Abstract
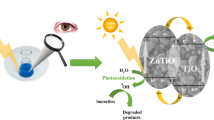
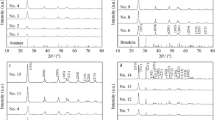
Zr/TiO2 anatase photocatalysts with 0.5, 1, 2, 5 and 7.5 mol.% Zr were prepared using pressurized hot water crystallization and their photocatalytic activity was explored in acid orange 7 photodegradation. Parent TiO2 was also prepared and tested. From all tested photocatalysts, 2 mol.% Zr/TiO2 showed the highest photoactivity, and 7.5 mol.% Zr/TiO2 showed the lowest photoactivity. The poor photoactivity of 7.5 mol.% Zr/TiO2 can be explained by the amorphous ZrO2 present in the surface layer (~1–3 μm depth) of TiO2 anatase nanocrystallite agregates which changed the aggregate morphology and shielded the anatase nanocrystallite surface. The type and amount of defects (e.g., oxygen vacancies, lattice defects) did not effect the photoactivity of Zr/TiO2 in AO7 photodegradation. The addition of Zr to TiO2 significantly affects the photocatalyst morphology and the location where amorphous ZrO2 forms. The optimal Zr loading in TiO2 was determined to be 2 mol.%.

Highlights
-
The type and amount of defects do no effect the Zr/TiO2 photoactivity.
-
Amorphous ZrO2 in surface layer of TiO2 agregates shields the anatase nanocrystallites surface.
-
Amorphous ZrO2 in surface layer of TiO2 agregates decreases the Zr/TiO2 anatase photoactivity
-
Zr4+ dopation in TiO2 affects crucially photocatalyst morphology.
-
2 mol.% Zr/TiO2 shows the highest photoactivity in acid orange 7 degradation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (1997). Kyoto https://unfccc.int/process/the-kyoto-protocol/status-of-ratification
Coronado JM, Fresno F, Hernández-Alonso MD, Portanela R (2013) Design of advanced photocatalytic materials for energy and environmental applications. Springer, London
Nakata K, Fujishima A (2012) TiO2 photocatalysis: design and applications. J Photochem Photobiol C Photochem Rev 13(3):169–189
Ong CB, Ng LY, Mohammad AW (2018) A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:536–551
Harandi D, Ahmadi H, Achachluei MM (2016) Comparison of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles for the improvement of consolidated wood with polyvinyl butyral against white rot. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 108:142–148
Znaidi L (2010) Sol-gel-deposited ZnO thin films: a review. Mater Sci Eng B Adv 174(1–3):18–30
Khedr TM, El-sheikh SM, Hakki A, Ismail AA (2017) Highly active non-metals doped mixed-phase TiO2 for photocatalytic oxidation of ibuprofen under visible light. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 346:530–540
Xing Z, Zhang J, Cui J, Yin J, Zhao T, Kuang J, Xiu Z, Wan N, Zhou W (2018) Recent advances in floating TiO2 -based photocatalysts for environmental application. Appl Catal B Environ 225:452–467
Mahy JG, Lambert SD, Léonard GLM, Zubiaur A, Olu P-Y, Mahmoud A, Boschini F, Heinrichs B (2016) Towards a large scale aqueous sol-gel synthesis of doped TiO2: study of various metallic dopings for the photocatalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol. J Photochem Photobiol 329:189–202
Wen J, Xie J, Chen X, Li X (2017) A review on g-C3N4 -based photocatalysts. Appl Surf Sci 391:72–123
Kharlamov A, Bondarenko M, Kharlamova G, Gubareni N (2016) Features of the synthesis of carbon nitride oxide (g-C3N4) at urea pyrolysis. Diam Relat Mater 66:16–22
Xiao H, Wang W, Liu G, Chen Z, Lv K, Zhu J (2015) Photocatalytic performances of g-C3N4 based catalysts for RhB degradation: effect of preparation conditions. Appl Surf Sci 358:313–318
Ma J, Wang C, He H (2016) Enhanced photocatalytic oxidation of NO over g-C3N4 -TiO2 under UV and visible light. Appl Catal B Environ 184:28–34
Zhang J, Xu LJ, Zhu ZQ, Liu QJ (2015) Synthesis and properties of (Yb, N)-TiO2 photocatalyst for degradation of methylene blue (MB) under visible light irradiation. Mater Res Bull 70:358–364
Naraginti S, Thejaswini TVL, Prabhakaran D, Sivakumar A, Satyanarayana VSV, Prasad ASA (2015) Enhanced photo-catalytic activity of Sr and Ag co-doped TiO2 nanoparticles for the degradation of Direct Green-6 and Reactive Blue-160 under UV & visible light. Spectrochim Acta A 149:571–579
