Abstract
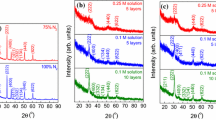
Indium tin oxide (ITO) is recognized as the best transparent and conductive material [transparent conducting oxide (TCO)] until now and its properties are dependent on the preparation method. In the present work ITO films with In:Sn atomic ratio 9:1 were prepared by a sol–gel route on different substrates (microscope glass slides, microscope glass covered with one layer of SiO2 and Si wafers) for TCO applications. The multilayer ITO films were obtained by successive deposition by the dip-coating method and the films were characterized from the structural, morphological, optical, and electrical points of view using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, spectroscopic ellipsometry and by Hall effect measurements, respectively. The results showed that the thickness, optical constants and carrier numbers depend strongly on the type of substrate, number of deposited layers and sol concentration. The optical properties of ITO films are closely related to their electrical properties. The enhancement of the conductivity was possible with the increase of crystallite size (which occurred after thermal treatment) and with the reduction of surface roughness.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lunt RR, Bulovic V (2011) Appl Phys Lett 98:113305
Tien WC, Chu AK (2014) Sol Energ Mater Sol C 120:18–22
Furukawa K, Terasaka Y, Ueda H, Matsumura M (1997) Synth Met 91(1–3):99–101
Li Z-H, Cho E-S, Kwon SJ (2010) Appl Surf Sci 257(3):776–780
Celik E, Aybarc U, Ebeoglugil MF, Birlik I, Culha O (2009) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 50:337–347
Sierros KA, Morris NJ, Kukureka SN, Cairns DR (2009) Wear 267(1–4):625–631
Ahn MH, Cho E-S, Kwon SJ (2011) Appl Surf Sci 258:1242–1248
Houng B, Lin SL, Chen SW, Wang A (2011) Ceram Int 37:3397–3403
Lee CJ, Lin HK, Li CH, Chen LX, Lee CC, Wu CW, Huang JC (2012) Thin Solid Films 522:330–335
Manavizadeh N, Boroumand FA, Asl-Soleimani E, Raissi F, Bagherzadeh S, Khodayari A, Rasouli MA (2009) Thin Solid Films 517:2324–2327
Song S, Yang T, Liu J, Xin Y, Li Y, Han S (2011) Appl Surf Sci 257:7061–7064
Stroescu H, Anastasescu M, Preda S, Nicolescu M, Stoica M, Stefan N, Kampylafka V, Aperathitis E, Modreanu M, Zaharescu M, Gartner M (2013) Thin Solid Films 541:121–126
Wasa K, Hayakawa S (1991) Handbook of sputter deposition technology. Noyes Publications, NJ
Facchetti A, Marks TJ (2010) Transparent electronics: from synthesis to applications. Wiley, New York
Ginley DS, Hosono H, Paine DC (2010) Handbook of transparent conductors. Springer, New York
Rozati SM, Ganj T (2004) Renew Energy 29(10):1671–1676
El Rhaleb H, Benamar E, Rami M, Roger JP, Hakam A, Ennaoui A (2002) Appl Surf Sci 201(1–4):138–145
Bisht H, Eun H-T, Mehrtens A, Aegerter MA (1999) Thin Solid Films 351:109–114
Madhi I, Saadoun M, Bessais B (2012) Procedia Eng 47:192–195
Mbarek H, Saadoun M, Bessais B (2006) Mater Sci Eng C 26(2–3):500–504
Meng L-J, Gao J, Silva RA, Song S (2008) Thin Solid Films 516:5454–5459
Zhinong Y, Yuqiong L, Fan X, Zhiwei Z, Wei X (2009) Thin Solid Films 517:5395–5398
Okuya M, Ito N, Shiozaki K (2007) Thin Solid Films 515:8656–8659
Fallah HR, Varnamkhasti MG, Vahid MJ (2010) Renew Energy 35:1527–1530
Senthilkumar V, Vickraman P, Jayachandran M, Sanjeeviraja C (2010) Vacuum 84:864–869
Stoica TF, Stoica TA, Vanca V, Lakatos E, Zaharescu M (1999) Thin Solid Films 348:273–278
Stoica TF, Stoica TA, Zaharescu M, Popescu M, Sava F, Popescu-Pogrion N, Frunză L (2000) J Optoelectron Adv Mater 2:684–688
Alam MJ, Cameron DC (2000) Thin Solid Films 377:455–459
Stoica TF, Gartner M, Losurdo M, Teodorescu VS, Blanchin M, Stoica T, Zaharescu M (2004) Thin Solid Films 455–456:509–512
Biswas PK, De A, Dua LK, Chkoda L (2006) Appl Surf Sci 253:1953–1959
Beaurain A, Luxembourg D, Dufour C, Koncar V, Capoen B, Bouazaoui M (2008) Thin Solid Films 516:4102–4106
Valencia HY, Moreno LC, Ardila AM (2008) Microelectron J 39:1356–1357
Prodi-Schwab A, Luthe Th, Jahn R, Herbig B, Lobmann P (2008) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 47:68–73
Soliemana A, Zayeda MK, Alamria SN, Al-Dahoudib N, Aegerter MA (2012) Mater Chem Phys 134:127–132
Liu J, Wu D, Zhang N, Wang Y (2010) Rare Met 29(2):143–148
Kittel C (1996) Introduction to solid state physics. Wiley, New York
Van Meerssche M, Feneau-Dupont J (1984) Introduction à la cristallographie et à la chimie structurale. Editions Peeters, Leuven
Su C, Sheu TK, Chang YT, Wan MA, Feng MC, Hung WC (2005) Synth Met 153:9–12
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Romanian PN-II-ID-PCE-2011-3-0446 Project and by EU (ERDF) and Romanian Government that allowed for acquisition of the research infrastructure under POS-CCE O 2.2.1 Project INFRANANOCHEM—Nr. 19/01.03.2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Predoana, L., Preda, S., Nicolescu, M. et al. Influence of the substrate type on the microstructural, optical and electrical properties of sol–gel ITO films. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 71, 303–312 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3373-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3373-x