Abstract
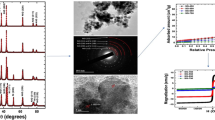
Nickel/nickel oxide (Ni/NiO) nanocomposite was synthesized by simple sol–gel process by using nickel nitrate as a precursor and citric acid as a gelling agent. The obtained samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray analysis, Fourier transformed infra-red spectroscopy and vibrating sample magnetometer studies. The influence of citric acid on the formation of Ni/NiO composition was primarily studied by varying the mole ratios of nickel nitrate and citric acid ((N:C) : 1:1, 1:2, 1:4, 1:6 and 1:8). The XRD studies confirmed that the synthesized samples had a mixture of Ni and NiO or single phase of NiO. The SEM observations confirmed that the composites were spherical in shape with an average size of about 70 nm for 1:1 mole ratio and about 40 nm for 1:8 mole ratio samples. At lower N:C mole ratios, the obtained samples had mixture of ferromagnetic Ni and NiO, while at high N:C mole ratios, the sample consisted of almost single phase of NiO. The formation of ferromagnetic Ni was attributed to reduction of some amount of NiO by residual carbon.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao CNR, Govindaraj A, Vivekchand SRC (2006) Annu Rep Prog Chem Sect. A Inorg Chem 102:20–45
Bruce PG, Scrosati B, Tarascon JM (2008) Angew Chem Int Ed 47:2930–2946
Wen W, Wu JM, Cao MH (2013) J Mater Chem A 1:3881–3885
Fujio Y, CN Xu, Terasaki N, Ueno N (2014) J Lumin 148:89–93
Lim J, Murugan P, Lakshminarasimhan N, Kim JY, Lee JS, Lee SH, Choi W (2014) J Catal 310:91–99
Jiang Y, Chen D, Song J, Jiao Z, Maa Q, Zhang H, Cheng L, Zhao B, Chu Y (2013) Electrochim Acta 91:173–178
Yuan F, Ni Y, Zhang L, Yuan S, Wei J (2013) J Mater Chem A 1:8438–8444
Hua B, Chen W, Zhou J (2013) Sens Actuators B Chem 176:522–533
Mahendraprabhu K, Miura N, Elumalai P (2013) Ionics 19:1681–1686
Schelter M, Zosel J, Oelßnera W, Gutha U, Mertig M (2013) Sens Actuators B Chem 187:209–214
Lee I, Choi SJ, Park KM, Lee SS, Choi S, Kim ID, Park CO (2014) Sens Actuators B Chem 197:300–307
Dutta A, Datta J (2014) J Mater Chem A 2:3237–3250
Cui E, Lu G (2014) Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:8959–8968
Hu Q, Jacobsen T, Hansen KV, Mogensen M (2012) J Electrochem Soc 159:B811–B817
Rahulan KM, Padmanathan N, Philip R, Balamurugan S, Kanakam CC (2013) Appl Surf Sci 282:656–661
Deraz NM (2012) Int J Electrochem Sci 7:4608–4616
Hwang JH, Dravid VP, Teng MH, Host JJ, Elliott BR, Johnson DL, Mason TO (1997) J Mater Res 12:1076–1082
Niasari MS, Davar F, Fereshteh Z (2010) J Alloys Compd 494:410–414
Davar F, Fereshteh Z, Niasari MS (2009) J Alloys Compd 476:797–801
Ren Y, Gao L (2010) J Am Ceram Soc 93:3560–3564
Aslani A, Oroojpour V, Fallahi M (2011) Appl Surf Sci 257:4056–4061
Hu C, Gao Z, Yang X (2007) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 44:171–176
Wu Y, He Y, Wu T, Chen T, Weng W, Wan H (2007) Mater Lett 61:3174–3178
Thota S, Kumar J (2007) J Phys Chem Solids 68:1951–1964
Teoh LG, Li KD (2012) Mater Trans 53:2135–2140
Ouyang JM, Deng SP (2003) Dalton Trans 2846–2851. doi:10.1039/B304319C
Proenca MP, Sousa CT, Pereira AM, Tavares PB, Ventura J, Vazquez M, Araujo JP (2011) Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:9561–9567
Dimitrov DV, Zhang S, Xiao JQ, Hadjipanayis GC, Prados C (1998) Phys Rev B 58:12090–12094
Acknowledgments
Department of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of India, New Delhi, is acknowledged for the financial support for the Fast-Track Grant (DST/FT/CS-64/2010). We extend our gratitude to CSIR-CECRI at Karaikudi and Chennai, and Central Instrumentation Facility - Pondicherry University for XRD and SEM measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahendraprabhu, K., Elumalai, P. Influence of citric acid on formation of Ni/NiO nanocomposite by sol–gel synthesis. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 73, 428–433 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3554-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3554-7