Abstract
(Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3 lead free ceramics have been synthesised by conventional sol-gel reaction method. The crystalline phase of calcined ceramics was studied at room temperature using X-ray diffraction. Rietveld refinement of the XRD measurements by FullProf showed that the samples have a rhombohedral structure with a space group R3c. In this study, NBT ceramics were sintered at different temperatures of 1000 °C, 1050 °C and 1100 °C for a period of 4 h. The sintering temperature was determined to be 1100 C, and the effect of sintering temperature on grain size was interpreted using dynamic crystal growth theory and, consequently, the electrical behaviour was also examined. The dielectric properties of these ceramic products were examined at different temperatures over a wide frequency range using an impedance analyser. It was found that the dielectric constant and dielectric loss decreased with increasing measurement frequency. The resulting ceramics have a large maximum dielectric permittivity at 320 °C and a dispersive permittivity at high temperatures. The exposant critique ɤ of the relationship between the dielectric constant and temperature \(\left( {{\upvarepsilon }}_{{{{\mathrm{rmax}}}}/{\upvarepsilon}_{{{\mathrm{r}}}}} \right)\) vs (T-Tm)ɣ) has been calculated with precision for NBT relaxor ferroelectrics at different frequencies. The (Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3 sample exhibits a diffuse ferroelectric behaviour.

Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics (Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3 are formed using the sol-gel method.
-
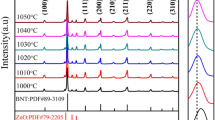
The ceramics have a pure perovskite structure with the rhombohedral phase.
-
Effects of sintering temperature on the electrical properties were investigated.
-
The NBT exhibits ferroelectric relaxer behavior.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang S, Alberta EF, Eitel RE, Randall CA, Shrout TR (2005) “Elastic, piezoelectric, and dielectric characterization of modified BiScO 3-PbTiO3 ceramics,”. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 52(11):2131–2139. https://doi.org/10.1109/TUFFC.2005.1561684
Cross LEric (1987) “Relaxor ferroelecirics,”. Ferroelectrics 76(1):241–267. https://doi.org/10.1080/00150198708016945
Mesrar M, Lamcharfi T, Echatoui N-S, and Abdi F (2022) “(1-x)(Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3-x(K0.5Bi0.5)TiO3 ceramics near morphotropic phase boundary: a structural and electrical study,” Materialia 101404.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MTLA.2022.101404
Chanda S, Maity R, Saha S, Dutta A, Sinha TP (2021) “Double perovskite nanostructured Dy2CoMnO6 an efficient visible-light photocatalysts: synthesis and characterization,”. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 99(3):600–613. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-021-05605-Y/TABLES/3
Madhan K, Murugaraj R (2020) “Structural, electrical, and weak ferromagnetic-to-antiferromagnetic nature of Ni and La co-doped BaTiO3 by sol–gel combustion route,”. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 95(1):11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-020-05311-1
Ozer N, Sands T (2000) “Preparation and optical characterization of sol-gel deposited Pb(Zr0.45Ti0.55)O3 films,”. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 19(1–3):157–162. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008711632646
Binkle O, Nass R (1998) Synthesis and Characterization of PZT Fibers via Sol-Gel J. Sol-Gel Sci.Technol 13(1):1023–1026. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008616516686
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Yan Z, Wang A, Jiang P, Zhong M (2020) “Fabrication and performance of PNN-PZT piezoelectric ceramics obtained by low-temperature sintering,”. Sci Eng Compos Mater 27(1):359–365. https://doi.org/10.1515/SECM-2020-0039/MACHINEREADABLECITATION/RIS
Verma A et al. (2019) Enhanced energy storage properties in A-site substituted Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ceramics. J Alloy Compd 792:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.03.304
Yang Y et al. (2021) “Enhancement of magnetoresistance and near room-temperature temperature coefficient of resistivity in polycrystalline La0.7Ca0.24Na0.06MnO3 by silver doping,”. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 99(3):627–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-021-05614-X/FIGURES/7
Shrout TR, Zhang SJ (2007) “Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics: Alternatives for PZT?,”. J Electroceram 19(1):111–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-007-9047-0
Otoničar M, Škapin SD, Spreitzer M, Suvorov D (2010) “Compositional range and electrical properties of the morphotropic phase boundary in the Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 system,”. J Eur Ceram Soc 30(4):971–979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2009.10.006
Yang Z et al. (2019) Grain size engineered lead-free ceramics with both large energy storage density and ultrahigh mechanical properties. Nano Energy 58:768–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.02.003
