Abstract
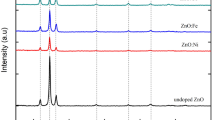
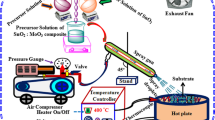
In this study, pure and doped ZnO thin films were prepared by sol–gel-based method and their electro-optical properties were investigated. For doping process, 1 at. % Al and Cu was incorporated in ZnO solution separately, and the thin films were prepared by dip coating method. The microstructure and morphology of calcined ZnO, Al-doped ZnO, and Cu-doped ZnO thin films were evaluated and compared by using various techniques X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). Results showed that nanostructured ZnO thin films with cross-linked nanoparticles (NPs) were formed, and the size of ZnO NPs increased with the Al and Cu doping. It was also found that the substitution and interstitial of Al and Cu dopants caused the instability of ZnO crystal structure and generation of extra point defects. Photoluminescence (PL) properties indicated that the dopants incorporation causes the decline of the PL intensity and the shift of the localized energy states of electrons and holes to lower energy levels. Evaluation of thin films in the UV–Vis range demonstrated that the transparency increased (>94%), and the band gap decreased to 3.08 and 3.06 eV with the incorporation of Al and Cu into ZnO thin films, respectively. The electrical conductivity also improved by Al and Cu doping of ZnO TFs.

Highlights
-
Nanostructured sol-gel doped ZnO thin films show the promising electro-optical properties.
-
Al and Cu dopant could change the parameters of ZnO lattice network.
-
Optical band gap reduced by generation of point defects those act as luminescence quenchers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ng ZN, Chan KY, Low CY, Kamaruddin SA, Sahdan MZ (2015) Al and Ga dopedZnO films prepared by a sol–gel spin coating technique. Ceram Int 41:254–258
Bouaine A, Bourebia A, Guendouz H, Riane Z (2018) Synthesis and characterization of In doped ZnO thin film as efficient transparent conducting oxide candidate. Optik 166:317–322
Viet Vu D, Hai Le D, Xuan Nguyen C, Quang Trinh T (2019) Comparison of structural and electric properties of ZnO-based n-type thin films with different dopants for thermoelectric applications. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 91:146–153
Jafari H, Sadeghzadeh S, Rabbani M, Rahimi R (2018) Effect of Nb on the structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of Aldoped ZnO thin films fabricated by the sol-gel method. Ceram Int 44:20170–20177
Prabhu RR, Saritha AC, Shijeesh MR, Jayaraj MK (2017) Fabrication of p-CuO/n-ZnO heterojunction diode via sol-gel spin coating technique. Mater Sci Eng B 220:82–90
AlArfaj E, Subahi A (2015) The influence of external magnetic field on the structural and optical properties of nanocrystalline ZnO thin films prepared by dip coating method. Superlattic Micros 86:508–517
Verma K, Chaudhary B, Kumar V, Sharma V, Kumar M (2017) Investigation of structural, morphological and optical properties of Mg: ZnO thin films prepared by sol-gel spin coating method. Vacuum 146:524–529
Aydın H, Aydın C, Al-Ghamdi AA, Farooq WA, Yakuphanoglu F(2016) Refractive index dispersion properties of Cr-doped ZnO thin films bysol–gel spin coating method Optik 127:1879–1883
Sharma SK, Singh SP, Kim DY (2018) Fabrication of the heterojunction diode from Y-doped ZnO thin films on p-Si, substrates by sol-gel method. Solid State Commun 270:124–129
Tyona MD, Osuji RU, Asogwa PU, Jambure SB, Ezema FI (2017) Structural modification and band gap tailoring of zinc oxide thin films using copper impurities. J Solid State Electrochem 21(9):2629–2638
Samadi M, Zirak M, Naseri A, Khorashadizade E, Moshfegh AZ (2016) Recent progress on doped ZnO nanostructures for visible-light photocatalysis. Thin Solid Films 605:2–19
Sandeep KM, Bhat Shreesha, Serrao FelcyJyothi, Dharmaprakash SM (2018) Effect of 8 MeV electrons irradiation on carrier transport mechanism in ZnO thin films fabricated by sol-gel spin coating technique. Surf Coat Tech 338:96–102
