Green synthesis approach for nano sized CoFe2O4 through aloe vera mediated sol-gel auto combustion method for high frequency devices. Mater Chem Phys 224:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.11.073
Mammo TW, Kumari CV, Margarette SJ et al. (2020) Synthesis, structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanomaterial prepared by sol-gel autocombustion technique. Phys B Condens Matter 581:411769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.411769
Patankar KK, Ghone DM, Mathe VL, Kaushik SD (2018) Structural and physical property study of sol–gel synthesized CoFe2-xHoxO4 nano ferrites. J Magn Magn Mater 454:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.01.039
Amiri M, Salavati-Niasari M, Akbari A (2019) Magnetic nanocarriers: evolution of spinel ferrites for medical applications. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 265:29–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2019.01.003
Zhang H, Wang J, Zeng Y et al. (2020) Leucine-coated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and potential biomedical applications for drug delivery. Phys Lett Sect A Gen At Solid State Phys 384:126600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2020.126600
Heiba ZK, Mohamed MB, Ahmed SI (2017) Cation distribution correlated with magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles defective by vanadium doping. J Magn Magn Mater 441:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.06.021
Mahajan P, Sharma A, Kaur B et al. (2019) Green synthesized (Ocimum sanctum and Allium sativum) Ag-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for antibacterial application. Vacuum 161:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.12.021
Elayakumar K, Dinesh A, Manikandan A et al. (2018) Structural, morphological, enhanced magnetic properties and antibacterial bio-medical activity of rare earth element (REE) Cerium (Ce3+) doped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.089
Virumbrales M, Blanco-Gutiérrez V, Delgado-Cabello A et al. (2018) Superparamagnetism in CoFe2O4nanoparticles: an example of a collective magnetic behavior dependent on the medium. J Alloys Compd 767:559–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.096
Maleki A, Hosseini N, Taherizadeh A (2018) Synthesis and characterization of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by the glycine-nitrate process. Ceram Int 44:8576–8581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.02.063
Noormohamadi HR, Fat’hi MR, Ghaedi M (2018) Fabrication of polyethyleneimine modified cobalt ferrite as a new magnetic sorbent for the micro-solid phase extraction of tartrazine from food and water samples. J Colloid Interface Sci 531:343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.07.026
Srinivasamurthy KM, Angadi VJ, Kubrin SP et al. (2018) Tuning of ferrimagnetic nature and hyperfine interaction of Ni2+ doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for power transformer applications. Ceram Int 44:9194–9203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.02.129
Abou Hammad AB, Abd El-Aziz ME, Hasanin MS, Kamel S (2019) A novel electromagnetic biodegradable nanocomposite based on cellulose, polyaniline, and cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 216:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.03.038
Gharibshahian M, Nourbakhsh MS, Mirzaee O (2018) Evaluation of the superparamagnetic and biological properties of microwave assisted synthesized Zn & Cd doped CoFe2O4nanoparticles via Pechini sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 85:684–692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4570-1
Prabhakaran T, Mangalaraja RV, Denardin JC, Jiménez JA (2017) The effect of calcination temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of co-precipitated CoFe 2 O 4 nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 716:171–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.048
Hossain A, Sarker MSI, Khan MKR et al. (2018) Structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of sol–gel derived cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Appl Phys A 124:608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2042-2
Kumar RV, Anupama AV, Kumar R et al. (2018) Cation distributions and magnetism of Al-substituted CoFe2O4 - NiFe2O4 solid solutions synthesized by sol-gel auto-combustion method. Ceram Int 44:20708–20715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.08.065
Gabal MA, Al-Juaid AA, El-Rashed S, Hussein MA (2017) Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized CoFe2O4 via facile methods: a comparative study. Mater Res Bull 89:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.12.048
Han G, Li M, Yu Y et al. (2019) Structure and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite foam with low mass density. J Alloys Compd 790:947–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.03.157
Venturini J, Wermuth TB, Machado MC et al. (2019) The influence of solvent composition in the sol-gel synthesis of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4): A route to tuning its magnetic and mechanical properties. J Eur Ceram Soc 39:3442–3449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.01.030
Maksoud MIAA, El-Sayyad GS, Ashour AH et al. (2019) Antibacterial, antibiofilm, and photocatalytic activities of metals-substituted spinel cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Microb Pathog 127:144–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.11.045
