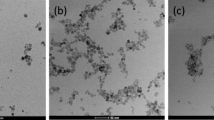
Abstract
Using a non-toxic precursor, we created a green chemical synthesis for colloidal spheres with a core@shell structure having a silica core and an iron oxide shell (SiO2@FexOy). Our synthesis pathway enabled an iron oxide shell formation with a 9 ± 6 nm thick shell onto colloidal silica spheres (ca. 700 nm). SiO2@FexOy particles reduced A549 cell viability and induced DNA damage. SiO2@FexOy particles showed the potential for removing fluoride from water.

Highlights
-
Green chemical synthesis for monodisperse, spherical SiO2@FexOy particles. A 9 ± 6 nm thick shell of iron oxide formed onto monodisperse silica spheres.
-
The presence of the shell reduced A549 cell viability and induced DNA damage.
-
SiO2@FexOy particles removed fluoride from water in batch systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available.
References
Loganathan P, Vigneswaran S, Kandasamy J, Naidu R (2013) Defluoridation of drinking water using adsorption processes. J Hazard Mater 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.12.043
He J, Yang Y, Wu Z, Xie C, Zhang K, Kong L, Liu J (2020) Review of fluoride removal from water environment by adsorption. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104516
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E(1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range J Colloid Interface Sci 26:62–69
Xu J, Wu P, Ye EC, Yuan BF, Feng YQ (2016) Metal oxides in sample pretreatment. Trends Anal Chem 80:41–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.02.027
Kuang L, Liu Y, Fu D, Zhao Y (2016) FeOOH-graphene oxide nanocomposites for fluoride removal from water: acetate mediated nano FeOOH growth and adsorption mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 490:259–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.11.071
Zhang AC, Li Y, Wang T (2017) Synthesis and properties of a high-capacity iron oxide adsorbent for fluoride removal from drinking water. Appl Surf Sci 425:272–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.06.159
Chae HS, Kim SD, Piao SH, Choi HJ (2016) Core-shell structured Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles fabricated by sol–gel method and their magnetorheology. Colloid Polym Sci 294:647–655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3818-y
Alavi Nikje MM, Tamaddoni Moghaddam S, Noruzian M, Farahmand Nejad MA, Shabani K, Haghshenas M, Shakhesi S (2014) Preparation and characterization of flexible polyurethane foam nanocomposites reinforced by magnetic core-shell Fe3O 4@APTS nanoparticles. Colloid Polym Sci 292:627–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-013-3099-2
Liu YD, Fang FF, Choi HJ (2011) Core-shell-structured silica-coated magnetic carbonyl iron microbead and its magnetorheology with anti-acidic characteristics. Colloid Polym Sci 289:1295–1298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-011-2452-6
Zhang JM, Zhai SR, Zhai B, An Q, Da, Tian G (2012) Crucial factors affecting the physicochemical properties of sol-gel produced Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 core-shell nanomaterials. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 64:347–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2864-x
Zhang J, Liu M, Liu Z, Yang T, He Q, Yang K, Wang H (2017) Studies of malachite green adsorption on covalently functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2–graphene oxides core–shell magnetic microspheres. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 82:424–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4307-1
Samiey B, Cheng CH, Wu J (2014) Organic-inorganic hybrid polymers as adsorbents for removal of heavy metal ions from solutions: a review. Materials (Basel) 7:673–726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7020673
Zhu Y, Jiang FY, Chen K, Kang F, Tang ZK (2013) Modified reverse microemulsion synthesis for iron oxide/silica core-shell colloidal particles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 66:180–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-013-2985-x
Meng SC, Wang H, Qing M, Qiu CW, Yang Y, Li YW (2015) Preparation and characterization of SiO2@Fe2O3 core-shell catalysts. J Fuel Chem Technol 43:692–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1872-5813(15)30020-7
Regulatory Affairs, T.F.S. Safety Data Sheet: Iron(III) acetylacetonate. (2018) https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AC119130010&productDescription=IRON%28III%29+ACETYLACETONAT+1KG&vendorId=VN00032119&countryCode=US&language=en. Accessed 19 Oct 2020
Anastas PT, Warner JC (1998) Green chemistry theory and practice. Oxford University Press, New York, ISBN 0-19-850698-8
Safety data sheet: Iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate. (2017) www.carlroth.com/downloads/sdb/en/5/SDB_5632_AU_EN.pdf. Accessed 19 Oct 2020
