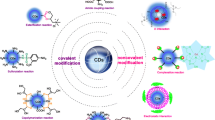
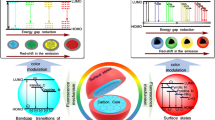
Abstract
Carbon dots (C-dots) are nanocarbon materials that exhibit a range of fluorescence and chemical/physical properties depending on the precursors employed and the conditions under which they were synthesized. However, the structural factors responsible for C-dot fluorescence remain unknown. This is because C-dots exhibit a wide distribution of sizes, structures, functional groups, heteroatoms, and defects, making structural analysis challenging. Therefore, a different experimental approach is necessary to explore the factors affecting the fluorescence. As a physicochemical approach, the surface properties of C-dots were altered by surface modification using organosilane, and the differences in fluorescence wavelength caused by the functionalization of C-dots were investigated in an organosilica matrix in this study. To explore the impact of varying chemical states of the C-dots surface on the fluorescence properties, it is necessary to evaluate them in a stable solid-state matrix that eliminates the effects of changes in the surrounding chemical state, dispersion state, and mobility. To compare the fluorescence properties, homogeneous hybrid organosilica films containing surface-functionalized C-dots were prepared using sol-gel method. For comparison, three types of C-dots were synthesized, each with a different fraction of surface reaction sites for functionalization. The fluorescence peak shift from pristine C-dots to functionalized C-dots in films was investigated for each. The reasons behind the fluorescence peak shifts and the local structures responsible for the fluorescence of the C-dots were explored based on the peak shift behavior and differences in the structural features of the as-prepared pristine C-dots.

Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
Contribution of C-dot surface and core structures to fluorescence was experimentally investigated.
-
Several C-dots with different surface states and similar fluorescence were synthesized.
-
C-dots were functionalized with organoalkoxysilane changing their surface structures.
-
The surface and core states of C-dots contribute to different fluorescence.
-
Fluorescence peak shift behavior indicates common local structures for the different C-dots.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding C, Zhu A, Tian Y (2014) Functional surface engineering of C‑Dots for fluorescent biosensing and in vivo bioimaging. Acc Chem Res 47:20–30
Fernando KAS, Sahu S, Liu Y, Lewis WK, Guliants EA, Jafariyan A, Wang P, Bunker CE, Sun Y-P (2015) Carbon quantum dots and applications in photocatalytic energy conversion. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:8363–8376
Yan F, Sun Z, Zhang H, Sun X, Jiang Y, Bai Z (2019) The fluorescence mechanism of carbon dots, and methods for tuning their emission color: a review. Microchimica Acta 186:583
Kurian M, Paul A (2021) Recent trends in the use of green sources for carbon dot synthesis–a short review. Carbon Trends 3:100032
Bao L, Liu C, Zhang Z-L, Pang D-W (2015) Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv Mater 27:1663–1667
Zheng XT, Ananthanarayanan A, Luo KQ, Chen P (2015) Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: properties, syntheses, and biological applications. Small 11:1620–1636
Yuan F, Yuan T, Sui L, Wang Z, Xi Z, Li Y, Li X, Fan L, Tan Z, Chen A, Jin M, Yang S (2018) Engineering triangular carbon quantum dots with unprecedented narrow bandwidth emission for multicolored LEDs. Nat Commun 9:2249
Sharma A, Das J (2019) Small molecules derived carbon dots: synthesis and applications in sensing, catalysis, imaging, and biomedicine. J Nanobiotechnol 17:92