Benaboud A, Zaabat M, Aida MS, Boudine B, Benzitouni S, Saidani T (2017) Fe2O4/ZnO-nanowires synthesis by dip-coating for Orange II-dye photodegradation. Optik 144:397–405
Kaushik VK, Mukherjee C, Ganguli T, Sen PK (2017) Electrical and optical characteristics of aerosol assisted CVD grown ZnO based thin film diode and transistor. J Alloy Compd 696(5):727–735
Mickan M, Helmersson U, Horwat D (2018) Effect of substrate temperature on the deposition of Al-doped ZnO thin films using high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Surf Coat Tech 347(15):245–251
Dai K, Ying MJ, Lian J, Shi YJ, Cao ZS, Song HN, Wei MY, Jiang QF, Zhang C (2019) Optical properties of polar thin films: ZnO (0001) and ZnO (000–1) on sapphire substrate. Opt Mater 94:272–276
Amuthan BK, Vinoth S, Karthikeyan V, Roy VAL, Thilakan P (2019) Influence of nitrogen dopant source on the structural, photoluminescence and electrical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by pulsed spray pyrolysis. Ceram Int 45(18):24324–24330
Cetin SS, Uslu I, Aytimur A, Ozcelik S (2012) Characterization of Mg doped ZnO nanocrystallites prepared via electrospinning. Ceram Int 38:4201–4208
Istrate AI, Nastase F, Mihalache I, Comanescu F, Gavrila R, Tutunaru O, Romanitan C, Tucureanu V, Nedelcu M, Müller R (2019) Synthesis and characterization of Ca doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 92:585
Yoon Yeo-Chang, Park Kyoung-Seok, Kim Sam-Dong (2015) Effects of low preheating temperature for ZnO seed layer deposited by sol–gel spin coating on the structural properties of hydrothermal ZnO nanorods. Thin Solid Films 597:125–130
Makableh YF, Vasan R, Sarker JC, Nusir AI, Seal S, Manasreh MO (2014) Enhancement of GaAs solar cell performance by using a ZnO sol–gel antireflection coating. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 123:178–182
Ariyakkani P, Suganya L, Sundaresan B (2017) Investigation of the structural, optical and magnetic properties of Fe doped ZnO thin films coated on glass by sol-gel spin coating method. J Alloy Compd 695:3467–3475
Sbeta M, Atilgan A, Atli A, Yildiz A (2018) Influence of the spin acceleration time on the properties of ZnO:Ga thin films deposited by sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 86:513
Islam MR, Rahman M, Farhad SFU, Podder J (2019) Structural, optical and photocatalysis properties of sol–gel deposited Aldoped ZnO thin films. Surf Interfaces 16:120–126
Beiraghdar N, Talebian N (2015) Surfactant-assisted ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel dip coating for applied antibacterial coatings: a comparative study with solvothermal-derived ZnO powders. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 75:383
Patterson A (1939) The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys Rev 56(10):978–982
Corami A, Mignardi S, Ferrini V (2007) Copper and Zinc decontamination from single- and binary-metal solutions using hydroxyapatite. J Hazard Mater 146(1–2):164–170
Omri K, Bettaibi A, Khirouni K, El Mir L (2018) The optoelectronic properties and role of Cu concentration on the structural and electrical properties of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys B Condens Matter 537:167–175
Peng Z, Wu D, Wang W, Tan F, Wang X, Chen J, Qiao X (2017) Effect of metal ion doping on ZnO nanopowders for bacterial inactivation under visible-light irradiation. Powder Technol 315:73–80
Osali S, Esfahani H, Karami HR (2018) Effect of Al doping on crystallography and electro-optical properties of ZnO semiconductor thin films prepared by electrospinning. Solid State Sci 83:90–98
Osali S, Esfahani H, Dabir F, Tajaslan P (2019) Structural and electro-optical properties of electrospun Cu-Doped ZnO thin films. Solid State Sci 98:106038
Chen Z, Yan Q, Zhao Y, Cao M, Wang J, Wang L (2019) The structure and the optical-electrical properties of the ZnO films and the Al:ZnO/N: ZnO homojunction photodiode. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 91:101
Dhamodharan P, Manoharan C, Bououdina M, Venkadachalapathy R, Ramalingam S (2017) Al-doped ZnO thin films grown onto ITO substrates as photoanode in dye sensitized solar cell. Sol Energy 141:127–144