Kennaz H, Harat A, Guellati O et al. (2018) Synthesis and electrochemical investigation of spinel cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles for supercapacitor application. J Solid State Electrochem 22:835–847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3813-y
Mohammadi Z, Attaran N, Sazgarnia A et al. (2020) Superparamagnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles as T2 contrast agent in MRI: in vitro study. IET Nanobiotechnol 14:396–404. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2019.0210
Muhamad Arshad J, Raza W, Amin N et al. (2020) Synthesis and characterization of cobalt ferrites as MRI contrast agent. Mater Today Proc 0–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.746
Wu H, Liu G, Wang X et al. (2011) Solvothermal synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles loaded on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Acta Biomater 7:3496–3504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2011.05.031
Shi Z, Zeng Y, Chen X et al. (2020) Mesoporous superparamagnetic cobalt ferrite nanoclusters: synthesis, characterization and application in drug delivery. J Magn Magn Mater 498:166222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166222
Georgiadou V, Makris G, Papagiannopoulou D et al. (2016) Octadecylamine-mediated versatile coating of CoFe2O4NPs for the sustained release of anti-inflammatory drug naproxen and in vivo target selectivity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:9345–9360. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b00408
Cai B, Zhao M, Ma Y et al. (2015) Bioinspired formation of 3D hierarchical CoFe2O4 porous microspheres for magnetic-controlled drug release. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:1327–1333. https://doi.org/10.1021/am507689a
Abdel Maksoud MIA, El-Sayyad GS, Ashour AH et al. (2018) Synthesis and characterization of metals-substituted cobalt ferrite [MxCo(1-x)Fe2O4; (M = Zn, Cu and Mn; x = 0 and 0.5)] nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents and sensors for Anagrelide determination in biological samples. Mater Sci Eng C 92:644–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.07.007
Pita M, Abad JM, Vaz-Dominguez C et al. (2008) Synthesis of cobalt ferrite core/metallic shell nanoparticles for the development of a specific PNA/DNA biosensor. J Colloid Interface Sci 321:484–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2008.02.010
Gandhi S, Issar S, Mahapatro AK, Roy I (2020) Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for bimodal hyperthermia and their mechanistic interactions with lysozyme. J Mol Liq 310:113194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113194
Sangeetha K, Ashok M, Girija EK (2019) Development of multifunctional cobalt ferrite/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites by microwave assisted wet precipitation method: a promising platform for synergistic chemo-hyperthermia therapy. Ceram Int 45:12860–12869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.209
Nam PH, Lu LT, Linh PH et al. (2018) Polymer-coated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and toxicity for hyperthermia applications. New J Chem 42:14530–14541. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ01701H
Mazario E, Menéndez N, Herrasti P et al. (2013) Magnetic hyperthermia properties of electrosynthesized cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 117:11405–11411. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4023025
Çelik Ö, Can MM, Firat T (2014) Size dependent heating ability of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles in AC magnetic field for magnetic nanofluid hyperthermia. J Nanoparticle Res 16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2321-6
Cruz MM, Ferreira LP, Ramos J et al. (2017) Enhanced magnetic hyperthermia of CoFe2O4and MnFe2O4nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 703:370–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.297
Mendo SG, Alves AF, Ferreira LP et al. (2015) Hyperthermia studies of ferrite nanoparticles synthesized in the presence of cotton. New J Chem 39:7182–7193. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ00009B
Fernandes de Medeiros IA, Lopes-Moriyama AL, de Souza CP (2017) Effect of synthesis parameters on the size of cobalt ferrite crystallite. Ceram Int 43:3962–3969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.10.105
Khan MA, Alam MM, Naushad M et al. (2015) Sol-gel assisted synthesis of porous nano-crystalline CoFe2O4 composite and its application in the removal of brilliant blue-R from aqueous phase: an ecofriendly and economical approach. Chem Eng J 279:416–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.042
Dippong T, Levei EA, Cadar O et al. (2017) Size and shape-controlled synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles embedded in a PVA-SiO2 hybrid matrix. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 128:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2017.10.018
Hashemi SM, Hasani S, Jahanbani Ardakani K, Davar F (2019) The effect of simultaneous addition of ethylene glycol and agarose on the structural and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by the sol-gel auto-combustion method. J Magn Magn Mater 492:165714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165714
Avazpour L, Zandi Khajeh MA, Toroghinejad MR, Shokrollahi H (2015) Synthesis of single-phase cobalt ferrite nanoparticles via a novel EDTA/EG precursor-based route and their magnetic properties. J Alloys Compd 637:497–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.03.041