Meierhofer F, Dissinger F, Weigert F, Jungclaus J, Müller-Caspary K, Waldvogel SR, Resch-Genger U, Voss T (2020) Citric acid based carbon dots with amine type stabilizers: pH-specific luminescence and quantum yield characteristics. J Phys Chem C 124:8894–8904
Li HT, He XD, Kang ZH, Huang H, Liu Y, Liu JL, Lian SY, Tsang CA, Yang XB, Lee ST (2010) Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:4430–4434
Kim S, Hwang SW, Kim MK, Dong YS, Dong HS, Chang OK, Yang SB, Park JH, Hwang E, Choi SH, Ko G, Sim S, Sone C, Choi HJ, Bae S, Hong BH (2012) Anomalous behaviors of visible luminescence from graphene quantum dots: interplay between size and shape. ACS Nano 6:8203–8208
Li QQ, Zhang S, Dai LM, Li LS (2012) Nitrogen-Doped colloidal graphene quantum dots and their size-dependent electrocatalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction. J Am Chem Soc 134:18932–18935
Song Y, Zhu S, Zhang S, Fu Y, Wang L, Zhao X, Yang B (2015) Investigation from chemical structure to photoluminescent mechanism: a type of carbon dots from the pyrolysis of citric acid and an amine. J Mater Chem C 3:5976–5984
Ding H, Yu S-B, Wei J-S, Xiong H-M (2016) Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 10:484–491
Zhang ZM, Pan Y, Fang YN, Zhang LL, Chen JY, Yi CQ (2016) Tuning photoluminescence and surface properties of carbon nanodots for chemical sensing. Nanoscale 8:500–507
Wang L, Zhu S-J, Wang H-Y, Qu S-N, Zhang Y-L, Zhang J-H, Chen Q-D, Xu H-L, Han W, Yang B, Sun H-B (2014) Common origin of green luminescence in carbon nanodots and graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 8:2541–2547
Zhu SJ, Zhao XH, Song YB, Lu SY, Yang B (2016) Beyond bottom-up carbon nanodots: citric-acid derived organic molecules. Nano Today 11:128–132
Schneider J, Reckmeier CJ, Xiong Y, von Seckendorff M, Susha AS, Kasák P, Rogach AL (2017) Molecular fluorescence in citric acid-based carbon dots. J Phys Chem C 121:2014–2022
Kasprzyk W, Świergosz T, Bednarz S, Walas K, Bashmakova NV, Bogdał D (2018) Luminescence phenomena of carbon dots derived from citric acid and urea – a molecular insight. Nanoscale 10:13889–13894
Zhu S, Song Y, Wang J, Wan H, Zhang Y, Ning Y, Yang B (2017) Photoluminescence mechanism in graphene quantum dots: Quantum confinement effect and surface/edge state. Nano Today 13:10–14
Tepliakov NV, Kundelev EV, Khavlyuk PD, Xiong Y, Leonov MY, Zhu W, Baranov AV, Fedorov AV, Rogach AL, Rukhlenko ID (2019) sp2−sp3‑Hybridized atomic domains determine optical features of carbon dots. ACS Nano 13:10737–10744
Chen B, Feng J (2015) White-light-emitting polymer composite film based on carbon dots and lanthanide complexes. J Phys Chem C 119:7865–7872
Suzuki K, Malfatti L, Carboni D, Loche D, Casula M, Moretto A, Maggini M, Takahashi M, Innocenzi P (2015) Energy transfer induced by carbon quantum dots in Porous Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite Films. J Phys Chem C 119:2837–2843
Wang Z, Zhao X, Guo Z, Miao P, Gong X (2018) Carbon dots based nanocomposite thin film for highly efficient luminescent solar concentrators. Org Electron 62:284–289
Suzuki K, Miyamura H, Balachandran J (2021) One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of Carbon dots-immobilized hydrozincite for ZnO-based nanocomposite lighting applications. J Asian Ceram Soc 9:1473–1480
Vassilakopoulou A, Georgakilas V, Koutselas I (2017) Encapsulation and protection of carbon dots within MCM-41 material. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 82:795–800