Madhan K, Jagadeeshwaran C, Murugaraj R (2019) “Enhancement of electrical and magnetic properties in acceptor-doped BaTiO3 ferroelectric ceramics,”. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30(3):2953–2965. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10854-018-00573-6
Liu G, Jiang W, Zhang L, Cai J, Wang Z, Liu K, ... Yan Y (2018) Effects of sintering temperature and KBT content on microstructure and electrical properties of (Bi.5Na.5)TiO3-BaTiO3-(Bi.5K.5)TiO3 Pb-free ceramics. Ceramics International, 44(8):9303–9311
Madhan K, Murugaraj R (2020) “Enrichment of optical, electrical, and magnetic properties of Li+, La3+ doped BaTiO3 perovskite multifunctional ceramics,” Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process, 126(2) https://doi.org/10.1007/S00339-020-3285-2
Madhan K, Selvadurai APB, Murugaraj R (2019) Conjuring of defect-induced short and long-range ferromagnetism ordering in Ba(1− x)NdxTi0.99Co0.01O3. Materials Letters 243:100–103
Elkechai O, Manier M, Mercurio JP (1996) “Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-K0.5Bi 0.5TiO3 (NBT-KBT) system: A structural and electrical study,”. Phys Status Solidi Appl Res 157(2):499–506. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.2211570234
Sidi MM, Ben M, and Sidi FA (2018) “Investigation of Morphotropic Phase Boundary by Rietveld Refinement and Raman Spectroscopy for (1-x)(Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3-xBaTiO3 Ceramics ASIAN JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY ASIAN JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY,”. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2018.21116
Fang X, Shen B, Zhai J, Yao X (2011) “Preparation, dielectric and ferroelectric properties of (Na 0.5Bi0.5)0.94Ba0.06TiO3 thin films by a sol-gel process,”. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 58(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-010-2346-Y/FIGURES/7
Smolenskii GA, Chupis IE (1982) “Ferroelectromagnets,”. Sov Phys - Uspekhi 25(7):415–448. https://doi.org/10.1070/PU1982v025n07ABEH004570
Yadav AK et al. (2017) “Structural and dielectric properties of Pb(1−x)(Na0.5Sm0.5)xTiO3 ceramics,”. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28(14):10730–10738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6849-y
Jones GO, Thomas PA (2002) “Investigation of the structure and phase transitions in the novel A-site substituted distorted perovskite compound Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3,”. Acta Crystallogr Sect B Struct Sci 58(2):168–178. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108768101020845
Li LQ, Xiong Y, Tang MH, Cheng CP, Ouyang J (2014) “Effect of BiFeO3 doping on ferroelectric properties of Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–BaTiO3 based thin film derived by sol–gel method,”. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 72(2):394–397. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-014-3448-8/FIGURES/3
Puli VS, Martínez RV, Kumar A, Scott JF, Katiyar RS (2011) “A quaternary lead based perovskite structured materials with diffuse phase transition behavior,”. Mater Res Bull 46(12):2527–2530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.08.017
Raghavender M, Kumar GS, Prasad G (2009) “A-site substitution-controlled dielectric dispersion in lead-free sodium bismuth titanate,”. Pramana - J Phys 72(6):999–1009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-009-0092-x
Kreisel J, Glazer AM, Bouvier P, Lucazeau G (2001) “High-pressure Raman study of a relaxor ferroelectric: The Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 perovskite,”. Phys Rev B—Condens Matter Mater Phys 63(17):1741061–17410610. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.63.174106
Bibi I et al. (2021) Effect of dopant on ferroelectric, dielectric and photocatalytic properties of chromium-doped cobalt perovskite prepared via micro-emulsion route. Results Phys 20:103726. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RINP.2020.103726
Hanžić N, Jurkin T, Maksimović A, Gotić M (2015) “The synthesis of gold nanoparticles by a citrate-radiolytical method,”. Radiat Phys Chem 106:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RADPHYSCHEM.2014.07.006
Mielewczyk-Gryn A et al. (2013) Characterization of CaTi0.9Fe0.1O3/La0.98Mg0.02NbO4 composite. Cent Eur J Phys 11(2):213–218. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11534-012-0152-6
Mesrar M, Lamcharfi T, Echatoui N-S, Abdi F, and Harrach A (2019) “High dielectric constant of (1-x)(Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3-xBaTiO3 prepared by the hydrothermal method,” Mediterr J Chem. https://doi.org/10.13171/10.13171/mjc8319051210mm
Aman D, El-Hafiz DRA, Ebiad MA(2018) “Thermodynamic parameter for steam reforming reaction of biodiesel by-product using nano-sized perovskite catalysts,” Moroccan J Chem 6(3):466–479. https://doi.org/10.48317/IMIST.PRSM/MORJCHEM-V6I3.6444
Madhan K, Murugaraj R (2020) “Investigation on microstructural, electrical and optical properties of Nd-Doped BaCo0.01Ti0.99O3 perovskite,”. J Electron Mater 49(1):377–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07751-0
Cernea M, Vasile BS, Capiani C, Ioncea A, Galassi C (2012) “Dielectric and piezoelectric behaviors of NBT-BT0.05 processed by sol-gel method,”. J Eur Ceram Soc 32(1):133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.07.038