Yadav RS, Kuřitka I, Vilcakova J et al. (2017) Structural, magnetic, optical, dielectric, electrical and modulus spectroscopic characteristics of ZnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via honey-mediated sol-gel combustion method. J Phys Chem Solids 110:87–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2017.05.029
Ghumare AB, Mane ML, Shirsath SE, Lohar KS (2018) Role of pH and sintering temperature on the properties of tetragonal–cubic phases composed copper ferrite nanoparticles. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 28:2612–2619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0927-3
Caldeira LE, Guaglianoni WC, Venturini J et al. (2020) Sintering-dependent mechanical and magnetic properties of spinel cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) ceramics prepared via sol-gel synthesis. Ceram Int 46:2465–2472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.240
Bhosale RR, Kumar A, Almomani F, Alxneit I (2016) Propylene oxide assisted sol-gel synthesis of zinc ferrite nanoparticles for solar fuel production. Ceram Int 42:2431–2438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.10.043
Shen SY, Zheng H, Zheng P et al. (2018) Microstructure, magnetic properties of hexagonal barium ferrite powder based on calcination temperature and holding time. Rare Met. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1153-4
Anila I, Mathew MJ (2019) Influence of pH on structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrites synthesized by sol–gel method. In: AIP Conference Proceedings. 2162:020077. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5130287
Sajjia M, Oubaha M, Prescott T, Olabi AG (2010) Development of cobalt ferrite powder preparation employing the sol–gel technique and its structural characterization. J Alloys Compd 506:400–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.07.015
Ansari F, Sobhani A, Salavati-Niasari M (2018) Simple sol-gel synthesis and characterization of new CoTiO3/CoFe2O4nanocomposite by using liquid glucose, maltose and starch as fuel, capping and reducing agents. J Colloid Interface Sci 514:723–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.12.083
Zhang W, Sun A, Zhao X et al. (2020) Structural and magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Co ferrites prepared from sol-gel auto combustion method with different complexing agents. J Alloys Compd 816:152501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152501
Mariosi FR, Venturini J, da Cas Viegas A, Bergmann CP (2020) Lanthanum-doped spinel cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles for environmental applications. Ceram Int 46:2772–2779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.266
Imanipour P, Hasani S, Seifoddini A et al. (2020) The possibility of vanadium substitution on Co lattice sites in CoFe2O4 synthesized by sol–gel autocombustion method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 95:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05316-w
Imanipour P, Hasani S, Afshari M et al. (2020) The effect of divalent ions of zinc and strontium substitution on the structural and magnetic properties on the cobalt site in cobalt ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 510:166941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166941
Ashour AH, El-Batal AI, Maksoud MIAA et al. (2018) Antimicrobial activity of metal-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel technique. Particuology 40:141–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2017.12.001
Venturini J, Zampiva RYS, Arcaro S, Bergmann CP (2018) Sol-gel synthesis of substoichiometric cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) spinels: Influence of additives on their stoichiometry and magnetic properties. Ceram Int 44:12381–12388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.026
Afshari M, Isfahani AR, Hasani S et al. (2019) Effect of apple cider vinegar agent on the microstructure, phase evolution, and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 MNPs. Int J Appl Ceram Technol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.13224
Rouhani AR, Esmaeil-Khanian AH, Davar F, Hasani S (2018) The effect of agarose content on the morphology, phase evolution, and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel autocombustion method. Int J Appl Ceram Technol 15:758–765. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.12832
Hunyek A, Sirisathitkul C, Mahaphap C et al. (2017) Sago starch: chelating agent in sol-gel synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J Aust Ceram Soc 53:173–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0022-1
Tian X, Zhou T, Wen J et al. (2020) Egg albumin assisted sol-gel synthesis of Eu3+ doped SnO2 phosphor for temperature sensing. Mater Res Bull 129:110882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.110882
Luxmi V, Kumar A (2019) Enhanced photocatalytic performance of m-WO3 and m-Fe-doped WO3 cuboids synthesized via sol-gel approach using egg albumen as a solvent. Mater Sci Semicond Process 104:104690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104690
Tian X, Lian S, Wen J et al. (2019) Microwave/starch-assisted sol-gel synthesis and photoluminescence of Eu3+-doped α-Al2O3 micro/nano-biscuits. J Lumin 207:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.10.068
Sun J, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al. (2019) Egg albumin-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Co3O4 quasi-cubes as superior electrode material for supercapacitors with excellent performances. Nanoscale Res Lett 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-019-3172-y