Tian Y, Ran Z, Yang W (2017) Carbon dot-silica composite nanoparticle: an excitation-independent fluorescence material with tunable fluorescence. RSC Adv 7:43839–43844
Mura S, Ludmerczki R, Stagi L, Garroni S, Carbonaro CM, Ricci PC, Casula MF, Malfatti L, Innocenzi P (2020) Integrating sol-gel and carbon dots chemistry for the fabrication of fluorescent hybrid organicinorganic films. Sci Rep 10:4770
Suzuki K, Malfatti L, Takahashi M, Carboni D, Messina F, Tokudome Y, Takemoto M, Innocenzi P (2017) Design of Carbon dots Photoluminescence through Organo-Functional silane grafting for solid-state emitting devices. Sci Rep 7:5469
Xu M, He G, Li Z, He F, Gao F, Su Y, Zhang L, Yang Z, Zhang Y (2014) A green heterogeneous synthesis of N-doped carbon dots and their photoluminescence applications in solid and aqueous states. Nanoscale 6:10307–10315
Khan WU, Wang D, Zhang W, Tang Z, Ma X, Ding X, Du S, Wang Y (2017) High quantum yield green-emitting carbon dots for Fe(ІІІ) detection, biocompatible fluorescent Ink and cellular imaging. Sci Rep 7:14866
Kasprzyk W, Świergosz T, Bednarz S, Walas K, Bashmakova NV, Bogdał D (2018) Luminescence phenomena of carbon dots derived from citric acid and urea – a molecular insight. Nanoscale 10:13889–13894
Strauss V, Wang H, Delacroix S, Ledendecker M, Wessig P (2020) Carbon nanodots revised: the thermal citric acid/urea reaction. Chem Sci 11:8256–8266
Stachowska JD, Murphy A, Mellor C, Fernandes D, Gibbons EN, Krysmann MJ, Kelarakis A, Burgaz E, Moore J, Yeates SG (2021) A rich gallery of carbon dots based photoluminescent suspensions and powders derived by citric acid/urea. Sci Rep 11:10554
Yang Z, Xu M, Liu Y, He F, Gao F, Su Y, Wei H, Zhang Y (2014) Nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, highly photoluminescent carbon dots from ammonium citrate. Nanoscale 6:1890–1895
Sheppard N, Simpson DM (1952) The infra-red and Raman spectra of hydrocarbons. Part I. Acetylenes and olefins. Quart Rev Chem Soc 6:1–33
Stewart JE (1959) Vibrational spectra of primary and secondary aliphatic amines. J Chem Phys 30:1259–1265
Derfer JM, Pickett EE, Boord CE (1949) Infrared absorption spectra of some cyclopropane and cyclobutane hydrocarbons. J Am Chem Soc 71:2482–2485
Stuart AV, Sutherland GBBM (1956) Effect of hydrogen bonding on the deformation frequencies of the hydroxyl group in alcohols. J Chem Phys 24:559–570
Li H, He X, Kang Z, Huang H, Liu Y, Liu J, Lian S, Tsang CHA, Yang X, Lee S-T (2010) Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:4430–4434
Zhu S, Meng Q, Wang L, Zhang J, Song Y, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun H, Wang H, Yang B (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:3953–3957
Liu H, Zhao X, Wang F, Wang Y, Guo L, Mei J, Tian C, Yang X, Zhao D (2017) High-efficient excitation-independent blue luminescent carbon dots. Nanoscale Res Lett 12:399
Bhattacharya D, Mishra MK, De G (2017) Carbon dots from a single source exhibiting tunable luminescent colors through the modification of surface functional groups in ORMOSIL Films. J Phys Chem C 121:28106–28116
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. S. Tanimoto (The University of Shiga Prefecture) for the technical support for DLS measurement.
Funding
This study was supported by JSPS bilateral joint research projects “MEAE-MESRI/SAKURA program” Grant Number JPJSBP120193218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, K., Nabata, H., Ueno, S. et al. Origin of carbon dot fluorescence in organosilica films explored experimentally by surface functionalization. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 104, 702–710 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05901-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05901-1