Matějová L, Šihor M, Brunátová T, Ambrožová N, Reli M, Čapek L, Obalová L, Kočí K (2015) Microstructure-performance study of cerium-doped TiO2 prepared by using pressurized fluids in photocatalytic mitigation of N2O Res Chem Intermed 41:9217–9231
Jiang H, Gomez-Abal RI, Rinke P, Scheffler M (2010) Electronic band structure of zirconia and hafnia polymorphs from the GW perspective Phys Rev B 81:085119
Kambur A, Pozan GS, Boz I (2012) Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of TiO2-ZrO2 binary oxide nanoparticles. Appl Catal B Environ 115:149–158
Lukáč J, Klementová M, Bezdička P, Bakardjieva S, Šubrt J, Szatmáry L, Bastl Z, Jirkovský J (2007) Influence of Zr as TiO2 doping ion on photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol. Appl Catal B Environ 74(1-2):83–91
Matějová L, Kočí K, Reli M, Čapek L, Matějka V, Šolcová O, Obalová L (2013) On sol-gel derived Au-enriched TiO2 and TiO2-ZrO2 photocatalysts and their investigation in photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. Appl Surf Sci 285:688–696
Zou H, Lin YS (2004) Structural and surface chemical properties of sol-gel derived TiO2-ZrO2 oxides. Appl Catal A Gen 265(1):35–42
Choina J, Fischer C, Flechsig GU, Kosslick H, Tuan VA, Tuyen ND, Tuyen NA, Schulz A (2014) Photocatalytic properties of Zr-doped titania in the degradation of the pharmaceutical ibuprofen. J Photoch Photobio A 274:108–116
Gao BF, Lim TM, Subagio DP, Lim TT (2010) Zr-doped TiO2 for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A. Appl Catal A Gen 375(1):107–115
Inturi SNR, Boningari T, Suidan M, Smirniotis PG (2014) Visible-light-induced photodegradation of gas phase acetonitrile using aerosol-made transition metal (V, Cr, Fe, Co, Mn, Mo, Ni, Cu, Y, Ce, and Zr) doped TiO2. Appl Catal B Environ 144:333–342
Naraginti S, Stephen FB, Radhakrishnan A, Sivakumar A (2015) Zirconium and silver co-doped TiO2 nanoparticles as visible light catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol, degradation of methyl orange and methylene blue. Spectrochim Acta A 135:814–819
Mattsson A, Lejon C, Štengl V, Bakardjieva S, Opluštil F, Andersson PO, Österlund L (2009) Photodegradation of DMMP and CEES on zirconium doped titania nanoparticles. Appl Catal B Environ 92(3-4):401–410
Mattsson A, Lejon C, Bakardjieva S, Štengl V, Osterlund L (2013) Characterisation, phase stability and surface chemical properties of photocatalytic active Zr and Y co-doped anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. J Solid State Chem 199:212–223
Cha JA, An SH, Jang HD, Kim CS, Song DK, Kim TO (2012) Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of N-doped TiO2/ZrO2 visible-light photocatalysts. Adv Powder Technol 23(6):717–723
Feng HJ, Zhang MH, Yu LYE (2012) Hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic performance of metal-ions doped TiO2. Appl Catal A Gen 413:238–244
Tian G, Pan K, Fu H, Jing L, Zhou W (2009) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of S-doped TiO2-ZrO2 nanoparticles under visible-light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 166(2-3):939–944
Kim CS, Shin JW, An SH, Jang HD, Kim TO (2012) Photodegradation of volatile organic compounds using zirconium-doped TiO2/SiO2 visible light photocatalysts. Chem Eng J 204:40–47
McManamon C, Holmes JD, Morris MA (2011) Improved photocatalytic degradation rates of phenol achieved using novel porous ZrO2-doped TiO2 nanoparticulate powders. J Hazard Mater 193:120–127
Fresno F, Hernandez-Alonso MD, Tudela D, Coronado JM, Soria J (2008) Photocatalytic degradation of toluene over doped and coupled (Ti,M)O2 (M = Sn or Zr) nanocrystalline oxides: influence of the heteroatom distribution on deactivation. Appl Catal B Environ 84(3-4):598–606
Das M, Bhattacharyya KG (2013) Oxidative degradation of orange II dye in water with raw and acid-treated ZnO, and MnO2 CLEAN Soil Air Water 41:984–991