Manikandan A, Sridhar R, Arul Antony S, Ramakrishna S (2014) A simple aloe vera plant-extracted microwave and conventional combustion synthesis: Morphological, optical, magnetic and catalytic properties of CoFe2O4 nanostructures. J Mol Struct 1076:188–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.07.054
Manju BG, Raji P (2018) Synthesis and magnetic properties of nano-sized Cu0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 via citrate and aloe vera: A comparative study. Ceram Int 44:7329–7333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.01.201
Phumying S, Labuayai S, Swatsitang E et al. (2013) Nanocrystalline spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M = Ni, Co, Mn, Mg, Zn) powders prepared by a simple aloe vera plant-extracted solution hydrothermal route. Mater Res Bull 48:2060–2065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.02.042
Kombaiah K, Vijaya JJ, Kennedy LJ et al. (2018) Okra extract-assisted green synthesis of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles and their optical, magnetic, and antimicrobial properties. Mater Chem Phys 204:410–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.10.077
Ghanbari M, Davar F, Shalan AE (2021) Effect of rosemary extract on the microstructure, phase evolution, and magnetic behavior of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and its application on anti-cancer drug delivery. Ceram Int 47:9409–9417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.073
Gingasu D, Mindru I, Patron L, et al. (2016) Green synthesis methods of CoFe2O4 and Ag-CoFe2O4 nanoparticles using hibiscus extracts and their antimicrobial potential. J Nanomater 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2106756
Iatridi Z, Vamvakidis K, Tsougos I et al. (2016) Multifunctional polymeric platform of magnetic ferrite colloidal superparticles for luminescence, imaging, and hyperthermia applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:35059–35070. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b13161
Amiri M, Salavati-Niasari M, Akbari A, Gholami T (2017) Removal of malachite green (a toxic dye) from water by cobalt ferrite silica magnetic nanocomposite: herbal and green sol-gel autocombustion synthesis. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:24846–24860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.08.077
Proveti JRC, Porto PSS, Muniz EP et al. (2015) Sol–gel proteic method using orange albedo pectin for obtaining cobalt ferrite particles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 75:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3671-y
Muniz EP, de Assunção LSD, de Souza LM et al. (2020) On cobalt ferrite production by sol-gel from orange fruit residue by three related procedures and its application in oil removal. J Clean Prod 265:121712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121712
Ansari F, Sobhani A, Salavati-Niasari M (2016) Green synthesis of magnetic chitosan nanocomposites by a new sol-gel auto-combustion method. J Magn Magn Mater 410:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.03.014
Erhardt CS, Caldeira LE, Venturini J et al. (2020) Sucrose as a sol-gel synthesis additive for tuning spinel inversion and improving the magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram Int 46:12759–12766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.044
Yadav RS, Havlica J, Hnatko M et al. (2015) Magnetic properties of Co1-xZnxFe2O4spinel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by starch-assisted sol-gel autocombustion method and its ball milling. J Magn Magn Mater 378:190–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.11.027
Yadav RS, Havlica J, Masilko J et al. (2016) Impact of Nd3+ in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles on cation distribution, structural and magnetic properties. J Magn Magn Mater 399:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.09.055
Gangulibabu, Bhuvaneswari D, Kalaiselvi N (2013) Comparison of corn starch-assisted sol-gel and combustion methods to prepare LiMnxCoyNizO2 compounds. J Solid State Electrochem 17:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-012-1851-z
Lima DR, Jiang N, Liu X et al. (2017) Employing calcination as a facile strategy to reduce the cytotoxicity in CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:39830–39838. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b13103
Yadav RS, Kuřitka I, Vilcakova J et al. (2017) Structural, dielectric, electrical and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by honey mediated sol–gel combustion method and annealing effect. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28:6245–6261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6305-4
Yadav RS, Kuřitka I, Vilcakova J et al. (2017) Structural, magnetic, dielectric, and electrical properties of NiFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by honey-mediated sol-gel combustion. J Phys Chem Solids 107:150–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2017.04.004
Alshehri SM, Alhabarah AN, Ahmed J et al. (2018) An efficient and cost-effective tri-functional electrocatalyst based on cobalt ferrite embedded nitrogen doped carbon. J Colloid Interface Sci 514:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.12.020
Tian X, Lian S, Wen J et al. (2018) Egg albumin-assisted sol–gel synthesis and photo-catalytic activity of SnO2 micro/nano-structured biscuits. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 85:402–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4547-0