Fu Z, Zhu R, Wu D, Li A (2008) “Preparation of (1−x%)(Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3–x%SrTiO3 thin films by a sol–gel method for dielectric tunable applications,” J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 49(1):29–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-008-1844-7
Li LQ, Xiong Y, Tang MH, Cheng CP, Ouyang J (2014) “Effect of BiFeO3 doping on ferroelectric properties of Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–BaTiO3 based thin film derived by sol–gel method,” J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 72(2):394–397. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-014-3448-8
Fang X, Shen B, Zhai J, Yao X (2010) “Preparation, dielectric and ferroelectric properties of (Na0.5Bi0.5)0.94Ba0.06TiO3 thin films by a sol–gel process,” J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 58(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-010-2346-Y
Wang Q, Lian G, Dickey EC (2004) “Grain boundary segregation in yttrium-doped polycrystalline TiO2,”. Acta Mater 52(4):809–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2003.10.016
Philips Analytical (2001) “New analytical software for XRD simplifies identification of complex phase mixtures. J Appl Crystallogr 34(6):788–788. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889801019264
Rodríquez-Carvajal J, Roisnel T (2004) Line broadening analysis using FullProf*: determination of microstructural properties. In Materials Science Forum (Vol. 443, pp. 123–126). Trans Tech Publications Ltd
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW(2012) “NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis,” Nat Methods 9(7):671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Igathinathane C, Pordesimo LO, Batchelor WD (2009) “Major orthogonal dimensions measurement of food grains by machine vision using ImageJ,”. Food Res Int 42(1):76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2008.08.013
Taïbi-Benziada L, Simon A (2009) “Sintering, microstructures and dielectric properties of Ba1-x Pbx(Ti1-xLix)O3-3x F3x ferroelectric ceramics,”. Cent Eur J Chem 7(2):159–163. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11532-008-0063-y
Dagar S, Hooda A, Khasa S, Malik M (2020) “Investigations of structural, enhanced dielectric and magnetic properties of NBT doped ferrite system,”. Mater Chem Phys 249:123214. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2020.123214
Mesrar M, Lamcharfi T, Echatoui N-S et al. (2019) High dielectric constant of (1-x)(Na0. 5Bi0. 5) TiO3-xBaTiO3 prepared by the hydrothermal method. Mediterranean Journal of Chemistry 8(3):213–219
Mesrar M, Lamcharfi T, Echatoui N, Abdi F, Harrach A, Ahjyaje FZ (2019) “Hydrothermal synthesis, microstructure and electrical properties of (1- x)(Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3-xBaTiO3 ceramics,”. Moroccan J Quant Qual Res 0(1):14–24
Roukos R, Dargham SA, Romanos J, Barakat F, Chaumont D (2019) “Complex structural contribution of the morphotropic phase boundary in Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3—CaTiO3 system,”. Ceram Int 45(4):4467–4473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.11.126
Dunce M et al. (2021) Influence of sintering temperature on microstructure of Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ceramics. J Alloy Compd 884:160955. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2021.160955
Bhattacharyya R, Das S, Das A, Omar S (2021) “Effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure and conductivity of Na0.54Bi0.46Ti0.99Mg0.01O3-δ. Solid State Ion 360:115547. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SSI.2020.115547
Mrharrab L, Nfissi A, Ababou Y, Belhajji M, Sayouri S, Faik A (2021) “Effect of starting materials on the structure of pure and Gd-doped BaTiO3 elaborated by the sol gel process,” Moroccan J Chem 9(4):628–638. https://doi.org/10.48317/IMIST.PRSM/morjchem-v9i4.27263
Elbasset A, Abdi F, Lamcharfi T-D et al. (2016) Characterization micro/nanostructures of barium strontium titanate. Orient J Chem 32(3):1521–1524
Wang X, Chan HLW, Choy CL (2003) “(Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3-Ba(Cu1/2W 1/2)O3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics,”. J Am Ceram Soc 86(10):1809–1811. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.2003.tb03562.x
Hiruma Y, Aoyagi R, Nagata H, Takenaka T (2005) “Ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of (Bi1/2K 1/2)TiO3 ceramics,”. Jpn J Appl Phys, Part 1 Regul Pap Short Notes Rev Pap 44(7A):5040–5044. https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.44.5040
Chourti K et al. (2020) “Relationships between crystalline structure and dielectric properties in Sr2Sm(1-x) NdxTi2Nb3O15 ceramics,”. Rev Imist Ma 8:304–317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mesrar, M., Lamcharfi, T., Echatoui, NS. et al. Effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure and electrical properties of (Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3 processed by the sol-gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 103, 820–831 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05885-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05885-y