Abstract
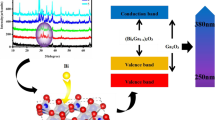
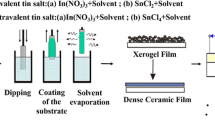
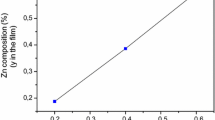
In this study, IZO/IGZO powders and films of different composition ratios were fabricated by sol–gel method. The influences of the composition ratio on the decomposition temperature, crystallization behavior, structural and optical properties of multi-component oxides were thoroughly examined. Thermogravimetric/differential scanning calorimetric results revealed that in contrast to zinc and indium oxides, the high crystallization temperature and low crystallinity of gallium oxide were attributed to the high dehydroxylation temperature of gallium hydroxide, which led to the high decomposition and crystallization temperatures of IGZO compound. The XRD analysis of the IGZO films confirmed that the addition of Ga amount made the films turn into amorphous easily. However, TEM analysis suggested that the IZO film (In:Zn = 1:2) and the IGZO (In:Ga:Zn = 1:1:1) film consisted of short-range-order nanostructure although the selected area diffraction of both samples indicated that they are amorphous. The transmittance measurements agreed well with the XRD results; that is, the band gaps of the IZO/IGZO films obviously depend on the composition ratio and are closely related to the change of the structural properties.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hosono H (2007) Thin Solid Films 515:6000
Phillips JM, Cava RJ, Thomas GA, Carter SA, Kwo J, Siegrist T, Krajewski JJ, Marshall JH, Peck WF Jr, Rapkine DH (1995) Appl Phys Lett 67:2246
Lee S-Y, Park B-O (2005) Thin Solid Films 484:184
Chen KJ, Hung FY, Chang SJ, Hu ZS (2009) Appl Surf Sci 255:6308
Choi CG, Seo SJ, Bae BS (2008) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 11:H7
Seo SJ, Choi CG, Hwang YH, Bae BS (2009) J Phys D Appl Phys 42:035106
Lee JH, Ko KH, Park BO (2003) J Cryst Growth 247:119
Jiménez-González AE, Urueta JAS, Suárez-Parra R (1998) J Cryst Growth 192:433
Bandyopadhyay S, Paul GK, Roy R, Sen SK, Sen S (2002) Mater Chem Phys 74:83
Ong BS, Li C, Li Y, Wu Y, Loutfy R (2007) J Am Chem Soc 129:2750
Cheng HC, Chen CF, Tsay CY, Leu JP (2009) J. Alloy Compd. 475:L46
Poznyak SK, Kulak AI (2000) Electrochim Acta 45:1595
Ho WH, Yen SK (2006) Thin Solid Films 498:80
Li E, Cheng Z, Xu J, Pan Q, Yu W, Chu Y (2009) Cryst Growth Des 9:2146
Pentyala N, Guduru RK, Shnerpunas EM, Mohanty PS (2011) Appl Surf Sci 257:6850
Lee I, Kwak J, Haam S, Lee SY (2010) J Cryst Growth 312:2107
Girija K, Thirumalairajan S, Avadhani GS, Mangalaraj D, Ponpandian N, Viswanathan C (2013) Mater Res Bull 48:2296
Kim GH, Shin HS, Ahn BD, Kim KH, Park WJ, Kimz HJ (2009) J Electrochem Soc 156:H7
Inoue K, Tominaga K, Tsuduki T, Mikawa M, Moriga T (2009) Vacuum 83:552
Jeon H, Na S, Moon MR, Jung D, Kim H, Lee HJ (2011) J Electrochem Soc 158:H949
Wang Y, Liu SW, Sun XW, Zhao JL, Goh GKL, Vu QV, Yu HY (2010) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 55:322
Lin K, Chen G -T, Hsu P -C, Sawada Y submitted to JSST
Kasper H (1967) Z. Anorg Allg. Chem. 349:113
Acknowledgments
Financial support was granted by the National Science Council of Republic of China under contact numbers NSC 102-2221-E-218-039.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Km., Hsu, Pc., Chen, Gt. et al. Compound-induced changes in thermal, structural and optical properties of indium–gallium–zinc oxides prepared by sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 71, 260–266 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3374-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3374-9