Arnal PM, Weidenthaler C, Schüth F (2006) Highly monodisperse zirconia-coated silica spheres and zirconia/ silica hollow spheres with remarkable textural properties. Chem Mater 18:2733–2739. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm052580a
Montgomery CD (2005) Design and analysis of experiments, 6th edn. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York, NY, USA. ISBN 0-471-48735-X
ASTM International ASTM D1179-99 Standard test methods for fluoride ion in water. (1999) https://doi.org/10.1520/D1179-99
Montgomery DC (2003) Applied statistics and probability for engineers, 3rd edn. John Wiley & Sons Inc, West Conshohocken, PA, USA. ISBN 0471204544
Rahman MM, Govindarajulu Z (1997) A modification of the test of Shapiro and Wilk for normality. J Appl Stat 24:219–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/02664769723828
Di Rienzo JA, Casanoves F, Balzarini M, Gonzalez L, Tablada M, Robledo CW (2014) InfoStat. Software estadístico. Versión estudiantil 2014
Grubbs FE (1950) Sample criteria for testing outlying observations. Ann Math Stat 21:27–58. https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177729885
Wright JD, Sommerdijk (2001) In: Phillips S (ed.) AJM sol-gel materials chemistry and applications, Vol. 4. Taylor & Francis, Liverpool (UK), ISBN 90-5699-326-7
Keller A, Wlokas I, Kohns M, Hasse H (2020) Thermophysical properties of solutions of Iron(III) nitrate-nonahydrate in mixtures of ethanol and water. J Chem Eng Data 65:3519–3527. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.0c00105
Ledda M, Fioretti D, Lolli MG, Papi M, Di Gioia C, Carletti R, Ciasca G, Foglia S, Palmieri V, Marchese R et al. (2020) Biocompatibility assessment of sub-5 nm silica-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in human stem cells and in mice for potential application in nanomedicine. Nanoscale 12:1759–1778. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr09683c
Williams LJ, Zosky GR (2019) The inflammatory effect of iron oxide and silica particles on lung epithelial cells. Lung 197:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-019-00200-z
Andujar P, Simon-Deckers A, Galateau-Sallé F, Fayard B, Beaune G, Clin B, Billon-Galland MA, Durupthy O, Pairon JC, Doucet J et al. (2014) Role of metal oxide nanoparticles in histopathological changes observed in the lung of welders. Part Fibre Toxicol 11:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-11-23
Rushton L (2007) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and occupational exposure to silica. Rev Environ Health 22:255–272. https://doi.org/10.1515/REVEH.2007.22.4.255
Iler RK (1979) The chemistry of silica. Solubility, polymerization, colloid and surface properties, and biochemistry. John Wiley & Sons, New York, (EEUU), ISBN 0-471-02404-X
Mukherjee S, Halder G (2018) A review on the sorptive elimination of fluoride from contaminated wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 6:1257–1270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.01.046
Habuda-Stanić M, Ravančić M, Flanagan A (2014) A review on adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution. Materials (Basel) 7:6317–6366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7096317
Vinati A, Mahanty B, Behera SK (2015) Clay and clay minerals for fluoride removal from water: a state-of-the-art review. Appl Clay Sci 114:340–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.06.013
Di Virgilio AL, Maisuls I, Kleitz F, Arnal PM (2013) A new synthesis pathway for colloidal silica spheres coated with crystalline titanium oxide and its comparative cyto- and genotoxic study with titanium oxide nanoparticles in rat osteosarcoma (UMR106) cells. J Colloid Interface Sci 394:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.11.005
Acknowledgements
Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET) (PIP-2013-0105, Long’s doctoral fellowship), Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCYT) (PICT-2014-2583 and PICT 2016-0508), and Universidad Nacional de La Plata (UNLP) (PPID 2018) partially supported this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FL performed investigation. LAL performed formal analysis. ALDV performed conceptualization, funding acquisition, and writing—review and editing. PMA performed conceptualization, funding acquisition, and writing—original draft and review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
This study is dedicated to Professor Dr. Ferdi Schüth on the occasion of his 60th birthday.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leis, F., Long, L.A., Di Virgilio, A.L. et al. Green chemical synthesis for well-defined and sharply distributed SiO2@FexOy particles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 98, 541–548 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05521-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05521-1