Konstantinou IK, Albanis TA (2004) TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations - a review. Appl Catal B Environ 49(1):1–14
Lang J, Matějová L, Troppová I, Čapek L, Endres J, Daniš S (2017) Novel synthesis of ZrxTi1-xOn mixed oxides using titanyl sulphate and pressurized hot and supercritical fluids, and their photocatalytic comparison with sol-gel prepared equivalents. Mater Res Bull 95:95–103
Lang J, Matějová L, Matěj Z, Čapek L, Svoboda L (2018) Crystallization of Zr0.1Ti0.9On mixed oxide by pressurized hot water and its effect on microstructural properties and photoactivity J Supercrit Fluid 141:39–48
Matějová L, Polách L, Lang J, Šihor M, Reli M, Brunátová T, Daniš S, Peikertová P, Troppová I, Kočí K (2017) Novel TiO2 prepared from titanyl sulphate by using pressurized water processing and its photocatalytic activity evaluation. Mater Res Bull 95:30–46
Matěj Z, Kužel R, Nichtová L (2010) XRD total pattern fitting applied to study of microstructure of TiO2 films. Powder Diffr 25(2):125–131
Zdeněk M (2014) Refining bimodal microstructure of materials with MSTRUCT. Powder Diffr 29(S2):35–41
Gregg SJ, Sing KSW (1982) Adsorption, surface area and porosity, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319
Shannon RD (1976) Revised effective ionic-radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr A 32(Sep1):751–767
Li Z, Wang W, Greenham NC, McNeill CR (2014) Influence of nanoparticle shape on charge transport and recombination in polymer/nanocrystal solar cells. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16(47):25684–25693
Tang H, Prasad K, Sanjinès R, Schmid PE, Lévy F (1994) Electrical and optical properties of TiO2 anatase thin films. J Appl Phys 75(4):2042–2047
Abazović ND, Čomor MI, Dramićanin MD, Jovanović DJ, Ahrenkiel SP, Nedeljković JM (2006) Photoluminescence of anatase and rutile TiO2 particles. J Phys Chem B 110(50):25366–25370
Sabry RS, Al-Haidarie YK, Kudhier AM (2016) Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 78(2):299–306
Liu B, Wen L, Zhao X (2007) The photoluminescence spectroscopic study of anatase TiO2 prepared by magnetron sputtering. Mater Chem Phys 106(2-3):350–353
Kernazhitsky L, Shymanovska V, Gavrilko T, Naumov V, Fedorenko L, Kshnyakin V, Baran J (2014) Laser-excited excitonic luminescence of nanocrystalline TiO2 powder. Ukr J Phys 59(3):246–253
Fu C, Gong Y, Wu Y, Liu J, Zhang Z, Li C, Niu L (2016) Photocatalytic enhancement of TiO2 by B and Zr co-doping and modulation of microstructure. Appl Surf Sci 379:83–90
Reli M, Edelmannová M, Šihor M, Praus P, Svoboda L, Mamulová KK, Otoupalíková H, Čapek L, Hospodková A, Obalová L, Kočí K (2015) Photocatalytic H2 generation from aqueous ammonia solution using ZnO photocatalysts prepared by different methods. Int J Hydrog Energy 40(27):8530–8538
Acknowledgements
This work was supported from ERDF “Institute of Environmental Technology – Excellent Research” (No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000853). Experimental results were accomplished using Large Research Infrastructure ENREGAT supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic under project No. LM2018098. The financial support of the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (project No. 14-23274S) is also gratefully acknowledged. XPS measurements were carried out with the equipment purchased thanks to the financial support of the NanoEnviCZ supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic under project No. LM2015073. The authors also thank Dr. Martin Reli from IET VŠB-TUO for his guidance in photoelectrochemical measurements and advices with spectra interpretation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lang, J., Matějová, L., Matěj, Z. et al. The effect of Zr loading in Zr/TiO2 prepared by pressurized hot water on its surface, morphological and photocatalytic properties. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 90, 369–379 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-04956-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-04956-x