Ahamad T, Ruksana, Naushad M et al. (2019) Fabrication of highly porous adsorbent derived from bio-based polymer metal complex for the remediation of water pollutants. J Clean Prod 208:1317–1326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.174
Gabal MA (2010) Structural and magnetic properties of nano-sized Cu-Cr ferrites prepared through a simple method using egg white. Mater Lett 64:1887–1890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2010.05.022
Hou X, Feng J, Ren Y et al. (2010) Synthesis and adsorption properties of spongelike porous MnFe2O4. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 363:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2010.03.016
Hou X, Feng J, Liu X et al. (2011) Magnetic and high rate adsorption properties of porous Mn1-xZnxFe2O4 (0≤x≤0.8) adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 353:524–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.09.050
Hou X, Feng J, Liu X et al. (2011) Synthesis of 3D porous ferromagnetic NiFe 2O 4 and using as novel adsorbent to treat wastewater. J Colloid Interface Sci 362:477–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.06.070
Geng B, Zhan F, Jiang H et al. (2008) Egg albumin as a nanoreactor for growing single-crystalline Fe 3O4 nanotubes with high yields. Chem Commun 5773–5775. https://doi.org/10.1039/b813071j
Yan J, Wu G, Li L et al. (2010) Synthesis of uniform ti0 2 nanoparticles with egg albumen proteins as novel biotemplate. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10:5767–5775. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2010.2501
Prakash T, Neri G, Ranjith Kumar E (2015) A comparative study of the synthesis of CdO nanoplatelets by an albumen-assisted isothermal evaporation method. J Alloys Compd 624:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.10.204
Prakash T, Jayaprakash R, Raj DS et al. (2013) Sensing properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by using albumen as a biotemplate for acetic acid monitoring in aqueous mixture. Sensors Actuators B Chem 176:560–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.09.011
Khandekar MS, Kambale RC, Patil JY et al. (2011) Effect of calcination temperature on the structural and electrical properties of cobalt ferrite synthesized by combustion method. J Alloys Compd 509:1861–1865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.10.073
Srinivasa Rao K, Ranga Nayakulu SV, Chaitanya Varma M et al. (2018) Controlled phase evolution and the occurrence of single domain CoFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by PVA assisted sol-gel method. J Magn Magn Mater 451:602–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.11.069
Emamian HR, Honarbakhsh-raouf A, Ataie A, Mirzaee O (2015) Characterization of mesoporous cobalt ferrite foam fabricated from sol-gel-derived nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 28:2831–2838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3124-4
Ferreira TAS, Waerenborgh JC, Mendonça MHRM et al. (2003) Structural and morphological characterization of FeCo2O4 and CoFe2O4 spinels prepared by a coprecipitation method. Solid State Sci 5:383–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1293-2558(03)00011-6
Desai KR, Alone ST, Wadgane SR et al. (2021) X-ray diffraction based Williamson–Hall analysis and rietveld refinement for strain mechanism in Mg–Mn co-substituted CdFe2O4 nanoparticles. Phys B Condens Matter 614:413054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2021.413054
Li X, Sun Y, Zong Y et al. (2020) Size-effect induced cation redistribution on the magnetic properties of well-dispersed CoFe2O4 nanocrystals. J Alloys Compd 841:155710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155710
Monisha P, Priyadharshini P, Gomathi SS, Pushpanathan K (2021) Influence of Mn dopant on the crystallite size, optical and magnetic behaviour of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles. J Phys Chem Solids 148:109654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109654
Vitor PAM, Venturini J, da Cunha JBM, Bergmann CP (2021) The influence of cation distribution on the magnetic properties of mixed Co1-yNiyFe2O4 nanoferrites produced by the sol-gel method. J Alloys Compd 851:156799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156799
Dippong T, Levei EA, Cadar O et al. (2019) Effect of nickel content on structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Ni Co1-Fe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposites. J Alloys Compd 786:330–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.363
Shyamaldas, Bououdina M, Manoharan C (2020) Dependence of structure/morphology on electrical/magnetic properties of hydrothermally synthesised cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 493:165703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165703
Stoner EC EP, Wohlfarth (1948) A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. Philos Trans R Soc London Ser A Math Phys Sci 240:599–642. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.1948.0007
Acknowledgements
The authors of the article thank the financial support of the Yazd University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemi, S.M., Ataollahi, Z., Hasani, S. et al. Synthesis of the cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles by sol–gel auto-combustion method in the presence of egg white (albumin). J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 106, 23–36 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06073-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06073-2