Liqiang J, Yichun Q, Baiqi W, Shudan L et al. (2006) Review of photoluminescence performance of nano-sized semiconductor materials and its relationships with photocatalytic activity. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90:1773–1787
Baradaran M, Ghodsi FE (2019) Highly efficient visible photocatalytic degradation of MB organic dye by heteromorphic ZnO/AZO/ZnO nanocatalysts: effect of AZO thickness. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 92:25–39
Hasabeldaim E, Ntwaeaborwa OM, Kroon RE, Swart HC (2019) Structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of Eu doped ZnO thin films prepared by spin coating. J Mol Struct 1192:105–114
Chen X, Qingshuang X, Jitao L (2020) Significantly improved photoluminescence properties of ZnO thin films by lithium doping. Ceram Int 46:2309–2316
Praveena R, Sameera VS, Mohiddon MdA, Krishna MG (2019) Surface plasmon resonance, photoluminescence and surface enhanced Raman scattering behaviour of Ag/ZnO, ZnO/Ag and ZnO/Ag/ZnO thin films. Phys B 555:118–124
Ghosh J, Ghosh R, Giri PK (2018) Tuning the visible photoluminescence in Al doped ZnO thin film and its application in label-free glucose detection. Sens Actuat B Chem 254:681–68
Musavi E, Khanlary M, Khakpour Z (2019) Red-orange photoluminescence emission of sol-gel dip-coated prepared ZnO and ZnO:Al nano-crystalline films. J Lumin 216:116696
Sajjad M, Ullah I, Khan MI, Khan J, Khan MY, Qureshi MT (2018) Structural and optical properties of pure and copper doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Results Phys 9:1301–1309
Zeng H, Duan G, Li Y, Yang S, Xu X, Cai W (2010) Blue luminescence of ZnO nanoparticles based on non-equilibrium processes, defect origins and emission controls. Adv Funct Mater 20(4):561–572
West C, Robbins DJ, Dean PJ, Hayes W (1983) The luminescence of copper in zinc oxide. Phys B+C 116(1–3):492–499
Kuriakose S, Satpati B, Mohapatra S (2015) Highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes by Cu doped ZnO nanostructures. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17(38):25172–25181
Srinatha N, Raghu P, Mahesh HM, Angadi B (2017) Spin-coated Al-doped ZnO thin films for optical applications, Structural, micro-structural, optical and luminescence studies. J Alloy Compd 722:888–895
Coman T, Timpu D, Nica V, Vitelaru C, Rambu AP, Stoian G, Olaru M, Ursu C (2017) Sequential PLD in oxygen/argon gas mixture of Al-doped ZnO thin films with improved electrical and optical properties. Appl Surf Sci 418:456–462
Salem M, Massoudi I, Akir S, Litaiem Y, Gaidi M, Khirouni K (2017) Photoelectrochemical and opto-electronic properties tuning of ZnO films, effect of Cu doping content. J Alloy Compd 722:313–320
Masjedi-Arani M, Salavati-Niasari M (2017) Metal (Mn, Co, Ni and Cu) doped ZnO-Zn2SnO4-SnO2 nanocomposites, Green sol-gel synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity. J Mol Liq 248:197–204
Alfaro Cruz MR, Ceballos-Sanchez O, Luévano-Hipólito E, Torres-Martínez LM (2018) ZnO thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering: effects of the annealing and atmosphere conditions on the photocatalytic hydrogen production. Int J Hydrog Energ 43(22):10301–10310
Tauc J, Grigorovici R, Vancu A (1966) Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys Status Solidi, B 15(2):627–637
Kumar V, Singh RG, Purohit LP, Mehra RM (2011) Structural, transport and optical properties of boron-doped zinc oxide nanocrystalline. J Mater Sci Technol 27(6):481–488
Hun JG, Kim SH, Koh JH (2018) Enhanced electrical and optical properties based on stress reduced graded structure of Al-doped ZnO thin films Ceram Int 44:735–741
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dabir, F., Esfahani, H., Bakhtiargonbadi, F. et al. Study on microstructural and electro-optical properties of sol–gel derived pure and Al/Cu-doped ZnO thin films. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 96, 529–538 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05269-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05269-0